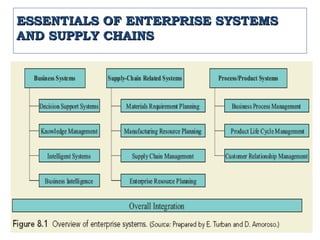
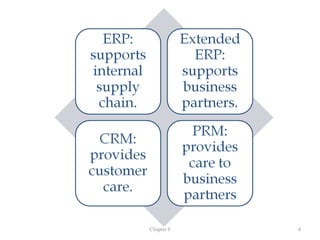
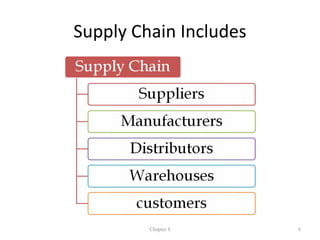
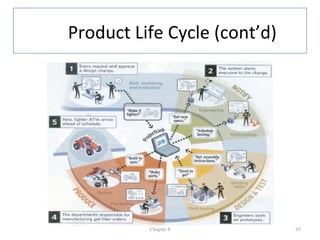
The document discusses enterprise systems, supply chains, and business process management. It defines ERP systems as software that integrates major business processes in real-time. Supply chains are described as the relationships between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers that transform raw materials into products. Business process management aims to optimize processes across departments and involves process modeling, reengineering, and measuring processes with tools like ISO 9000 and Six Sigma.