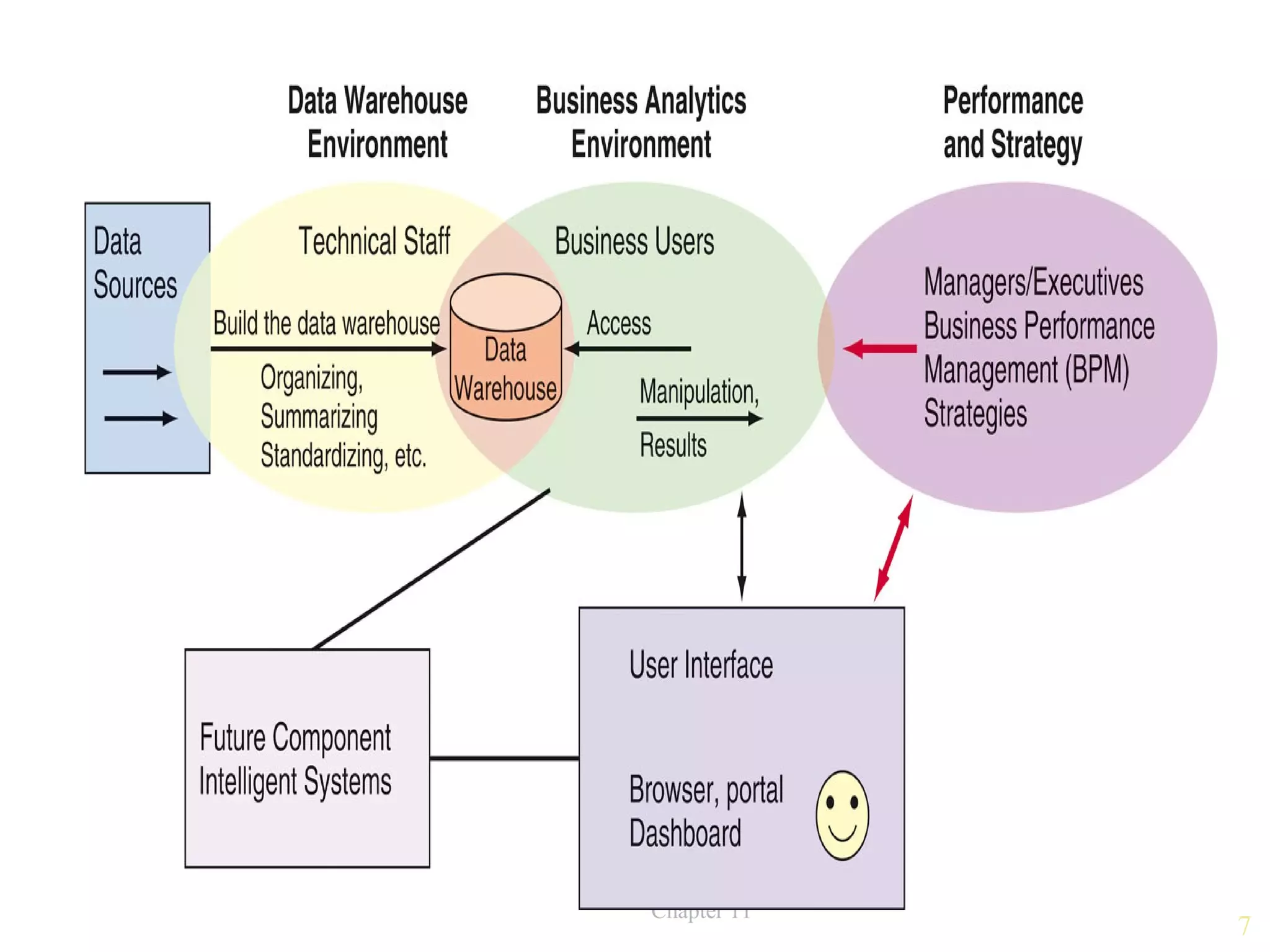
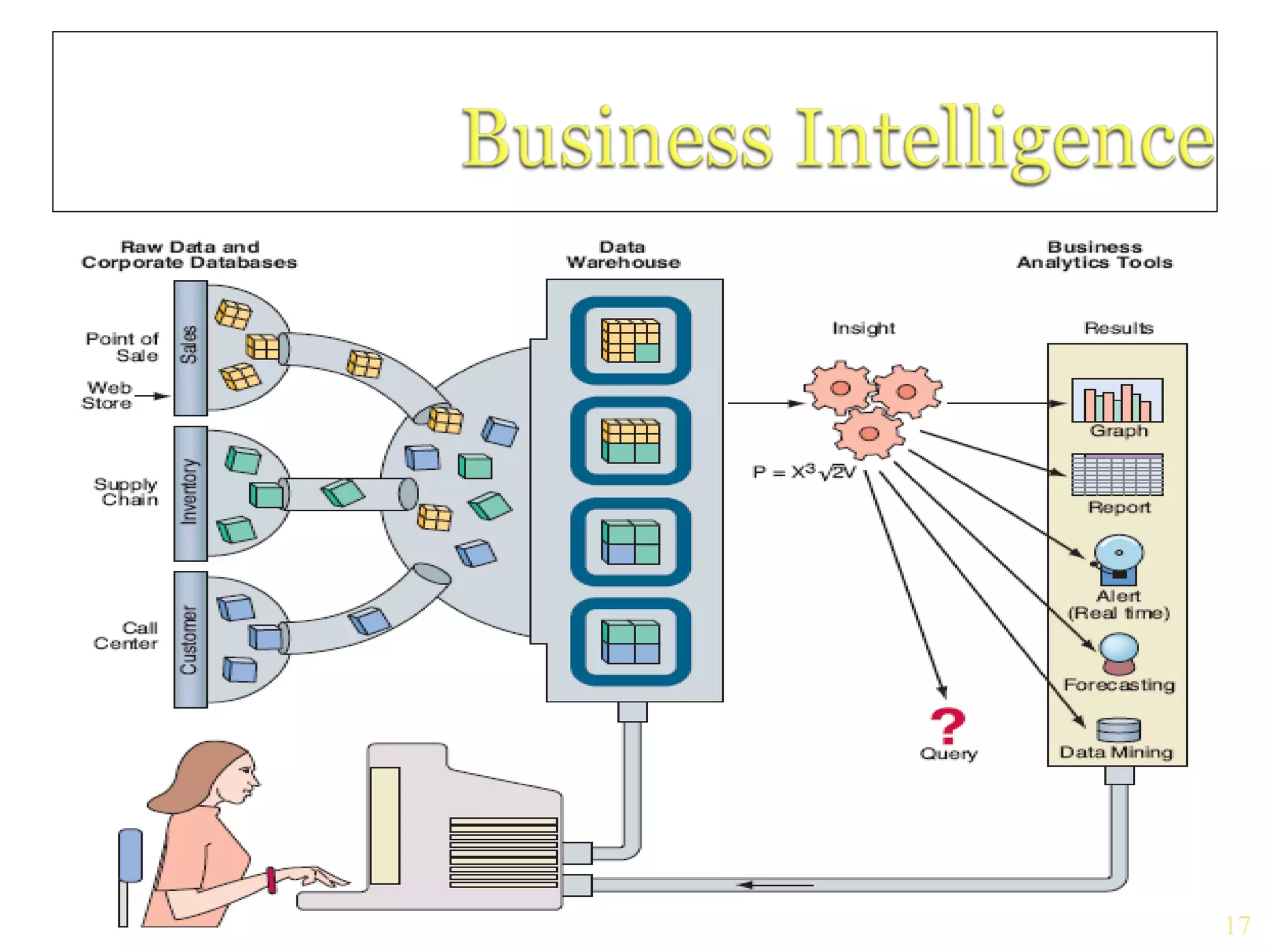
Business intelligence (BI) is an umbrella term that combines tools, databases, applications and methodologies to enable interactive access and manipulation of data to provide business managers and analysts the ability to conduct appropriate analysis. It includes data warehousing, business analytics, business performance management and user interfaces. BI provides benefits like time savings, improved strategies and decisions, increased revenue and improved customer relationships through faster and more accurate reporting and improved decision making.