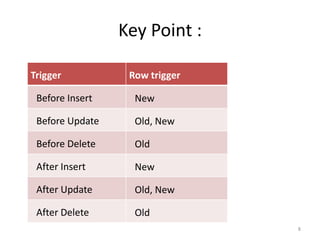
Triggers are database objects that are executed automatically in response to data modification statements like INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE on a table. There are different types of triggers - BEFORE triggers execute before the triggering statement while AFTER triggers execute after. Triggers can be used for data validation, integrity, auditing and more. Views can have INSTEAD OF triggers that allow modifications to views to be redirected to base tables.