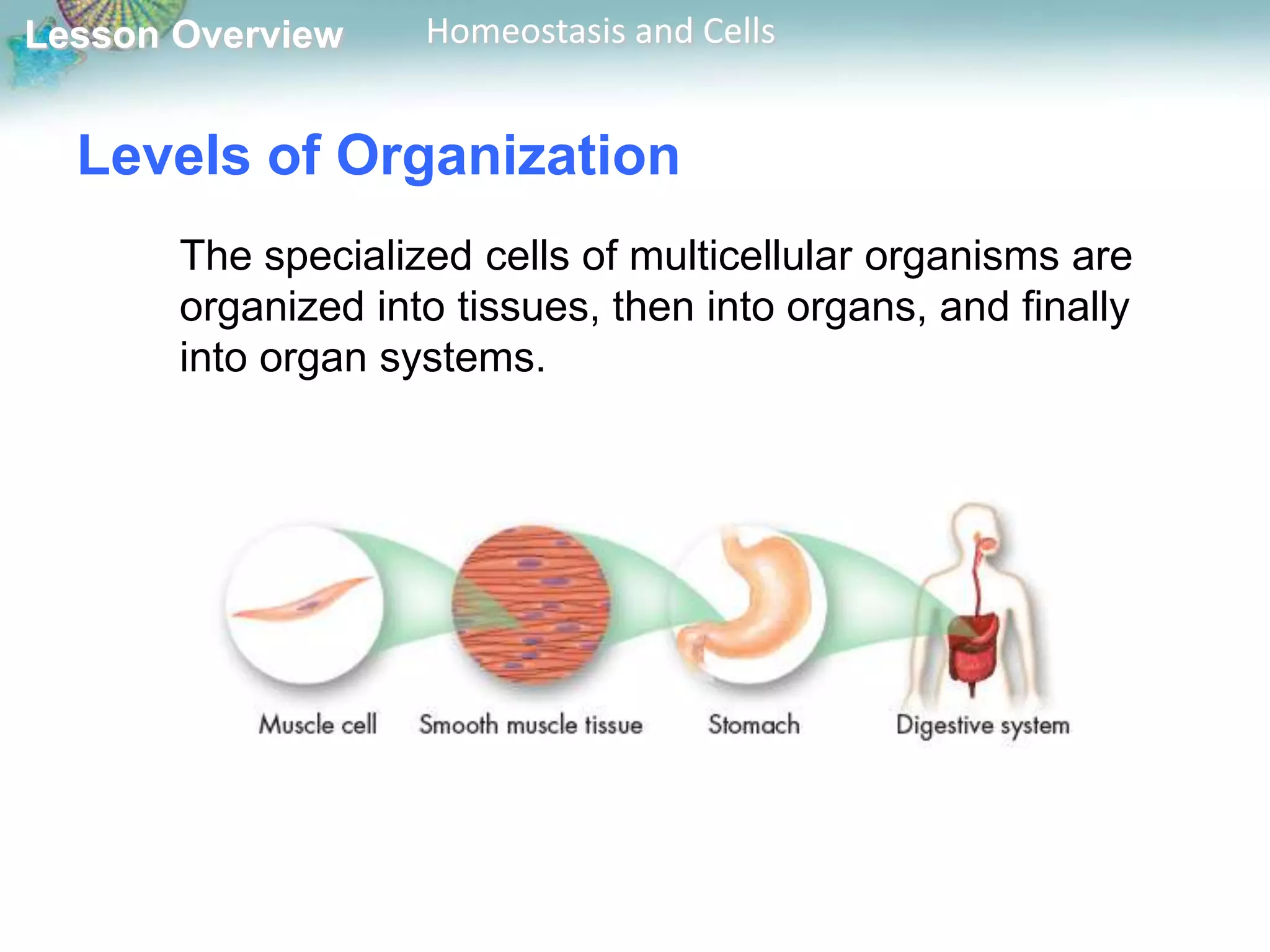
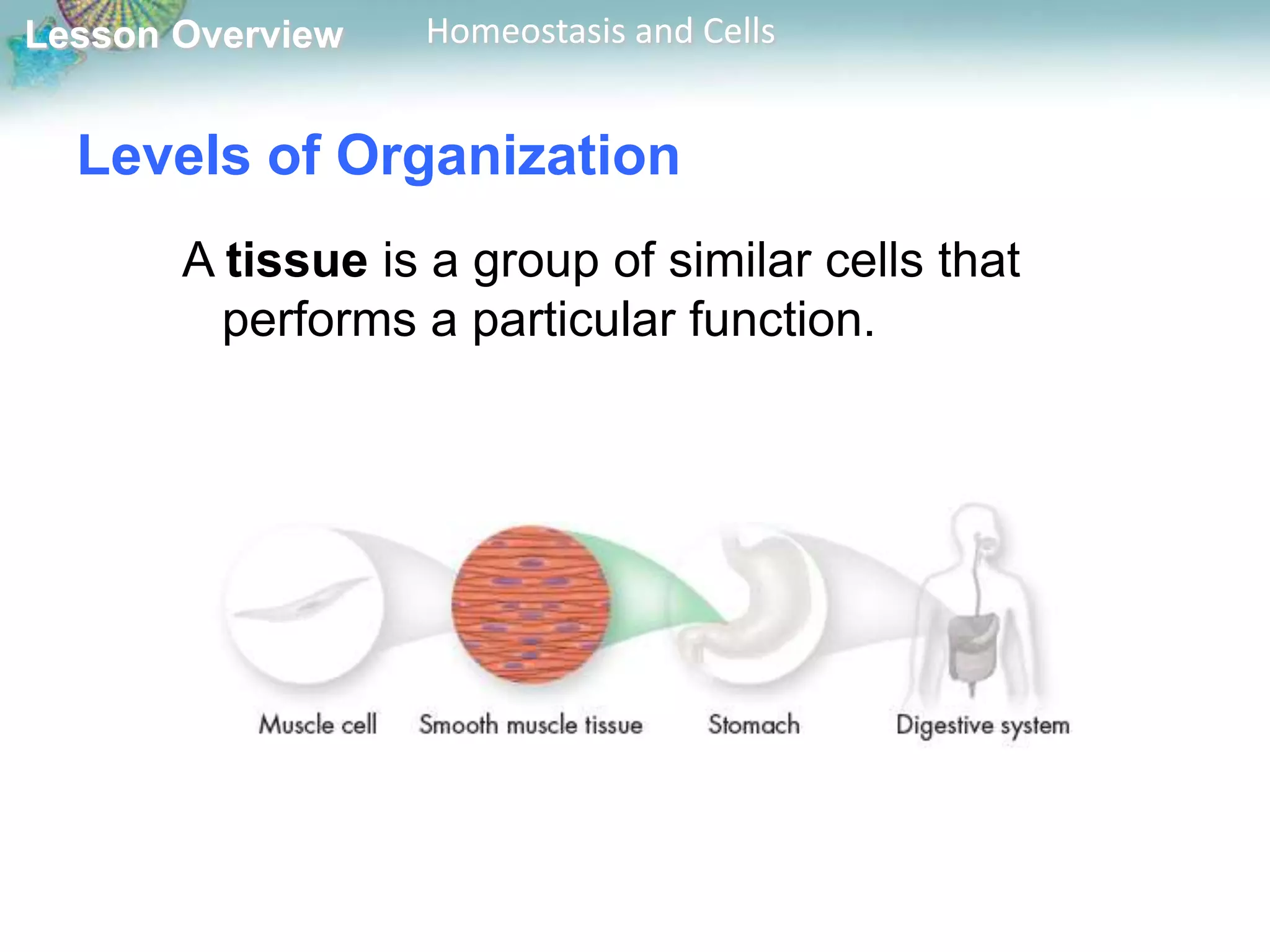
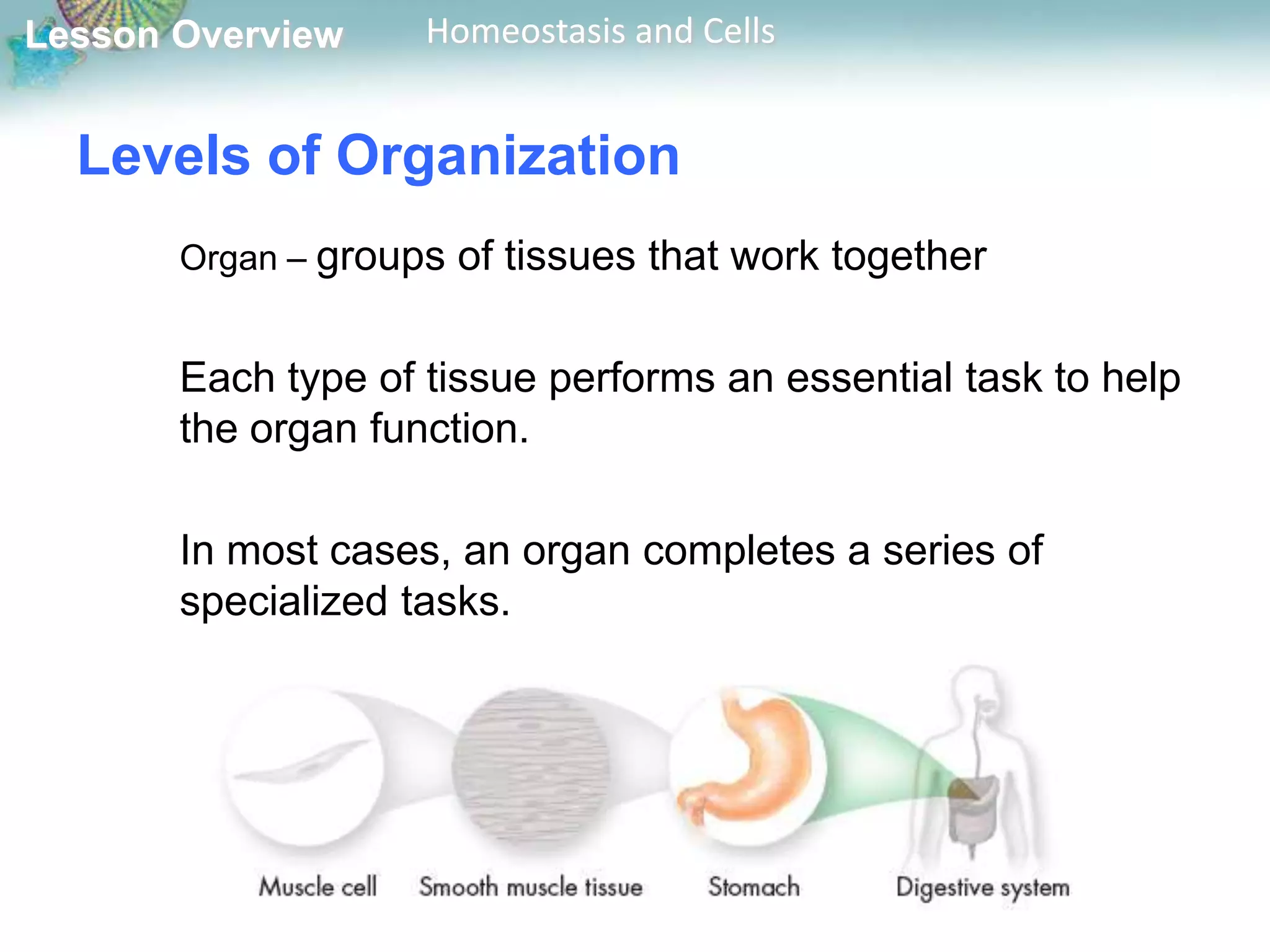
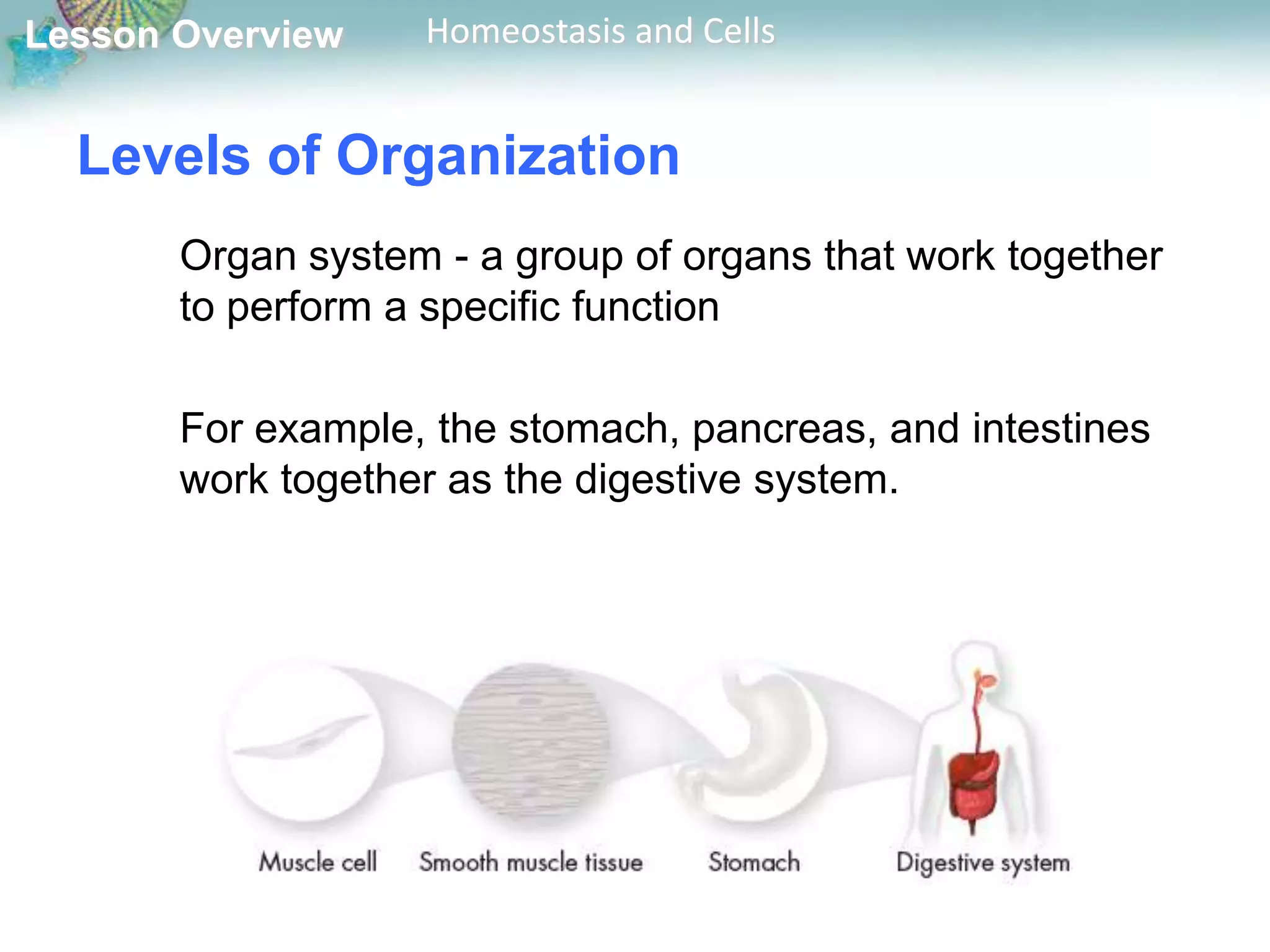
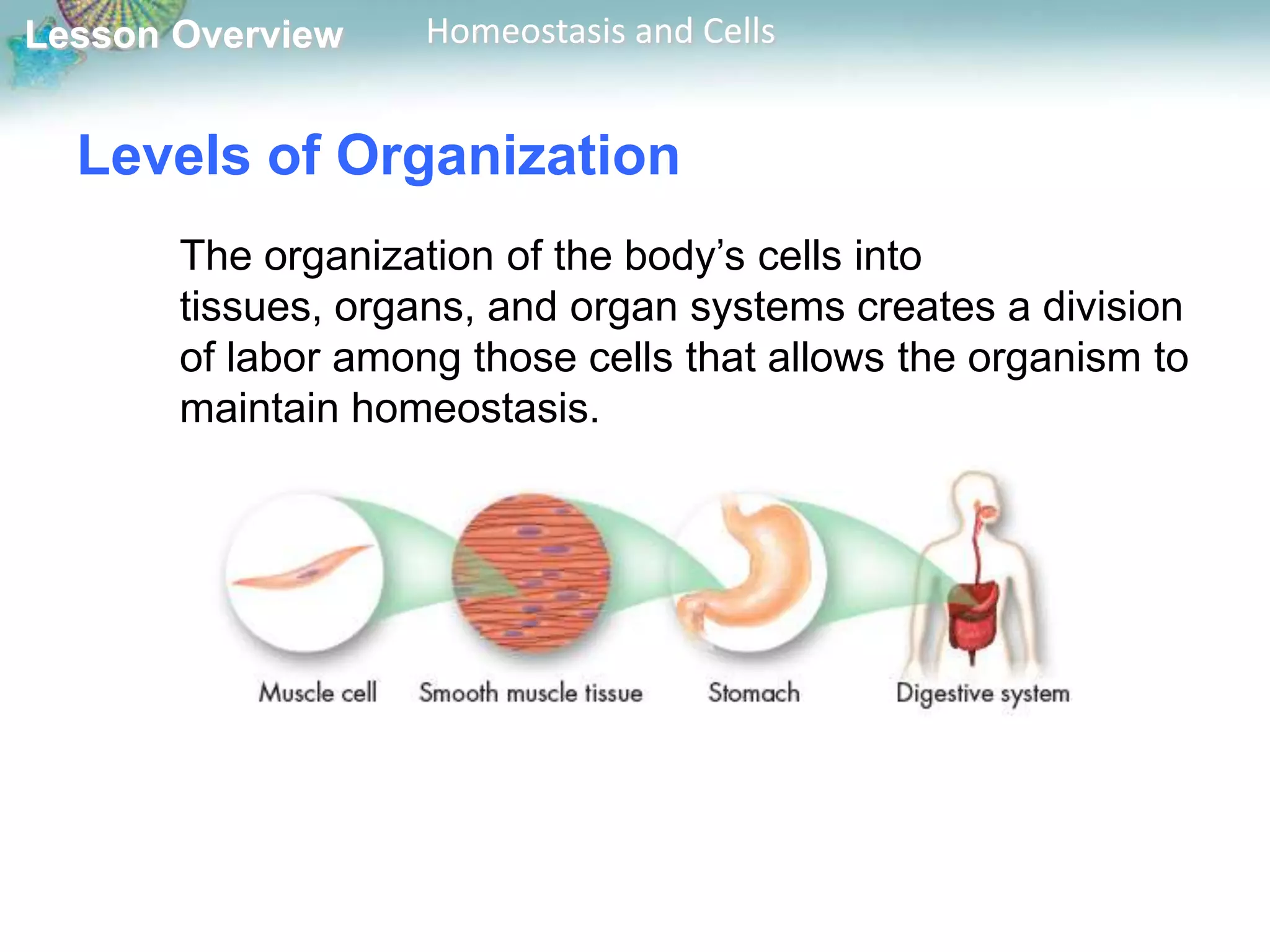
The document discusses how cells maintain homeostasis at different levels of organization. Individual cells maintain homeostasis by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, and reproducing. In multicellular organisms, cells become specialized and communicate with each other to maintain homeostasis. Specialized cells are organized into tissues, then organs, and finally organ systems, creating a division of labor that allows the organism to maintain homeostasis.