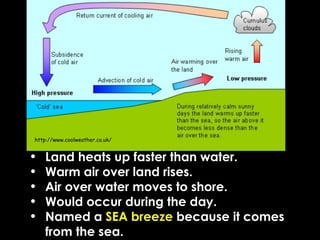
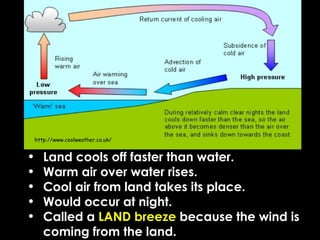
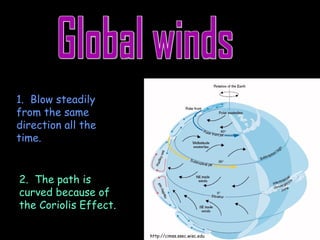
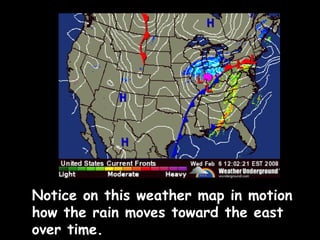
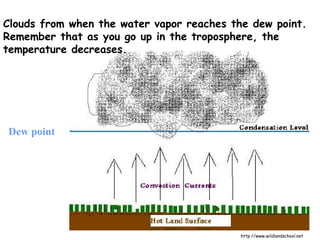
Wind is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface and is always named based on the direction it is blowing from, such as a north wind. There are two main types of winds: local winds that affect small areas and global winds that circulate across continents. Local winds include sea breezes and land breezes, which occur when air over land or water is heated and cooled at different rates, causing circulations. Global winds blow steadily in the same direction due to the Coriolis effect and include jet streams, fast currents of air in the upper troposphere. Moisture in the air, measured by humidity and dew point, can condense to form clouds and precipitation including rain.