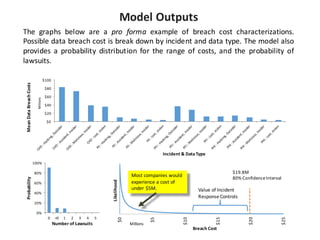
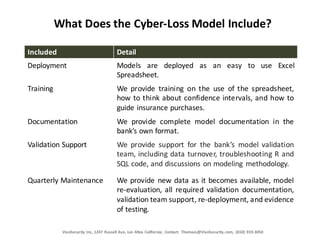
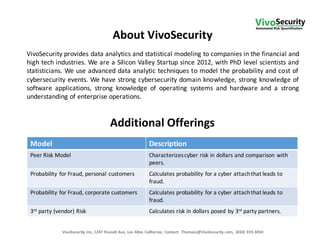
Vivosecurity Inc. specializes in providing statistical modeling and analysis for operational risk related to cybersecurity events, particularly focusing on banks' compliance with Federal Reserve guidance. They offer a cyber-loss model that quantifies breach costs and aids in insurance adequacy while ensuring SR 11-7 and SR 15-18 compliance. The company's services include model validation support, documentation, and training, leveraging advanced data analytic techniques and cross-company data to enhance risk management culture in financial institutions.