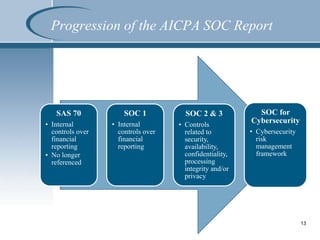
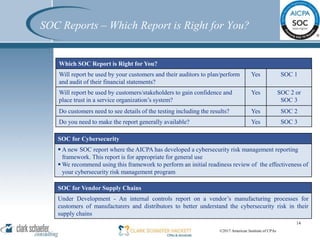
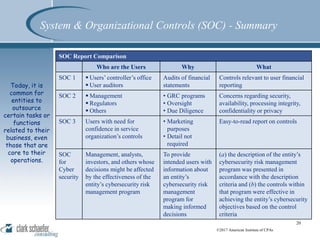
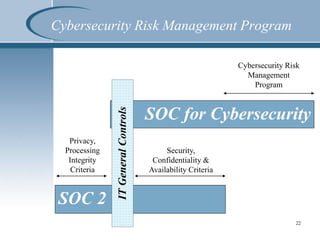
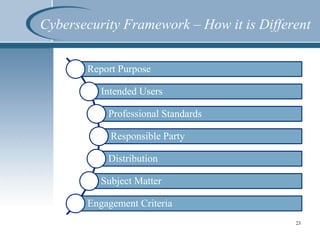
This document summarizes a presentation on SOC reporting and cybersecurity frameworks. It discusses the increasing need for cybersecurity frameworks due to rising data breaches and threats. It provides an overview of different SOC reports, including SOC 1, 2, and 3 reports, and introduces a new SOC for Cybersecurity report. This new report allows entities to demonstrate the effectiveness of controls in their cybersecurity risk management program. The presentation describes the components and structure of the SOC for Cybersecurity report, including describing the entity's cybersecurity risk management program and evaluating the effectiveness of controls. It recommends entities undertake a readiness review to identify gaps and determine next steps.