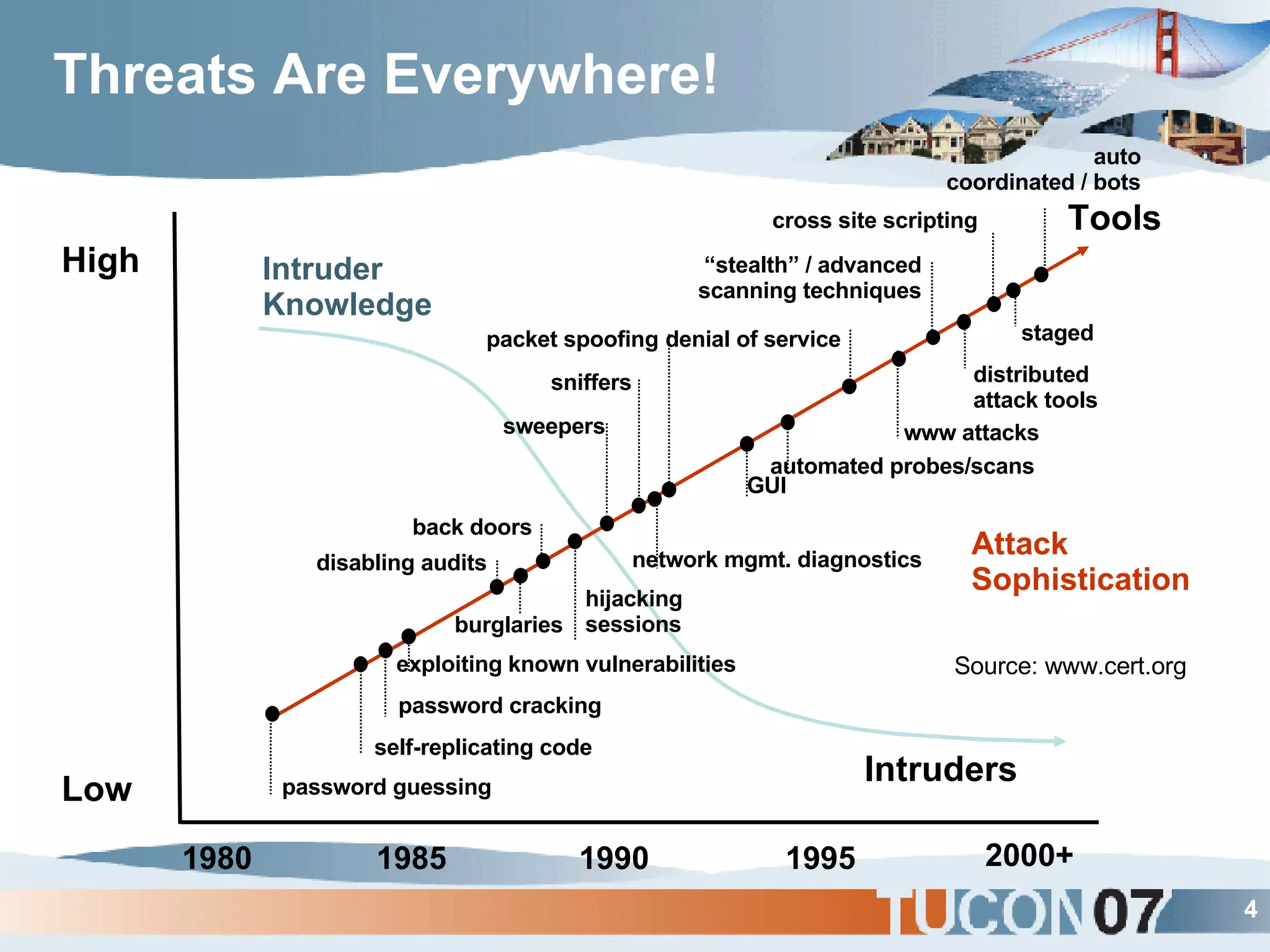
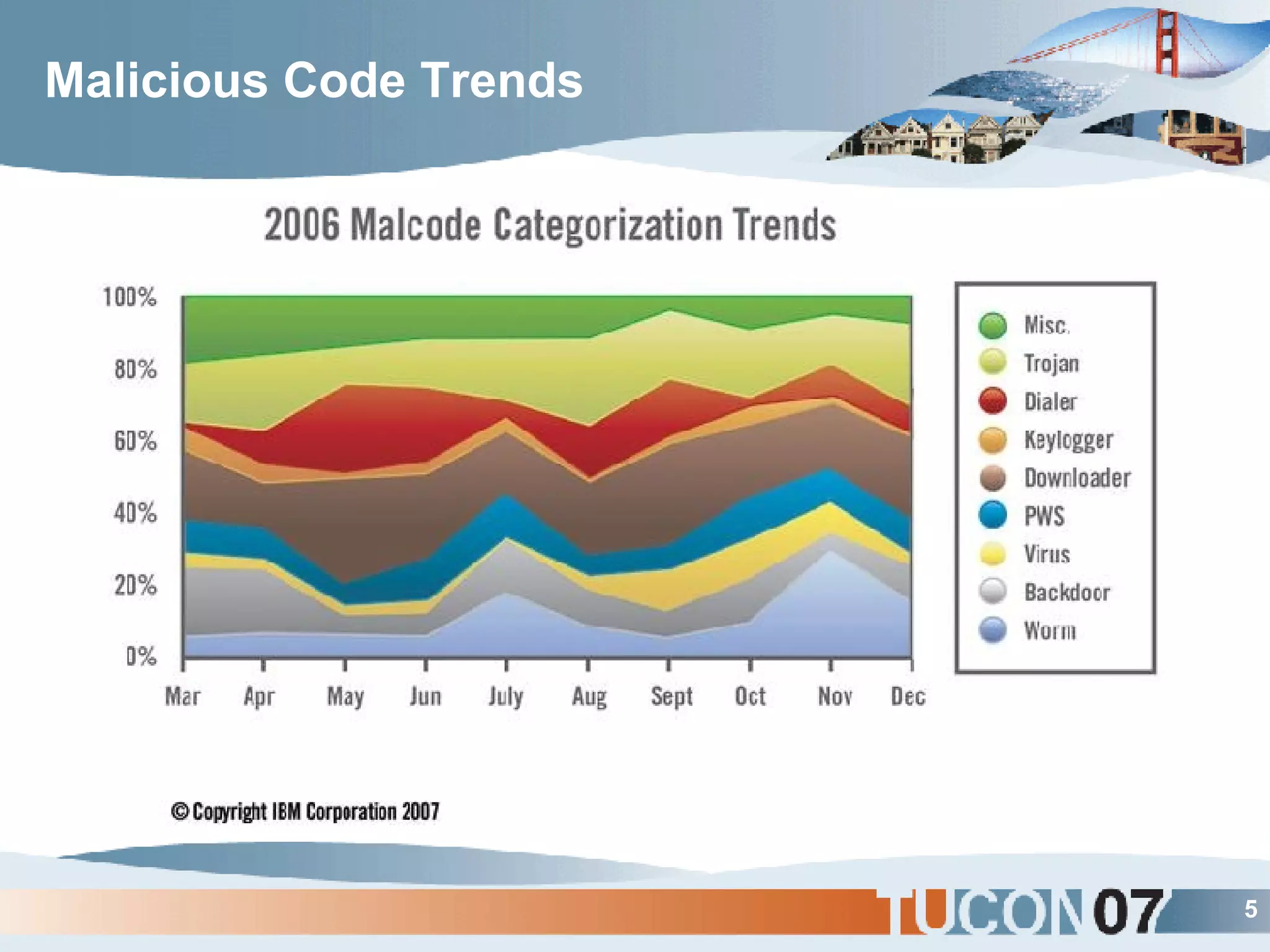
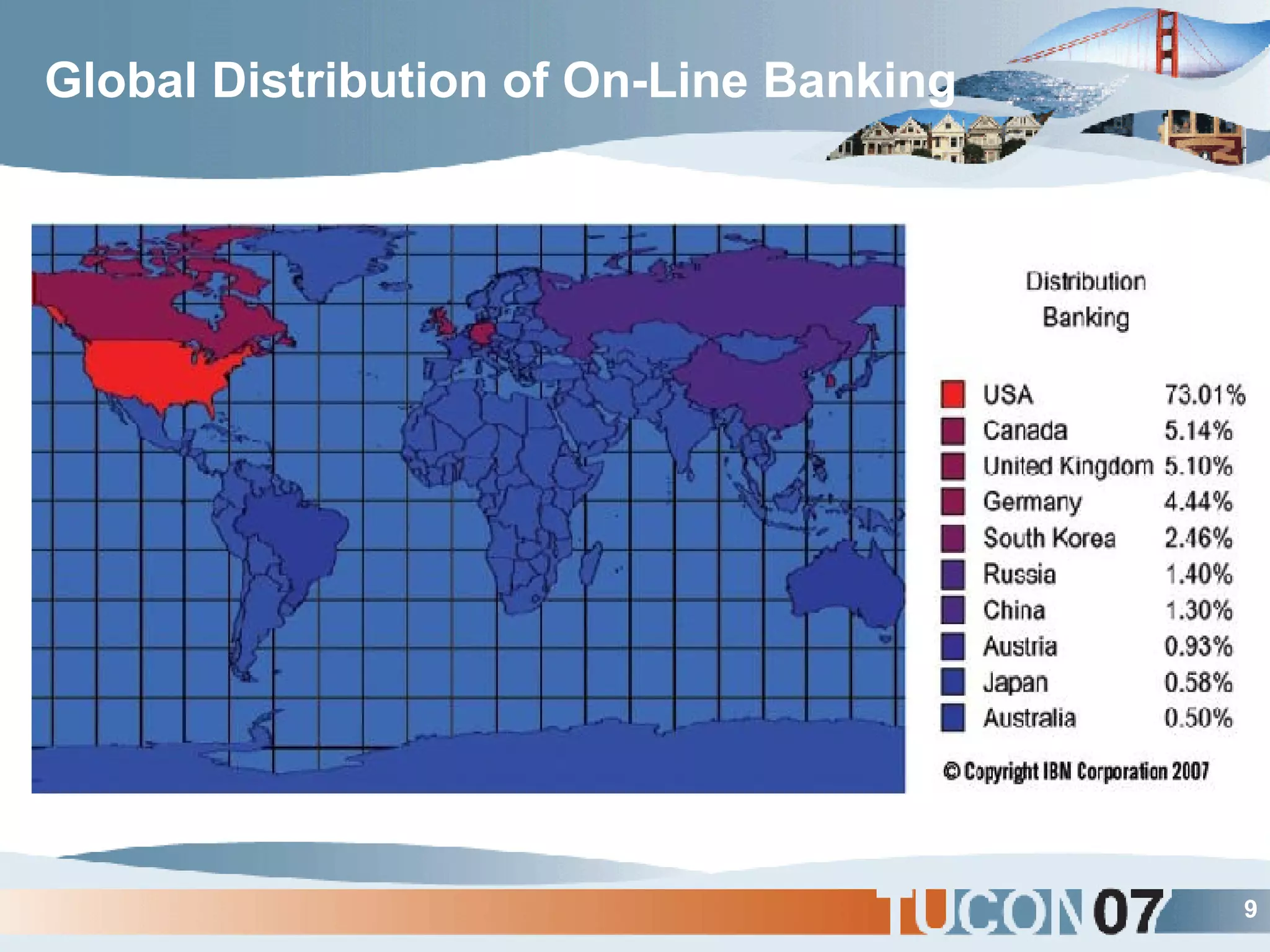
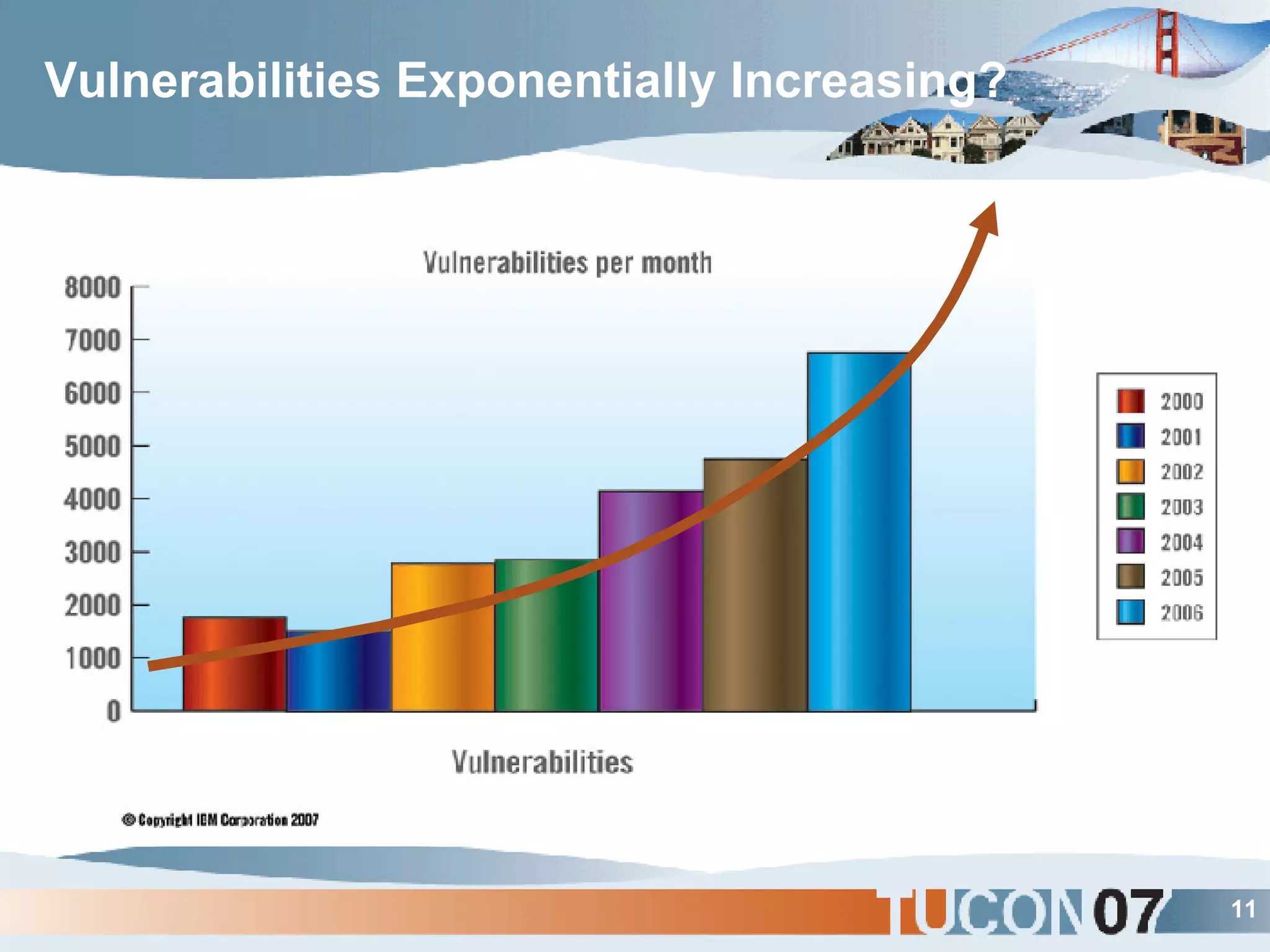
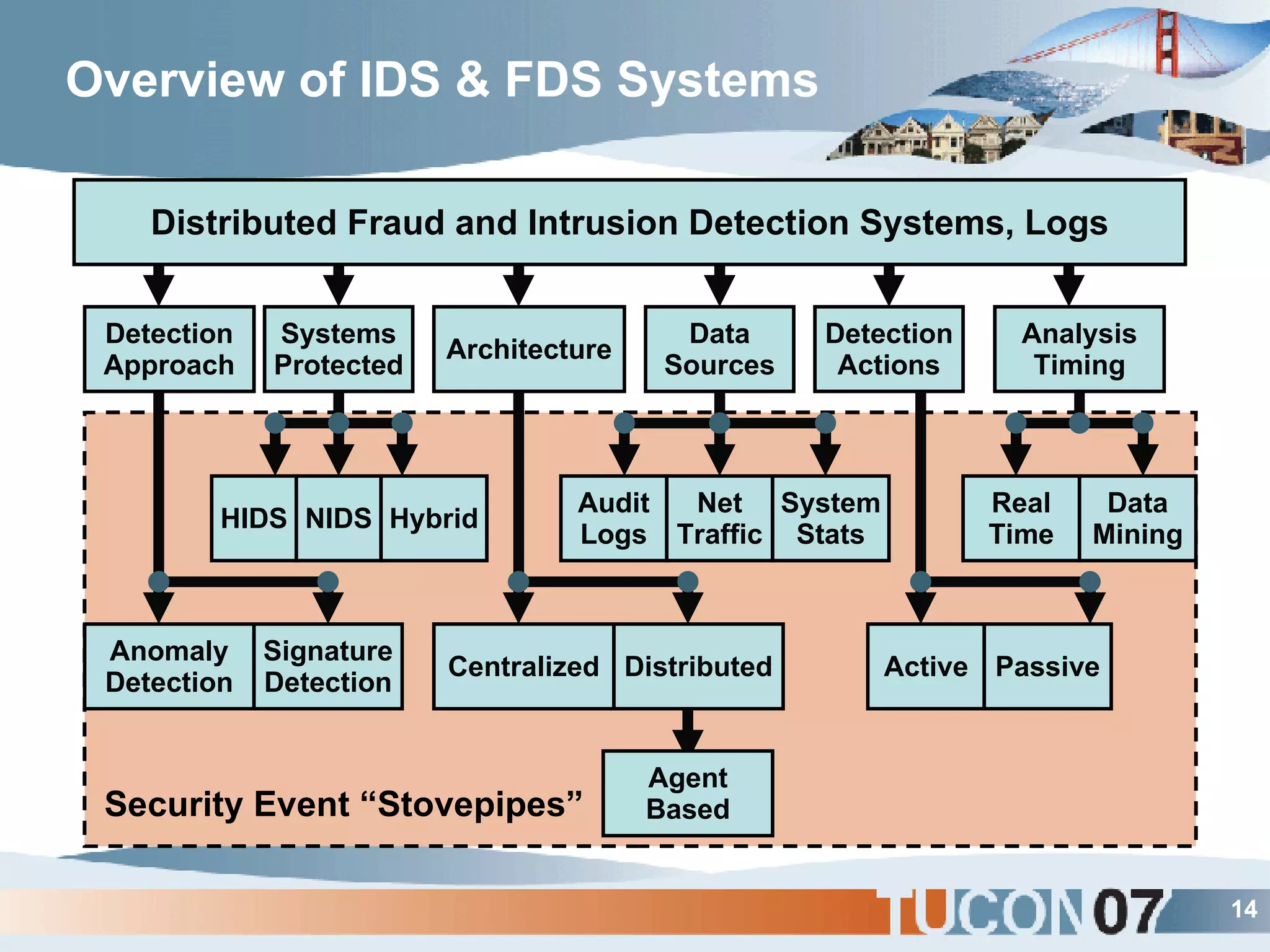
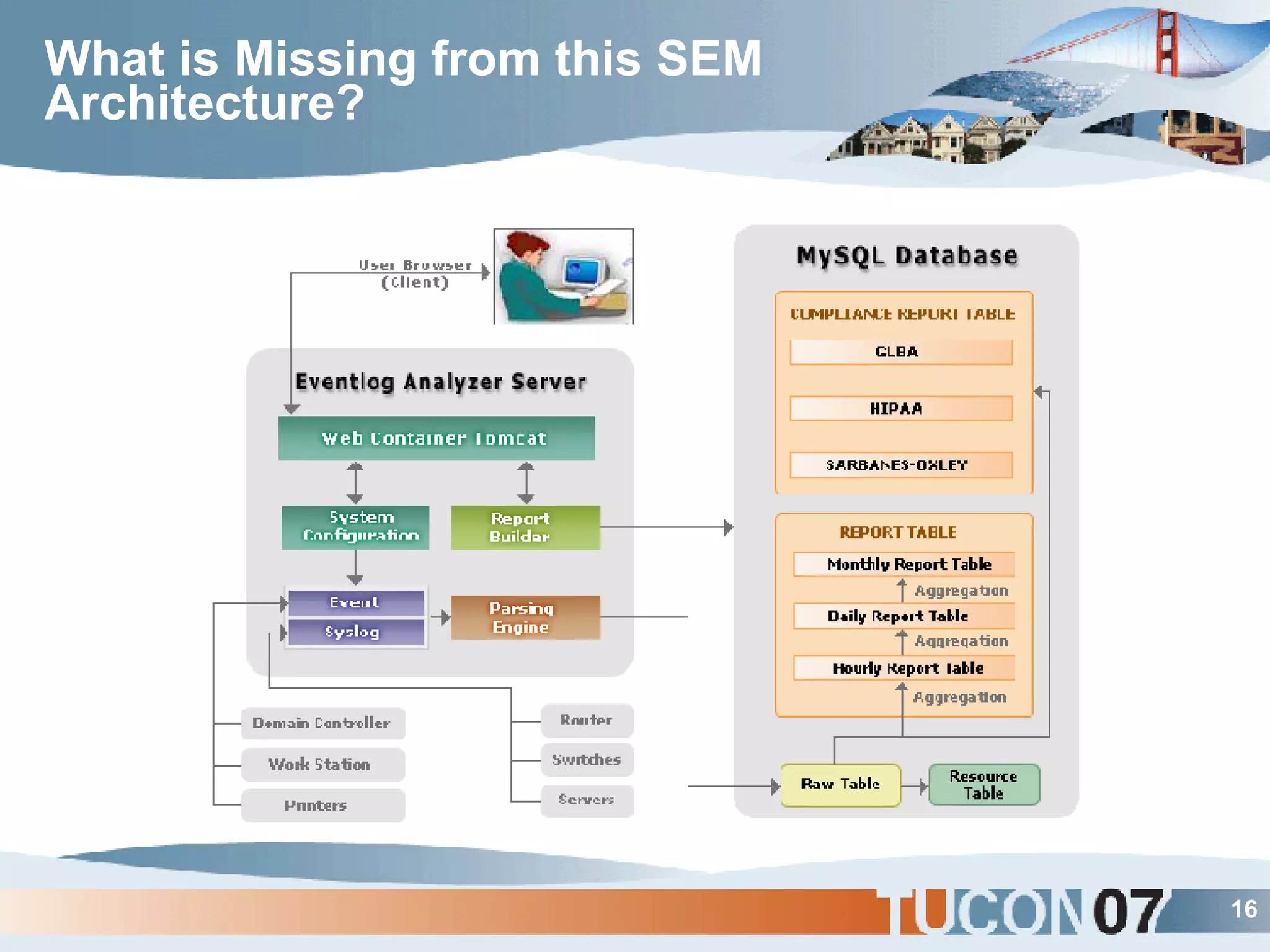
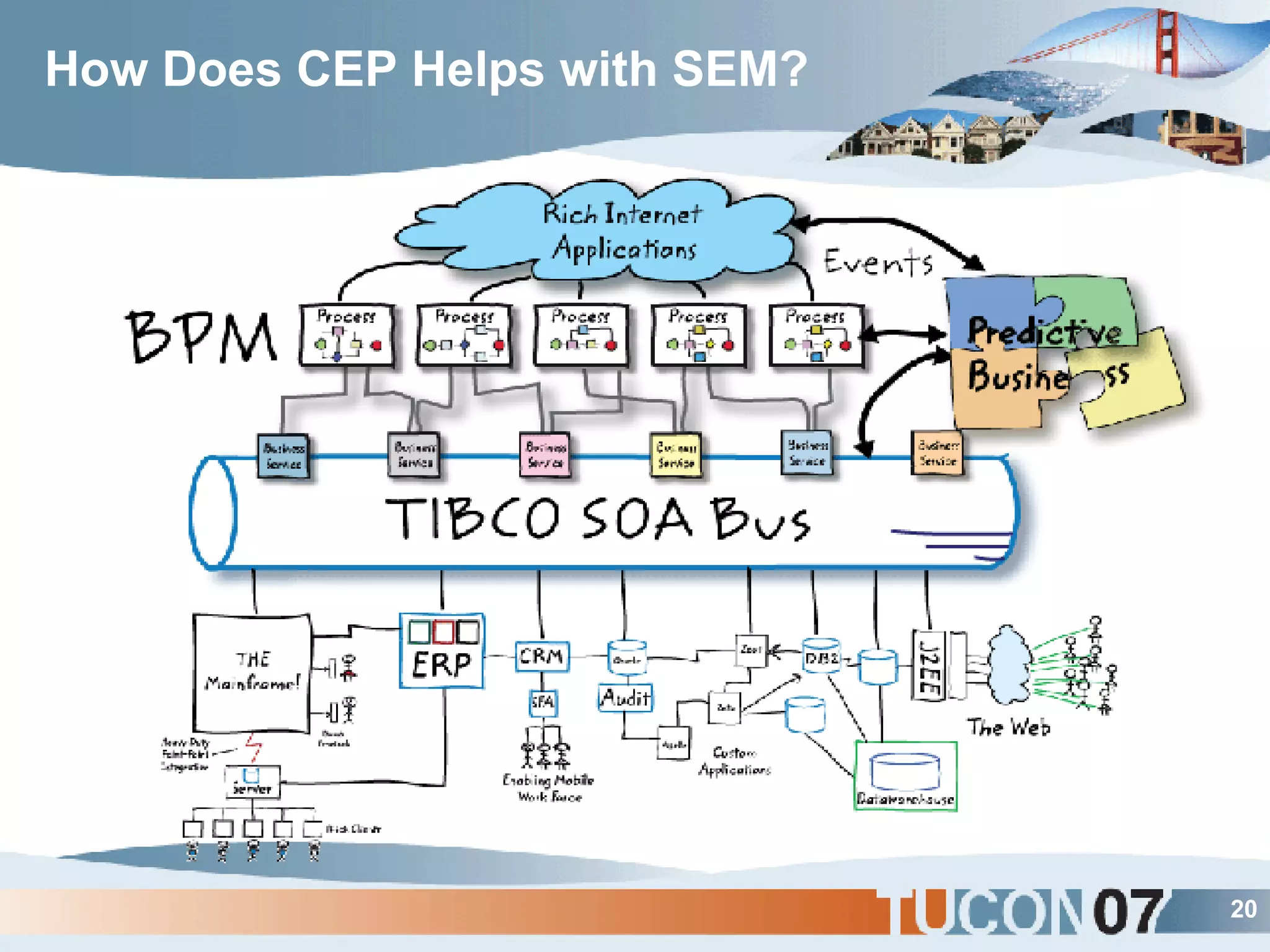
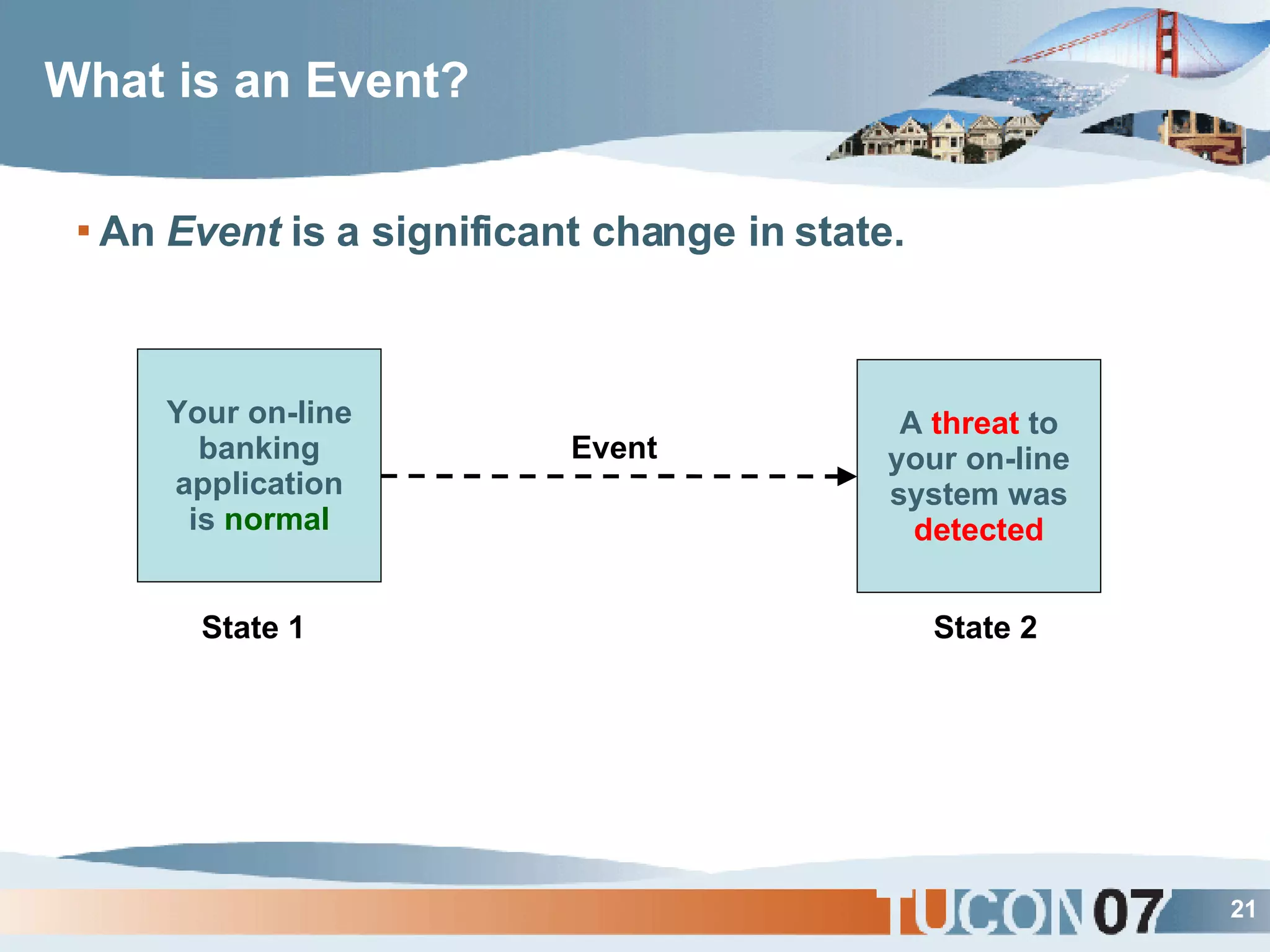
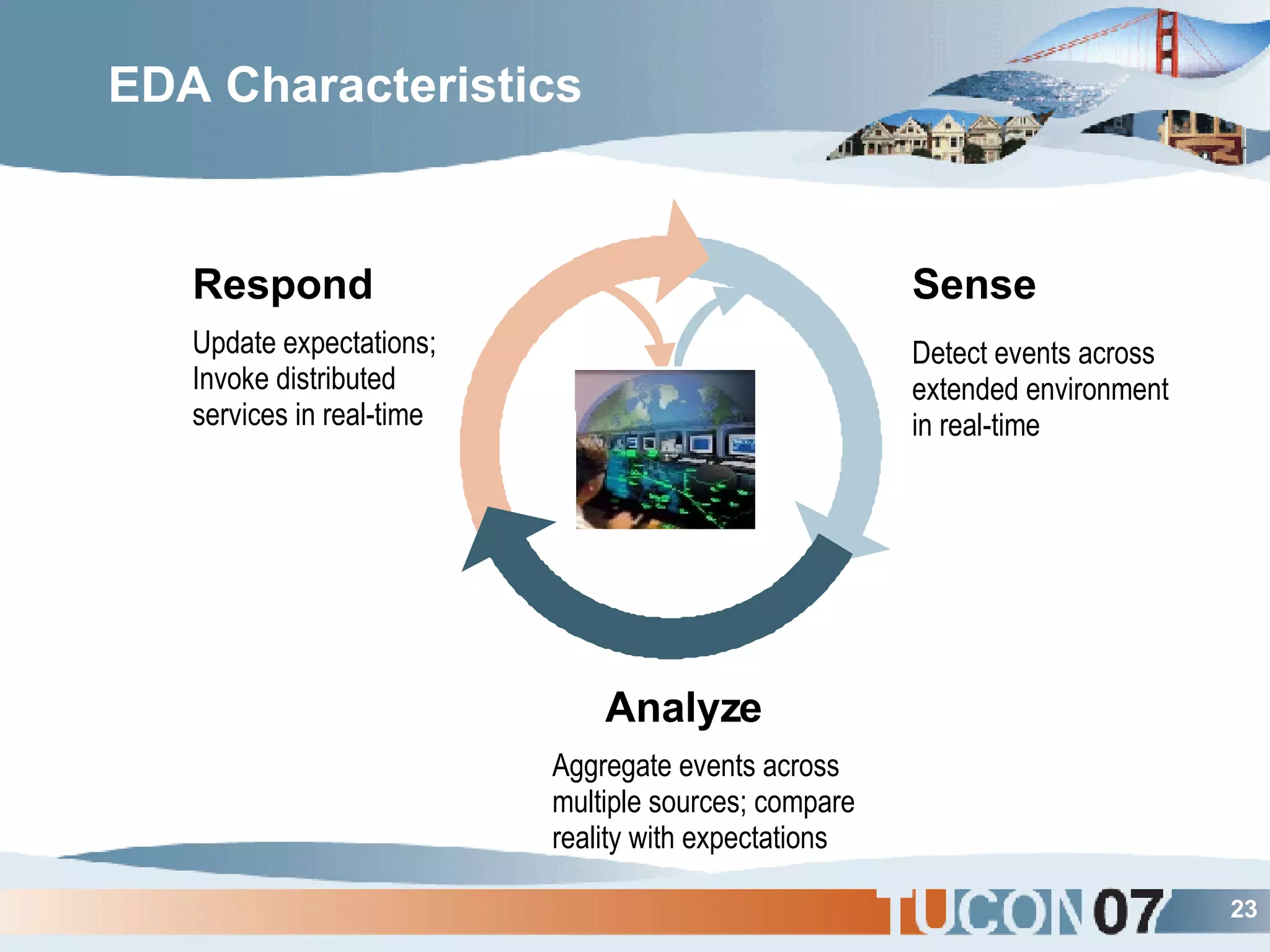
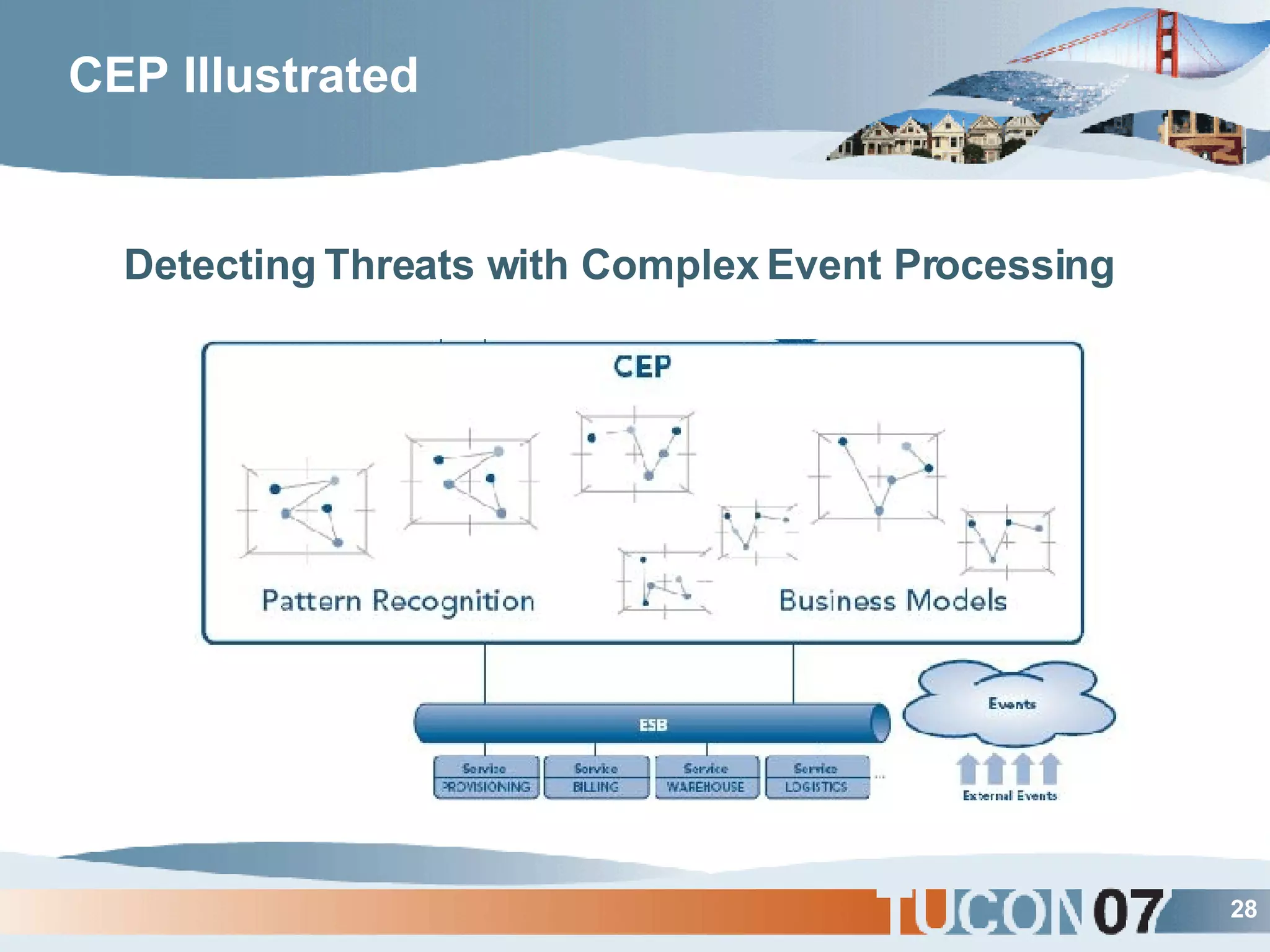
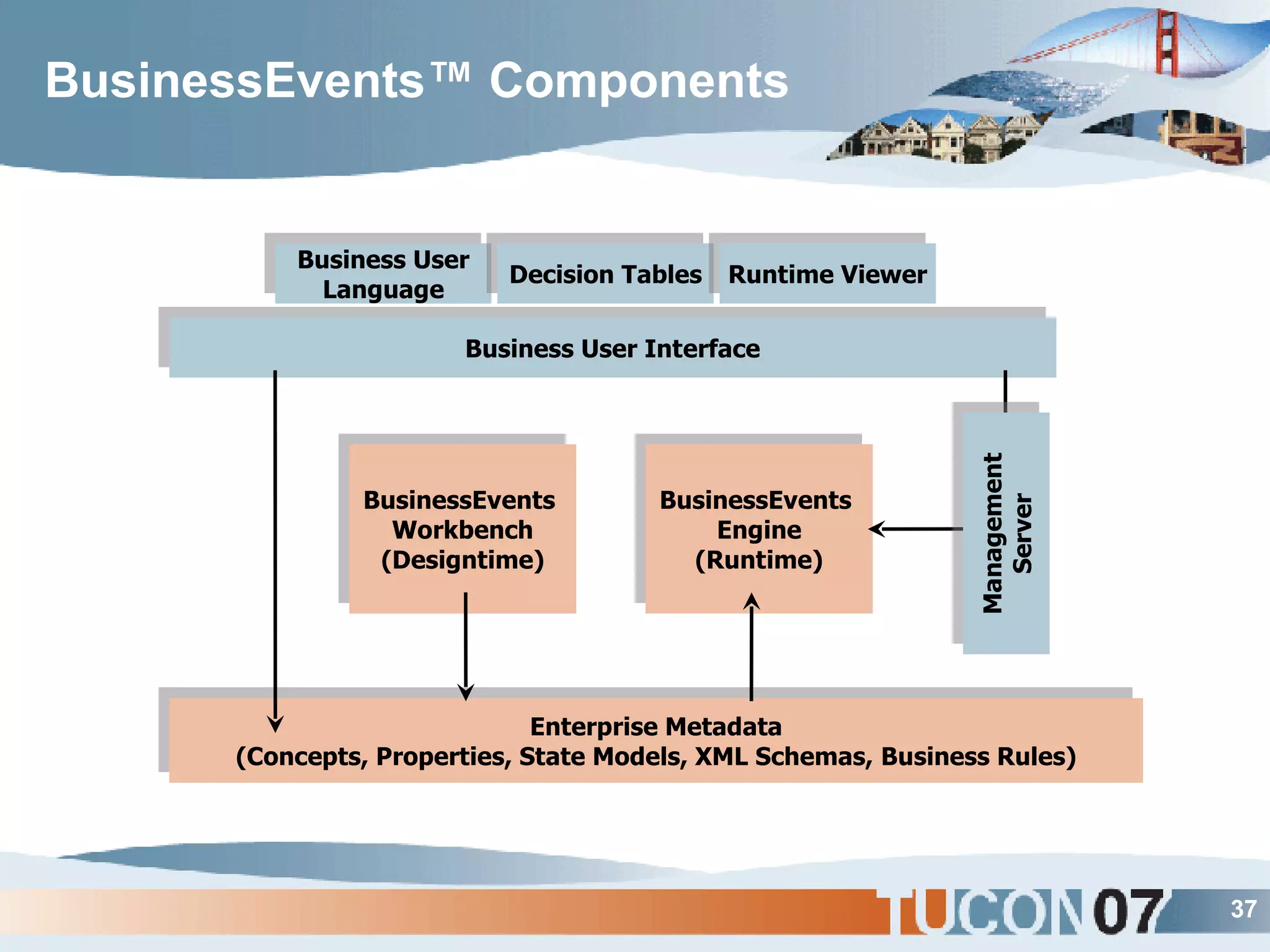
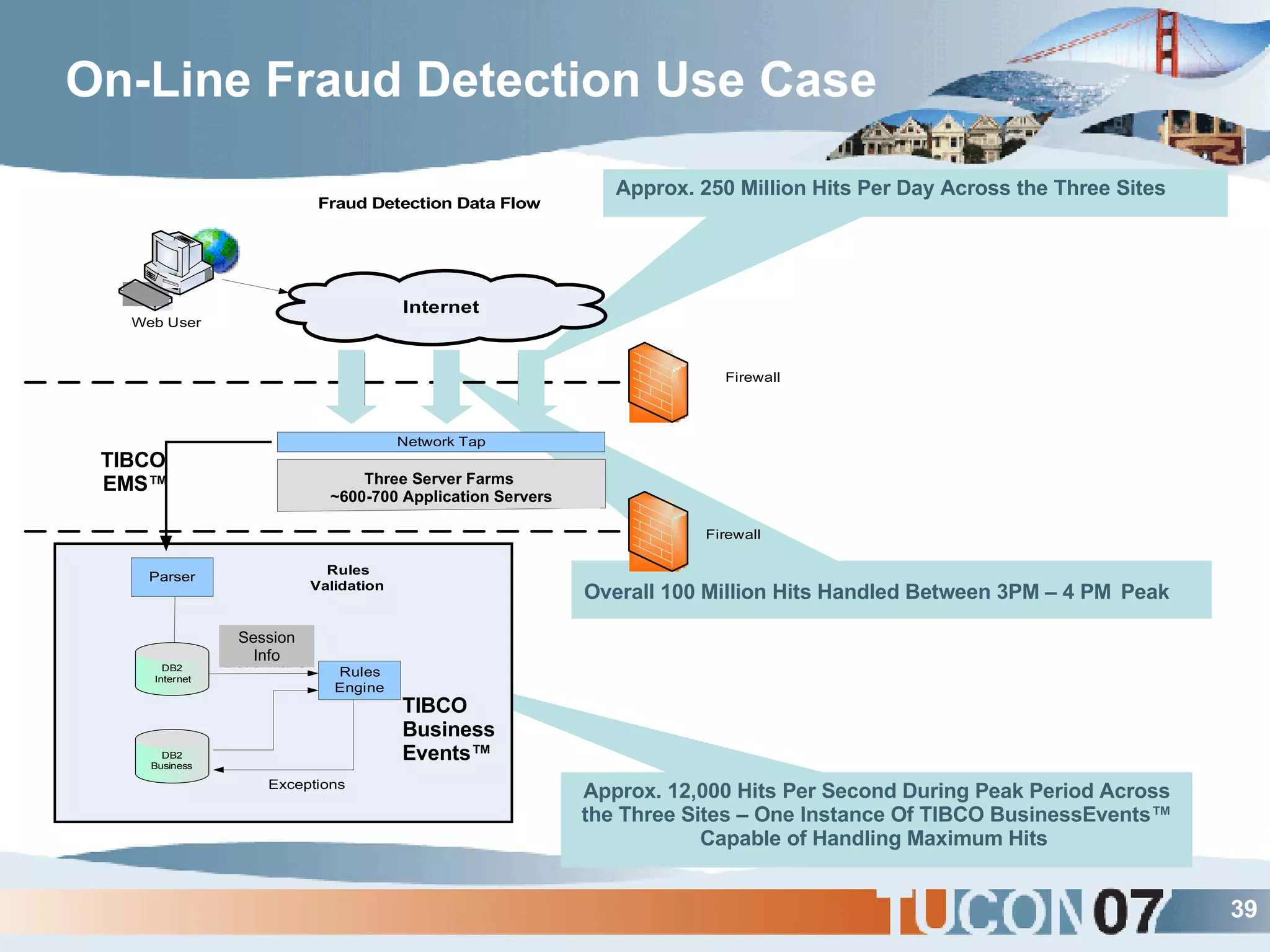
The document discusses the application of Complex Event Processing (CEP) in Security Event Management (SEM) to enhance threat detection and response capabilities for businesses. It outlines the weaknesses in existing SEM architectures, such as lack of secure communication infrastructure and insufficient analytics, while proposing a more scalable and automated framework using CEP. It also highlights the importance of real-time event processing and correlation of data from multiple sources to improve situational awareness and threat management.