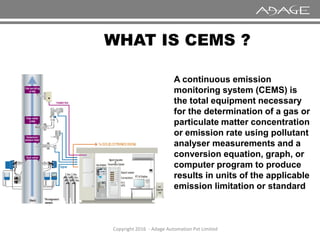
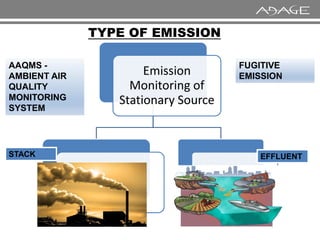
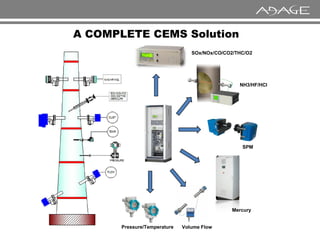
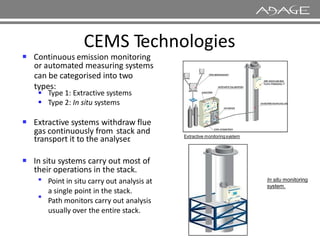
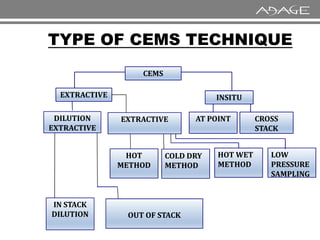
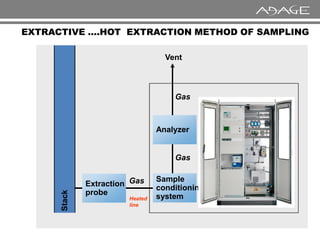
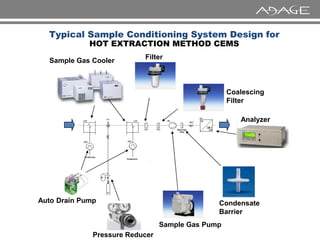
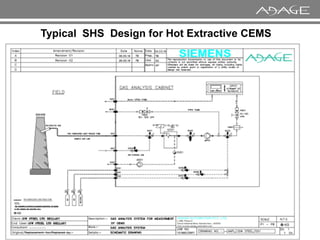
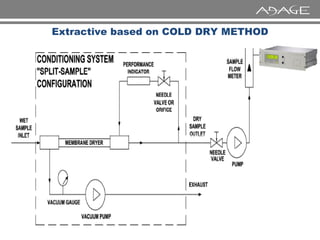
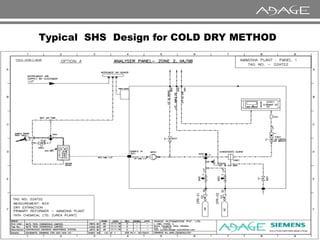
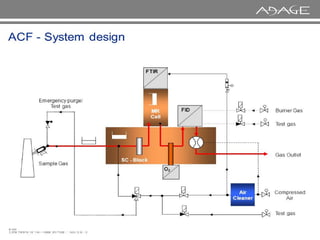
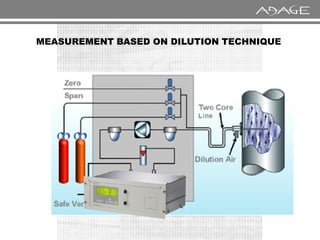
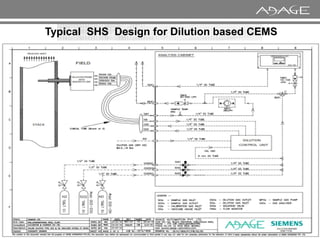
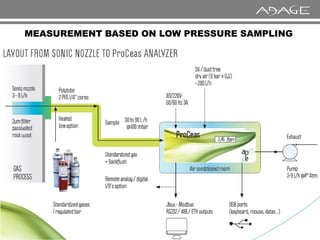
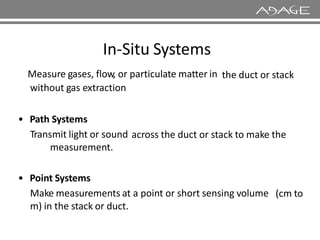
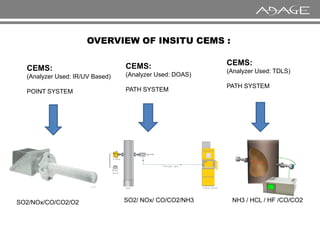
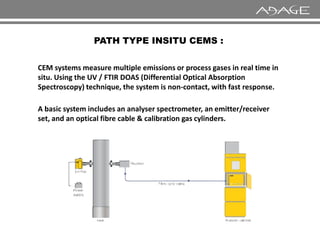
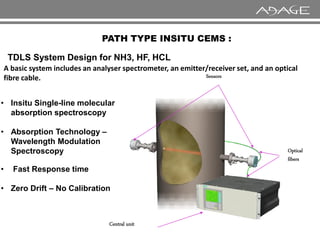
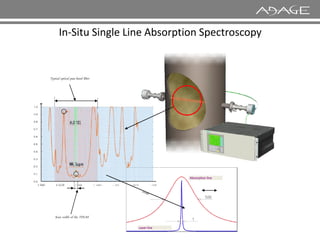
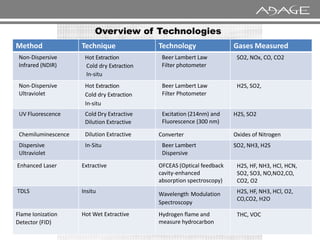
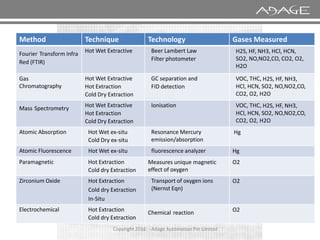
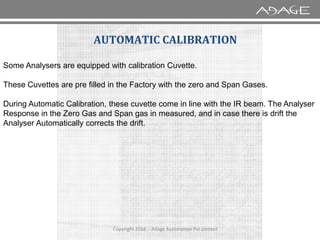
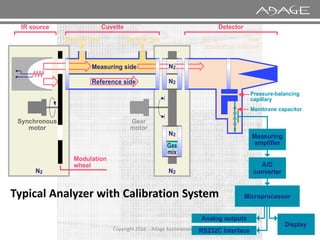
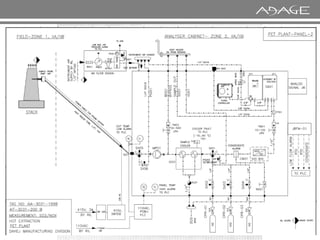
The document discusses continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS). It describes CEMS as equipment used to continuously determine the concentration of gas or particulate matter emissions from stationary sources like smokestacks. It outlines different types of CEMS including extractive systems that withdraw gas samples and in-situ systems that perform measurements inside the stack. Common CEMS technologies are also summarized, such as extractive, dilution, and in-situ systems. Key aspects of CEMS calibration and its importance are highlighted.