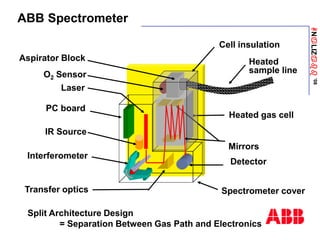
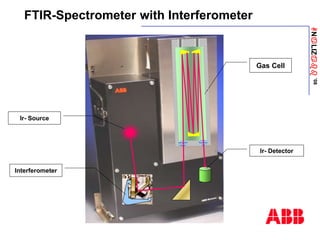
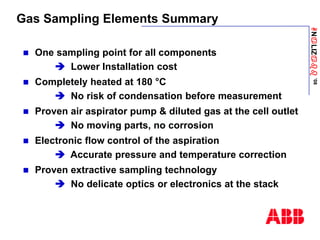
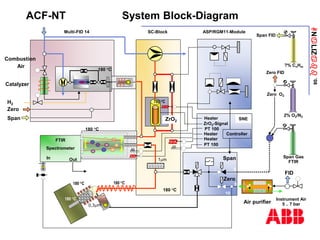
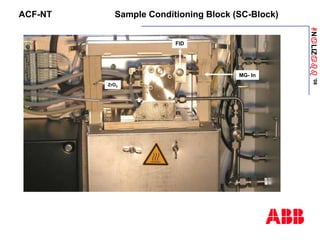
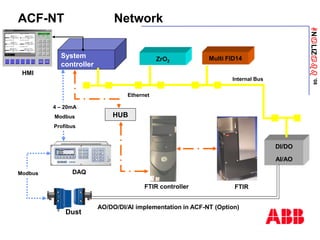
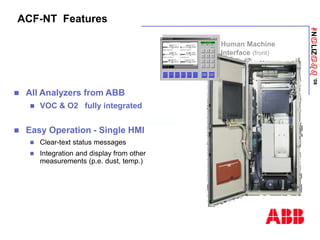
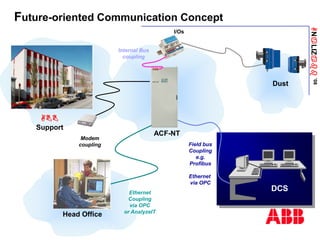
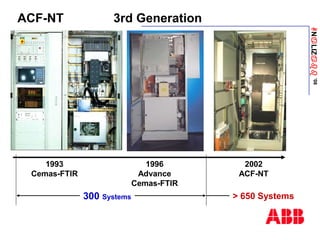
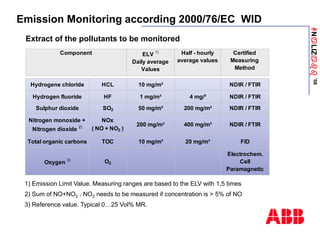
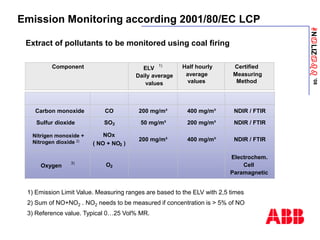
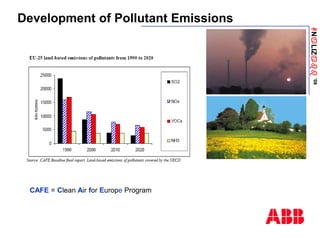
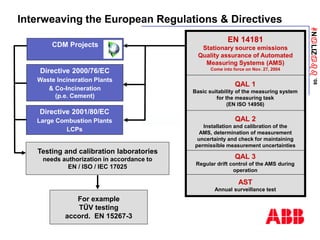
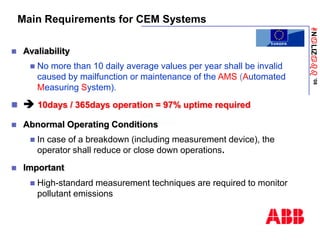
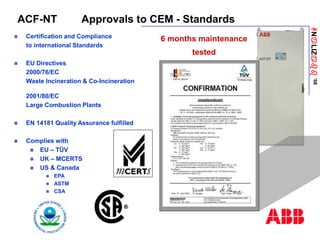
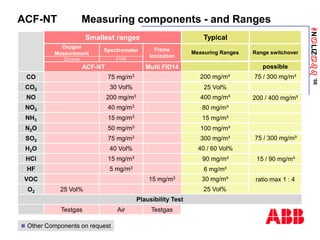
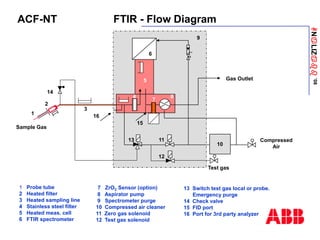
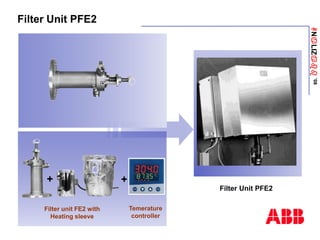
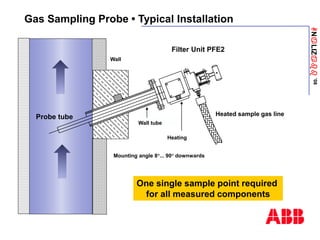
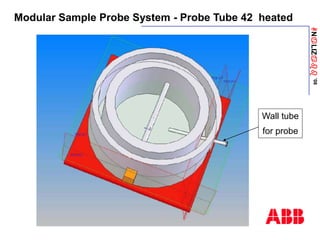
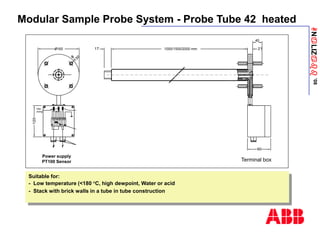
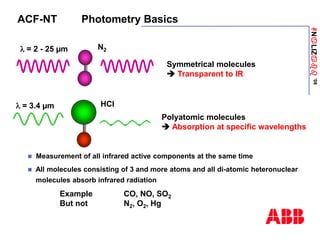
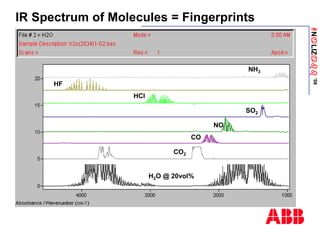
The document discusses an ACF-NT CEM system based on FTIR technology for emission monitoring. It provides an overview of relevant EU legislation for emission monitoring at waste incinerators, power plants, and other combustion processes. The ACF-NT system is a pre-engineered, multi-component emission monitoring solution that uses FTIR spectroscopy to continuously measure multiple pollutants like HCl, SO2, NOx, and CO according to EU standards. It also discusses the system's components, measurement principles, and approvals.









![ANaLIZabb
’08
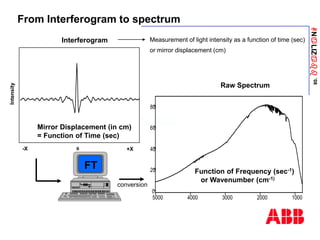
From Raw Spectrum to Absorbance
0
20
40
60
80
5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
- Raw gas -
spectrum
Intensity
0
.1
.2
.3
5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
Absorption
- Absorption -
spectrum
.6
.8
1
5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
Transmission
- Transmission -
spectrum
0
20
40
60
80
5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
Wavenumber n [ cm -1 ]
Intensity
- Reference Spectrum -
( Zero Spectrum )
I0
I
T = I / I0
E = - ln T
CO SO2
Wavenumber n [ cm -1 ]
Wavenumber n [ cm -1 ]
Wavenumber n [ cm -1 ]
Lambert Beer Law: I/Io = e-ε*c*l](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p3spainacf-nthbl01-221121215214-4270d8d0/85/P-3_Spain_ACF-NT_Hbl_01-ppt-30-320.jpg)