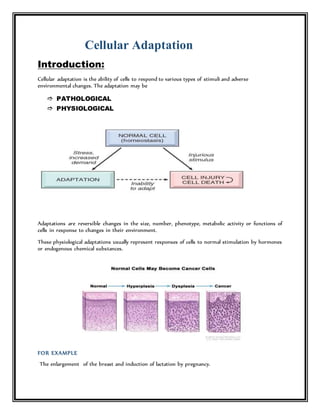
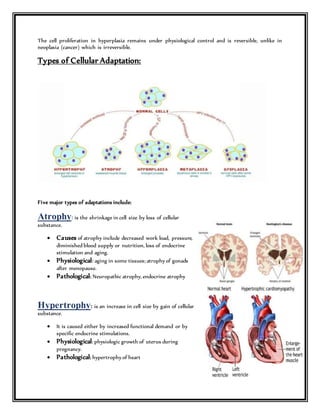
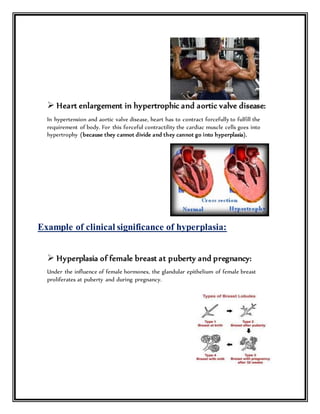
This document discusses various types of cellular adaptations including atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, and dysplasia. It provides examples of physiological and pathological adaptations and their clinical relevance. Physiological adaptations are reversible responses to normal stimulation, while pathological adaptations can be irreversible. The summary highlights examples of the clinical significance of hypertrophy in pregnancy, weightlifting, and heart disease. It also discusses the significance of hyperplasia in the breast, liver, and endometrium. Finally, it provides examples of the clinical relevance of metaplasia in smokers and vitamin A deficiency.