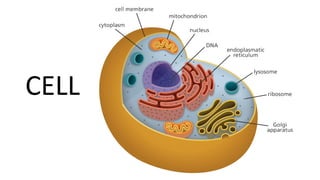
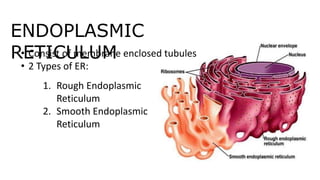
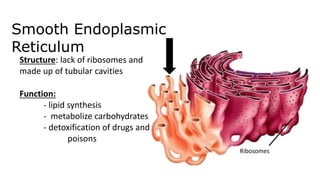
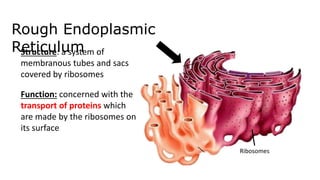
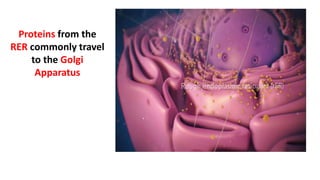
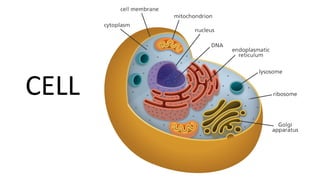
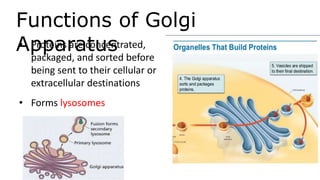
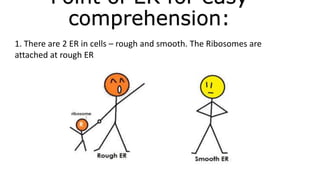
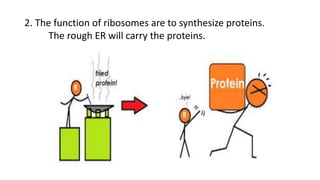
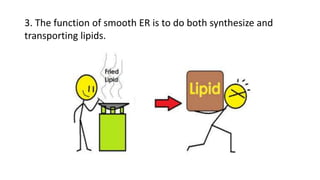
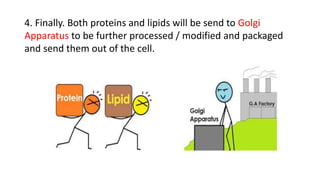
The document discusses the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, two important organelles in the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum consists of rough and smooth membranes and tubules. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes and transports proteins synthesized by the ribosomes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes lipids and metabolizes carbohydrates. Proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum travel to the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and chemically modifies them before packaging and sorting them for transport within and outside the cell.