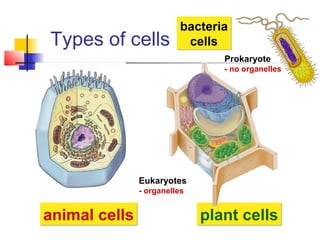
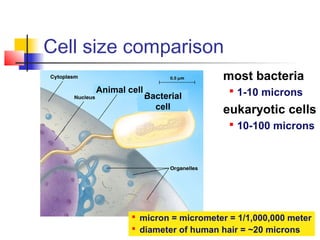
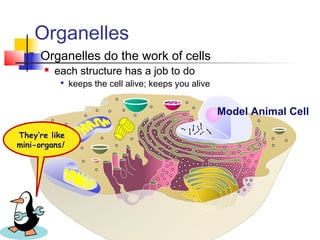
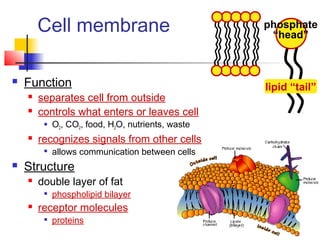
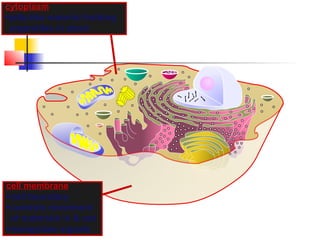
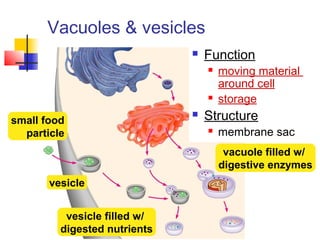
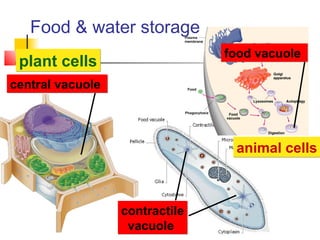
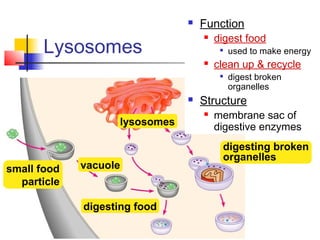
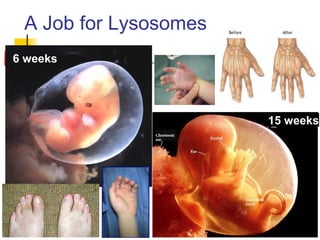
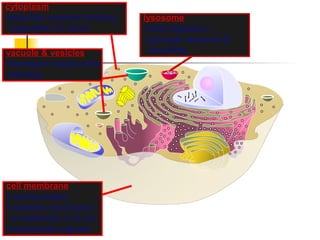
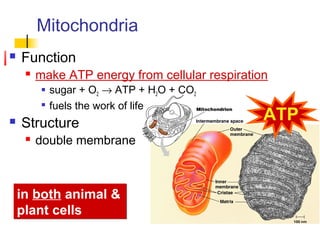
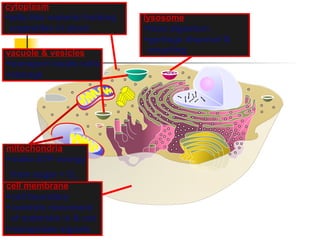
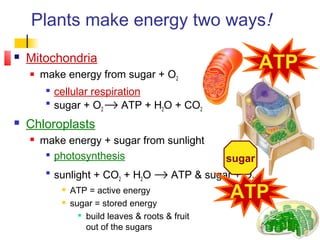
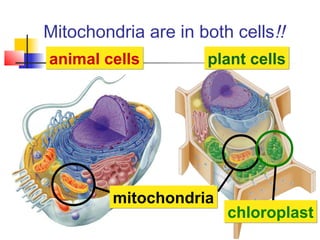
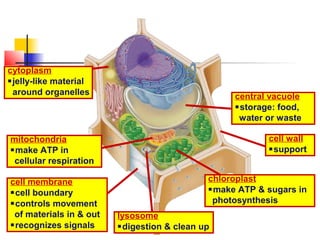
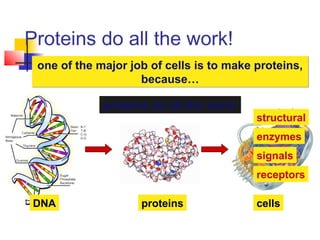
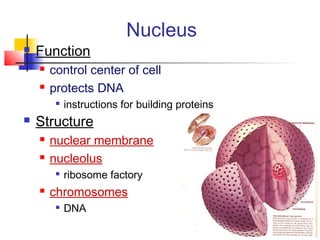
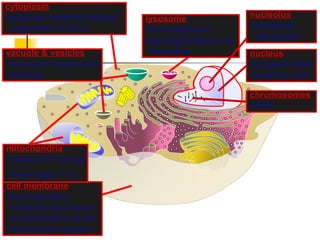
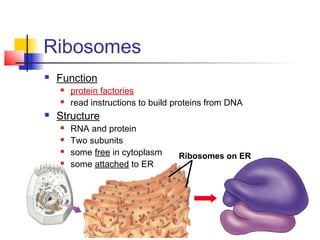
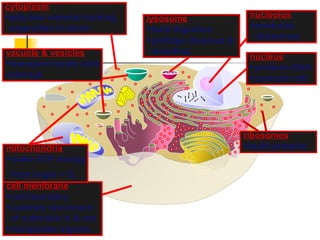
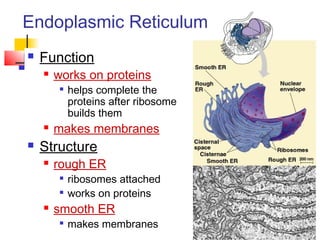
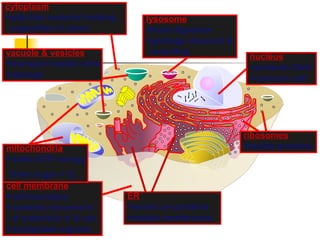
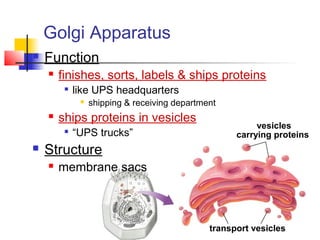
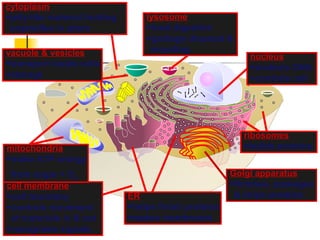
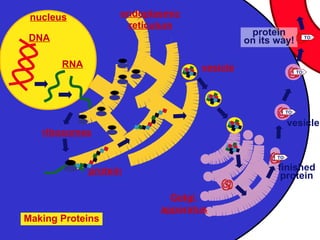
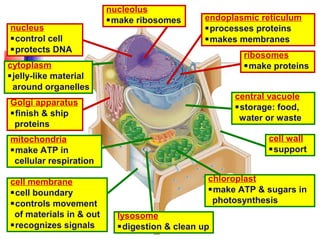
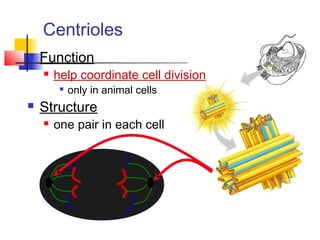
This document provides an overview of cells and their organelles. It discusses that cells are the basic unit of life and have three main jobs - to make energy, make proteins, and make more cells. It describes the various organelles found in plant and animal cells and their specific functions, such as mitochondria generating energy through cellular respiration, the nucleus housing DNA, and ribosomes producing proteins. The document emphasizes that cells work together through their organelles to perform all the necessary functions of life.