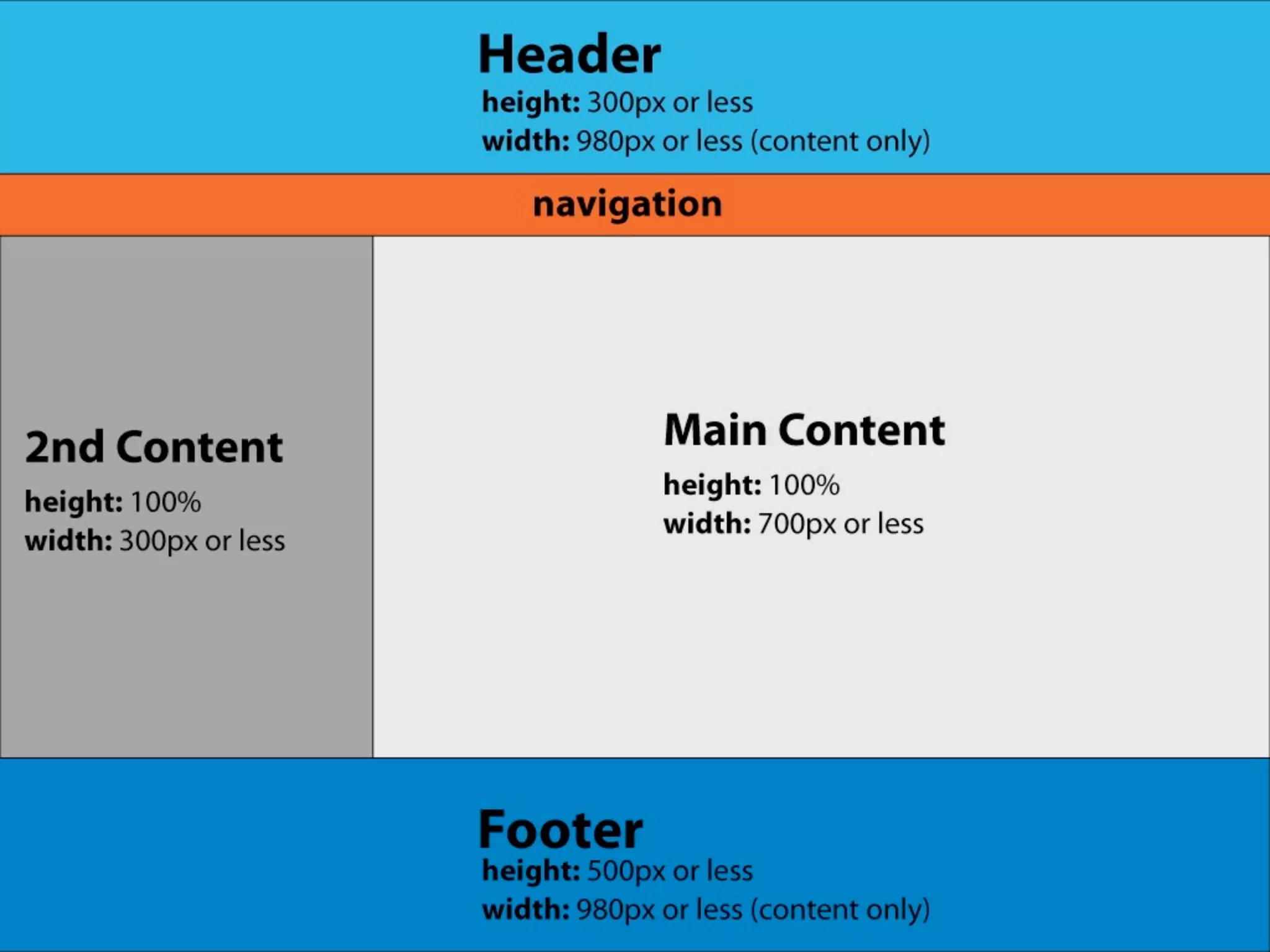
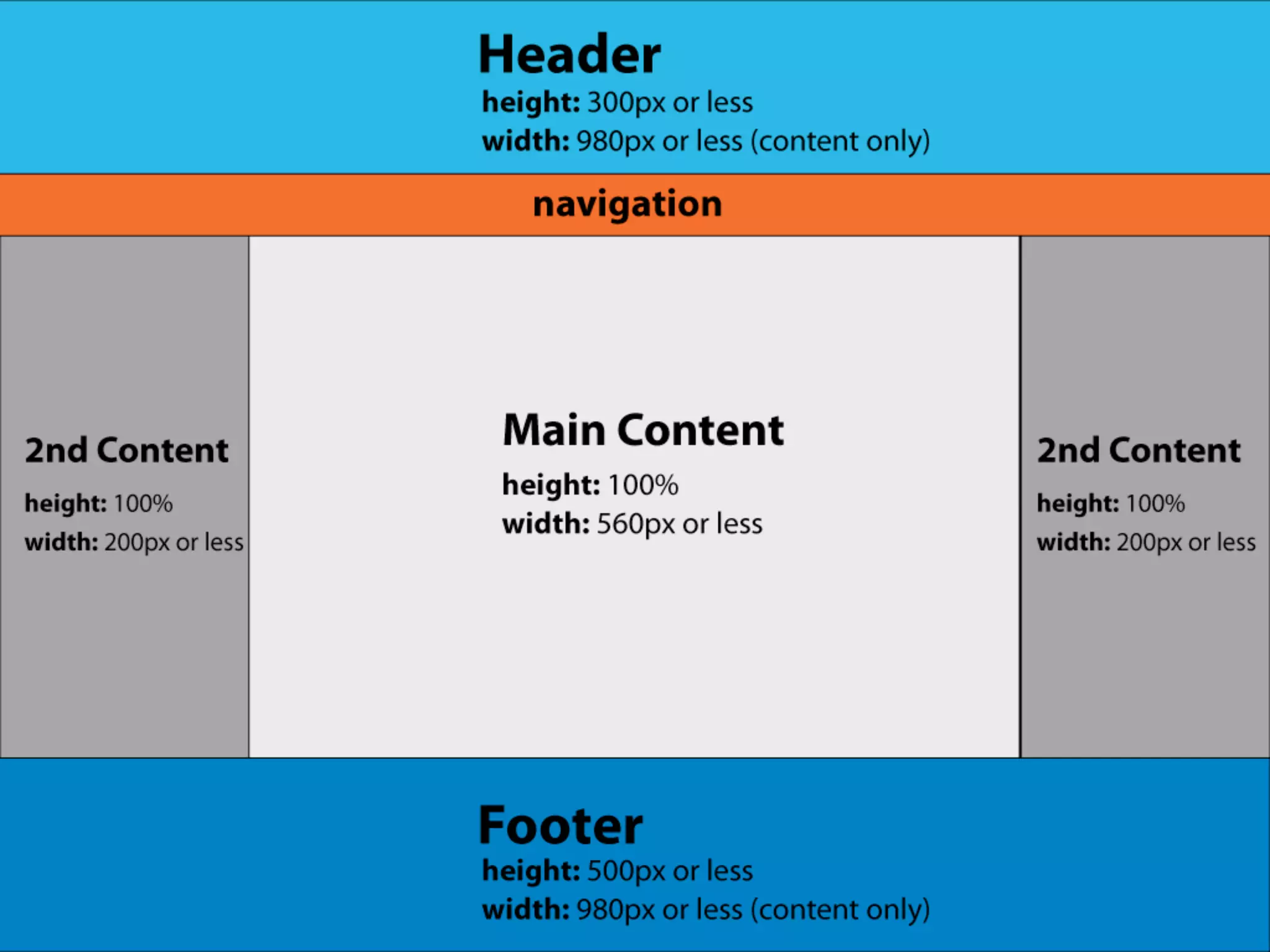
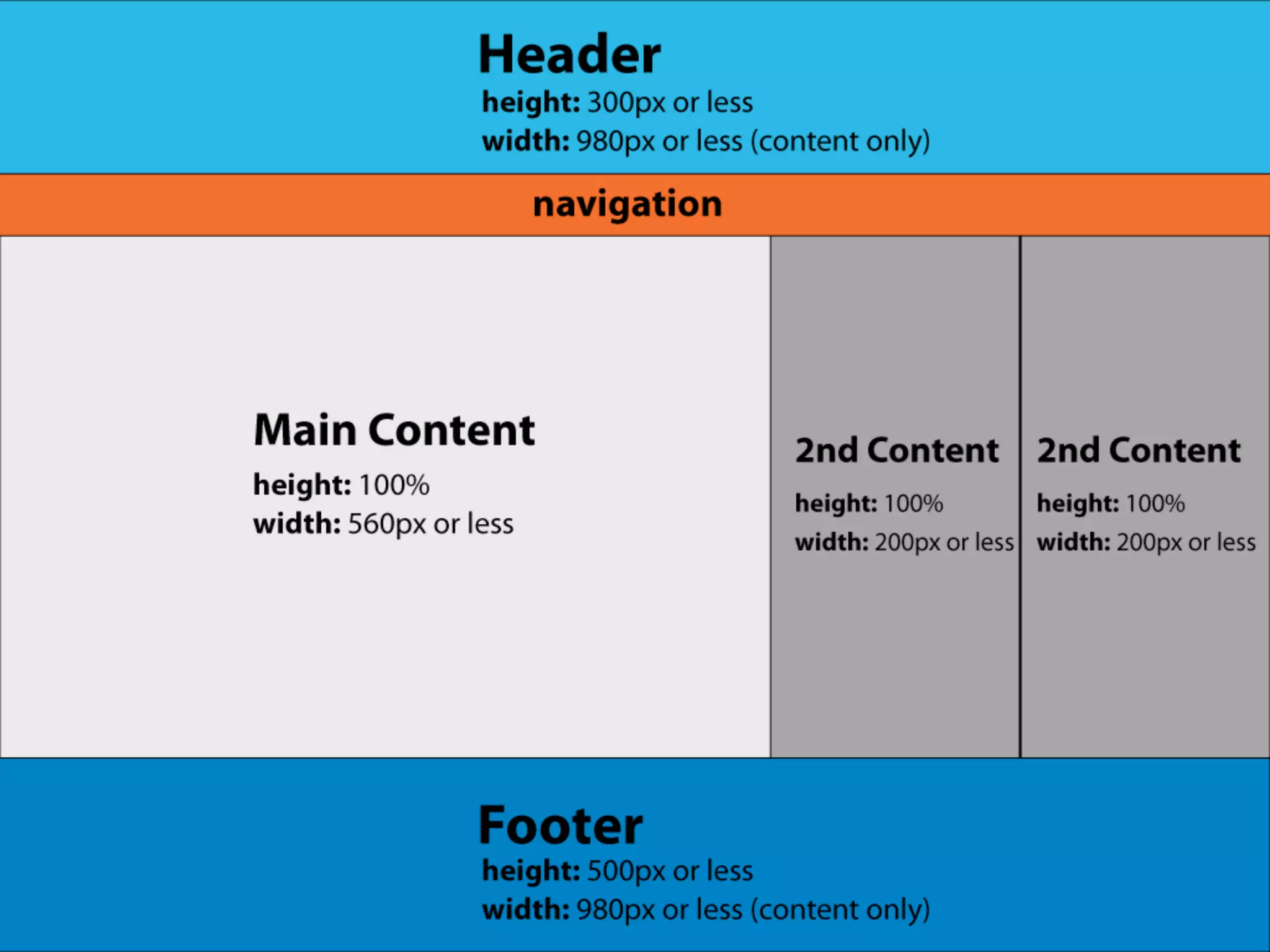
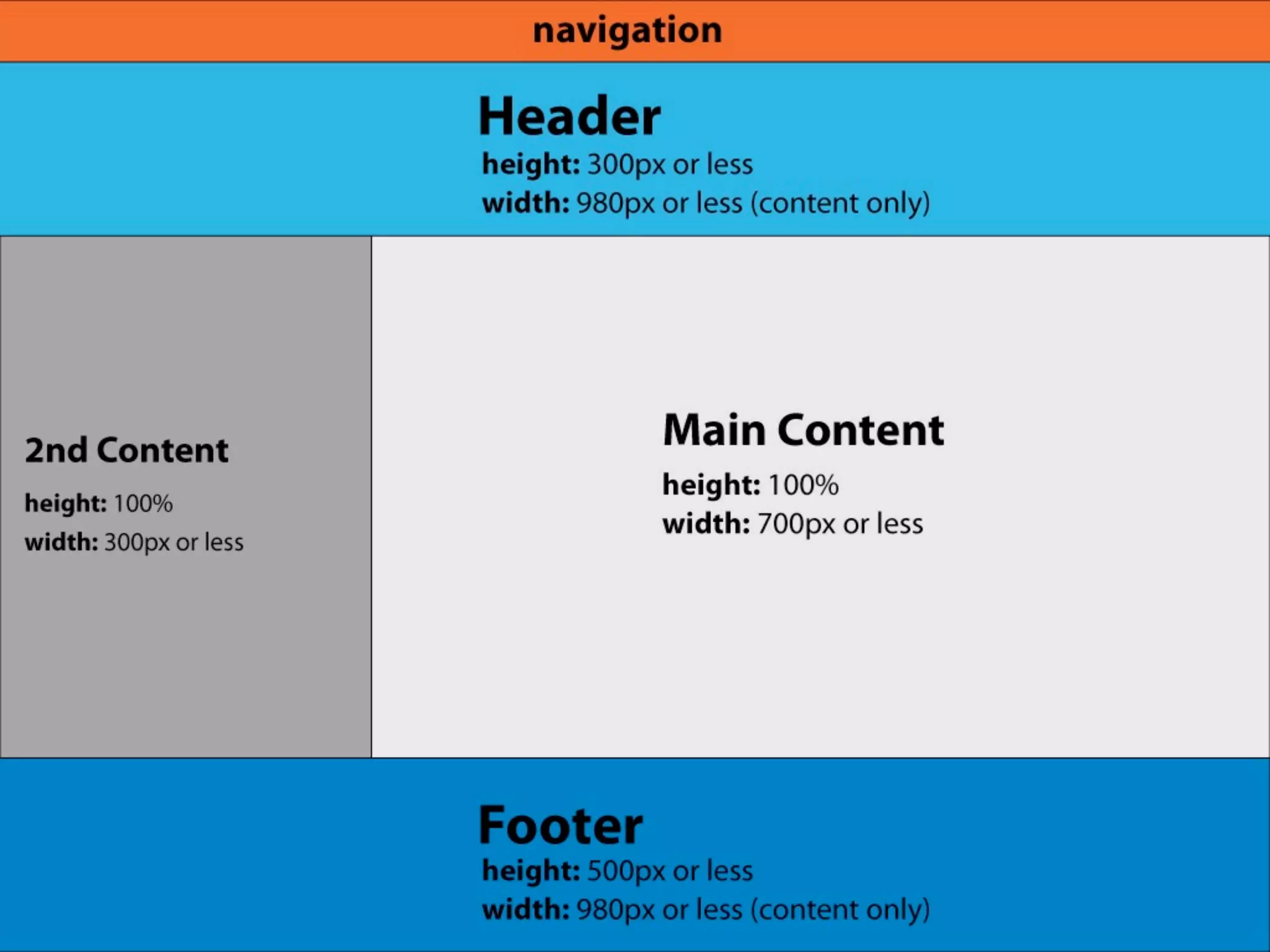
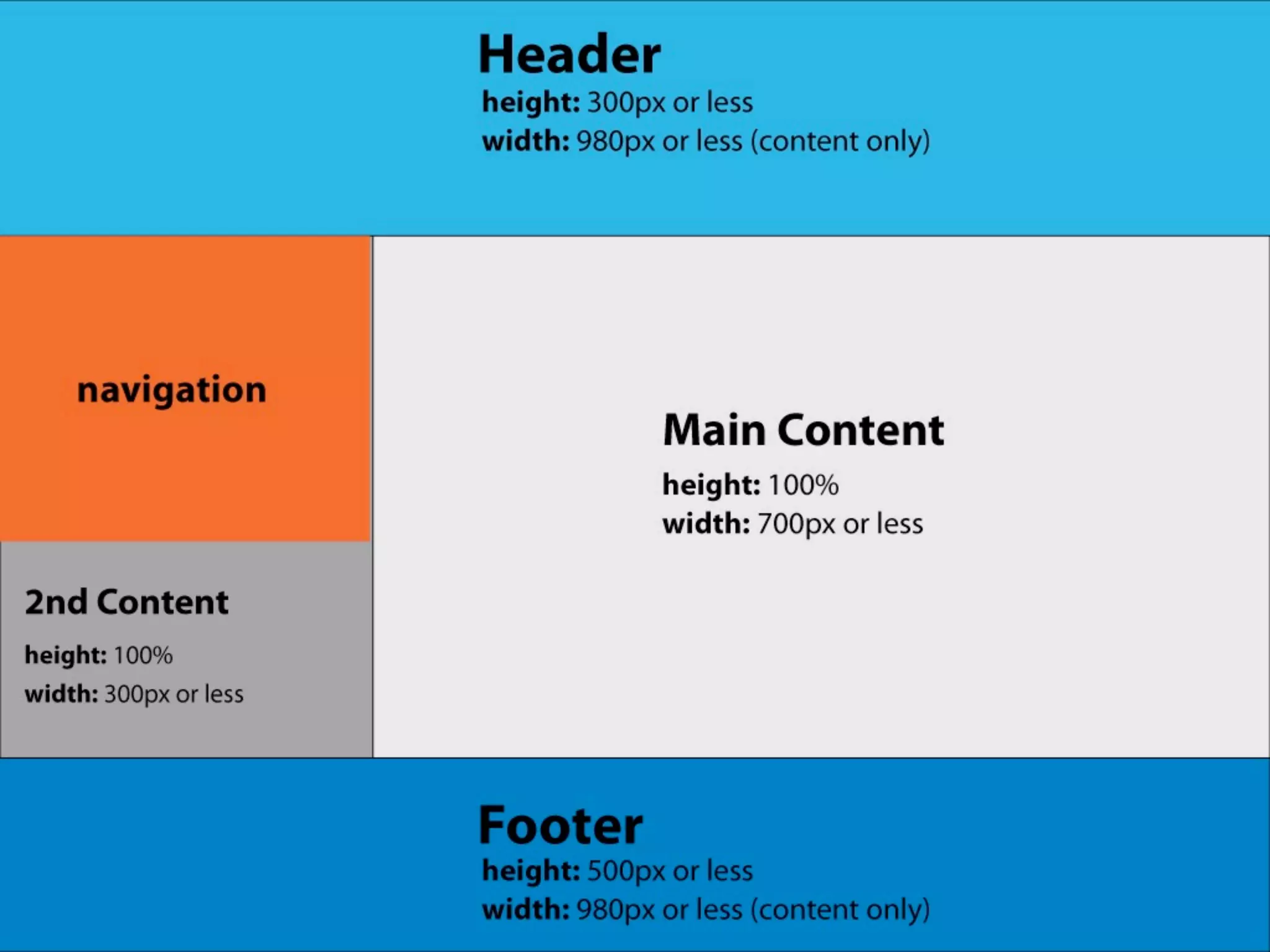
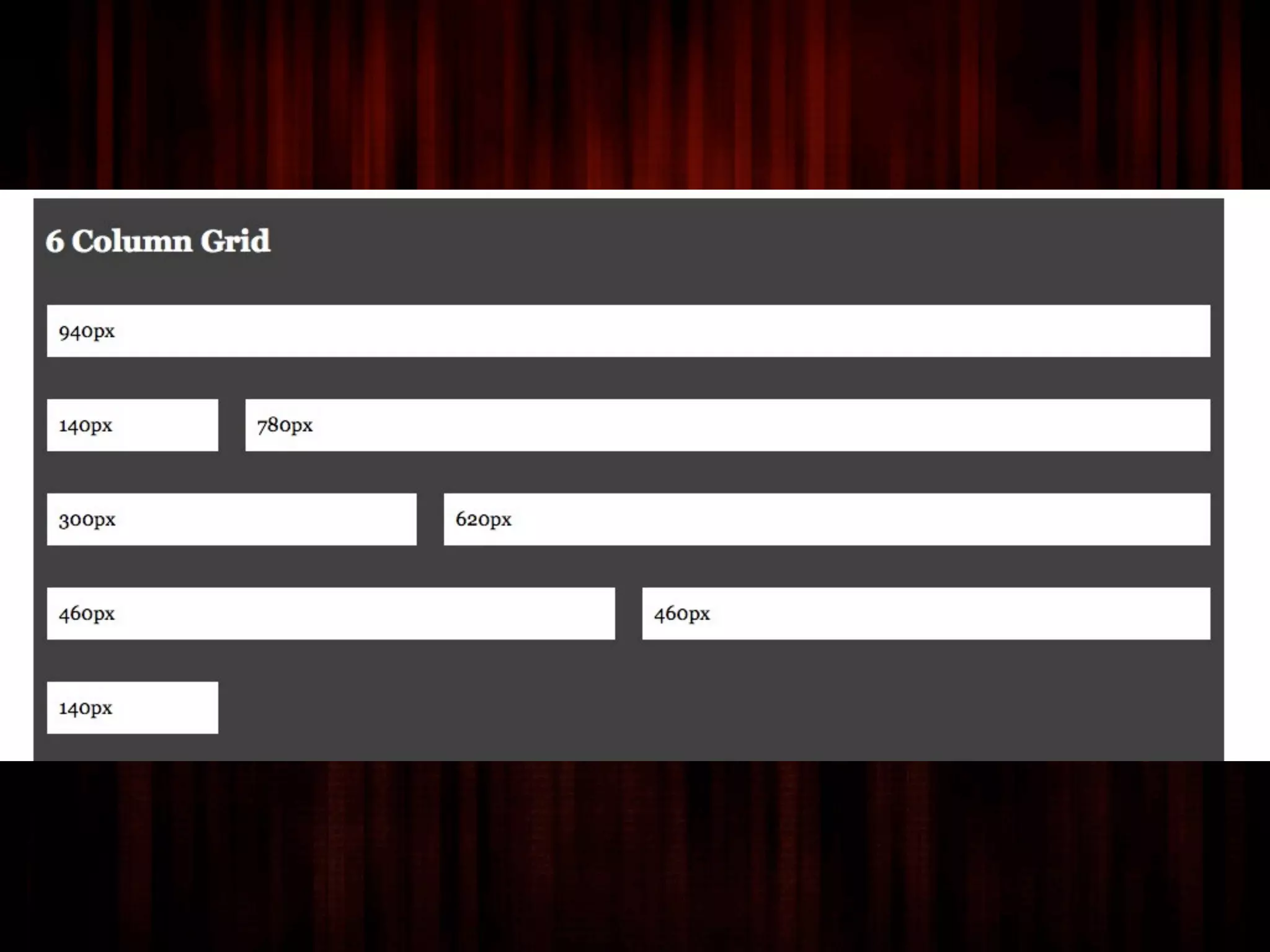
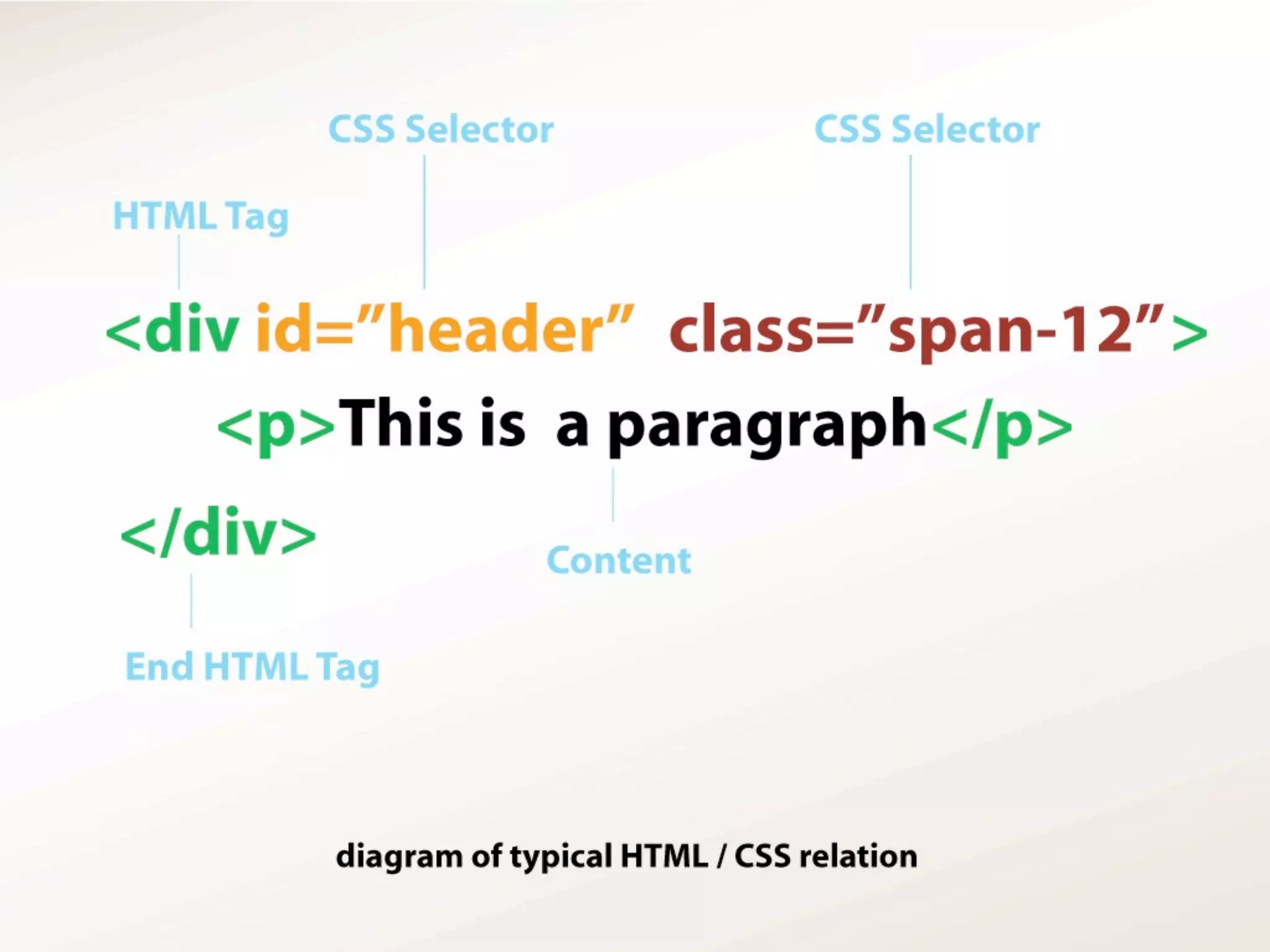
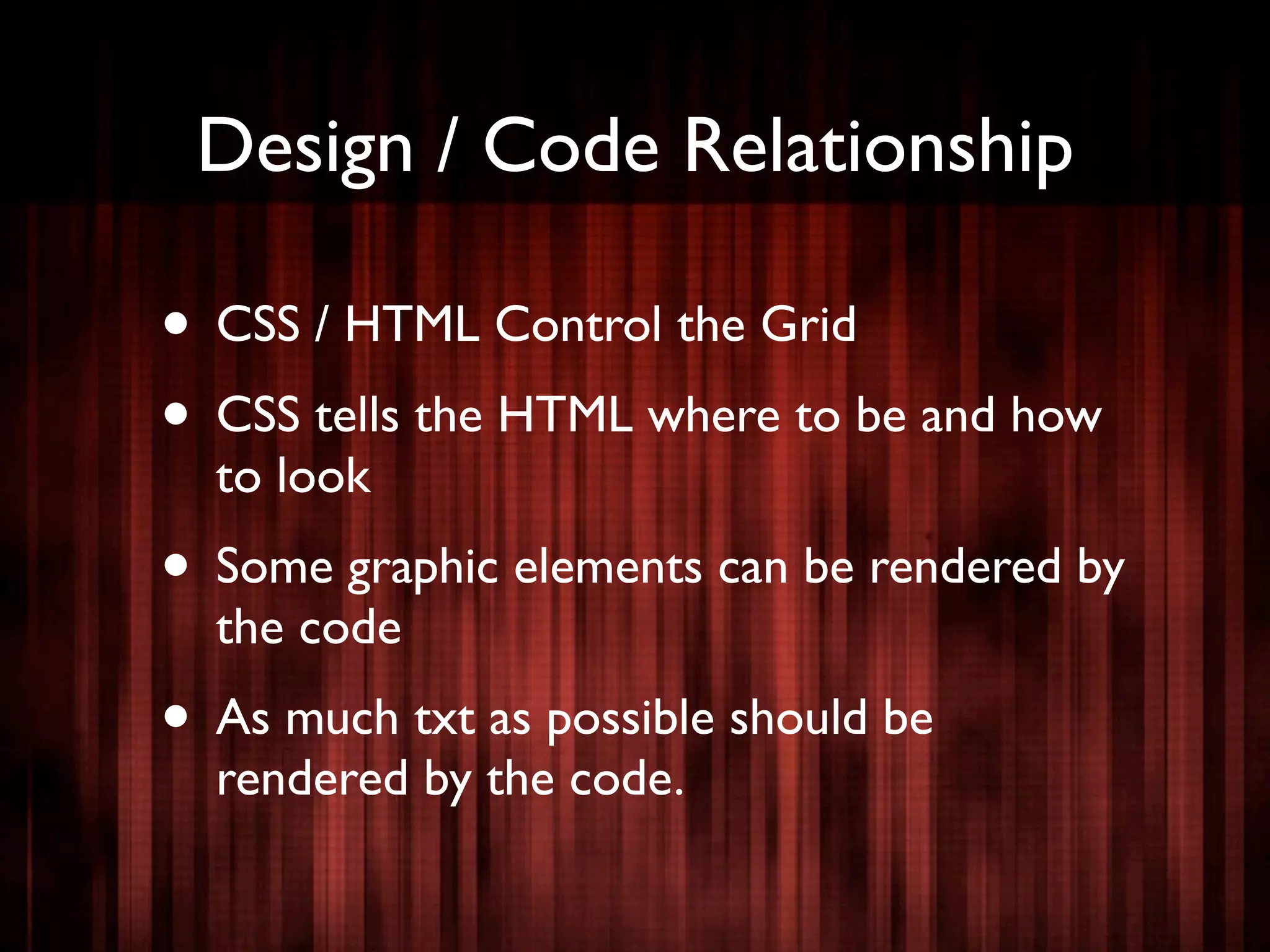
The document outlines the structure and functionality of websites, detailing their multi-layered design which includes content, media, and both front-end and back-end coding. It describes various types of websites such as mini-sites, marketing sites, and e-commerce platforms, while emphasizing the importance of grid systems for layout and design control. Additionally, it highlights the relationship between design and code, particularly surrounding HTML and CSS, and encourages web designers to become familiar with coding without needing to be experts.