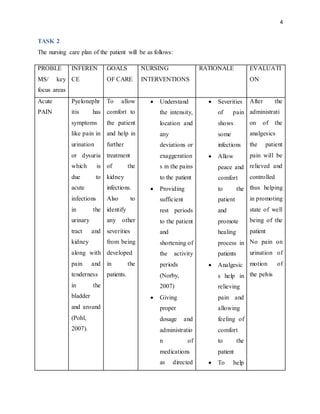
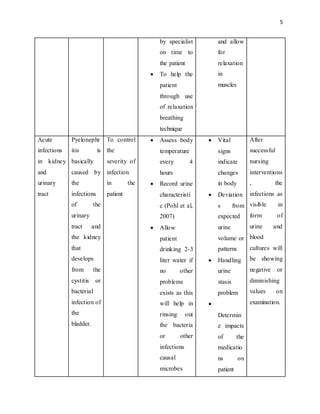
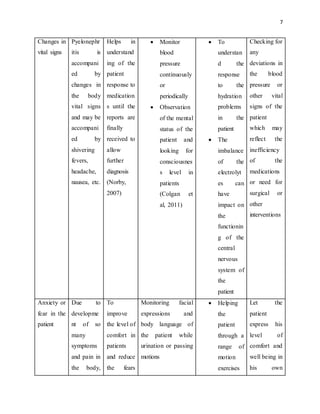
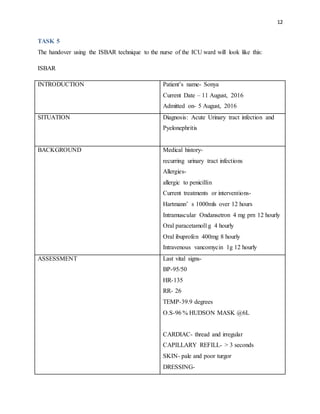
The document outlines the critical nursing care plan for a patient named Sonya suffering from acute urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis, highlighting essential diagnostic tests, treatment protocols, and necessary documentation. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring vital signs, pain management, and timely administration of medications to prevent complications such as renal failure and sepsis. The report also details the interventions required and the nursing responsibilities in ensuring patient safety and effective recovery.