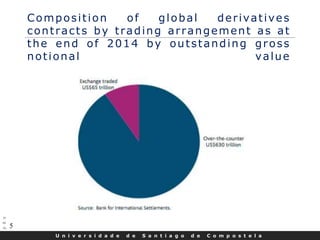
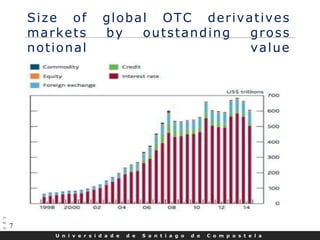
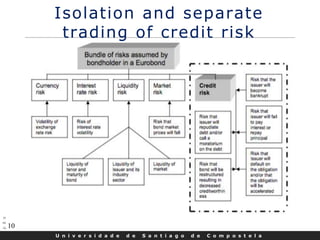
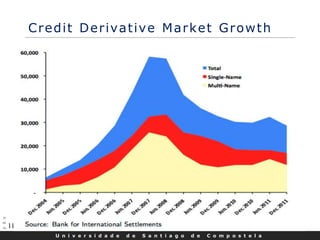
This document discusses credit default swaps (CDS), including:
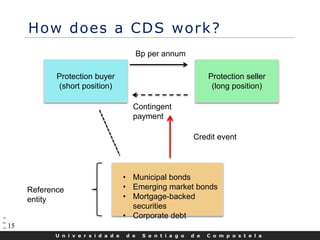
- CDS are a type of derivative that functions as a form of default insurance on a debt obligation.
- In a basic CDS transaction, the protection buyer makes periodic payments to the protection seller, and in exchange receives a payoff if the reference entity defaults or experiences another credit event.
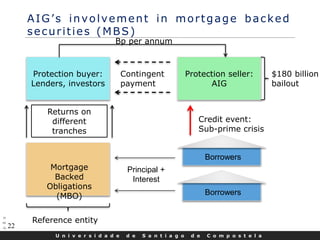
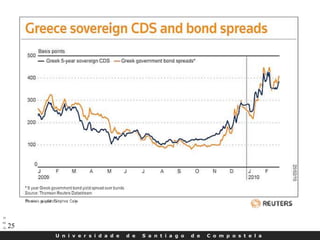
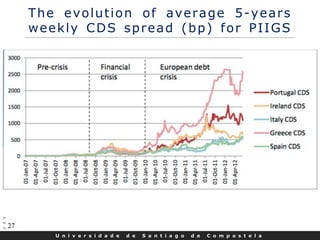
- CDS markets grew rapidly in the early 2000s but also contributed to the 2008 financial crisis when American International Group's massive CDS exposures led to its government bailout.