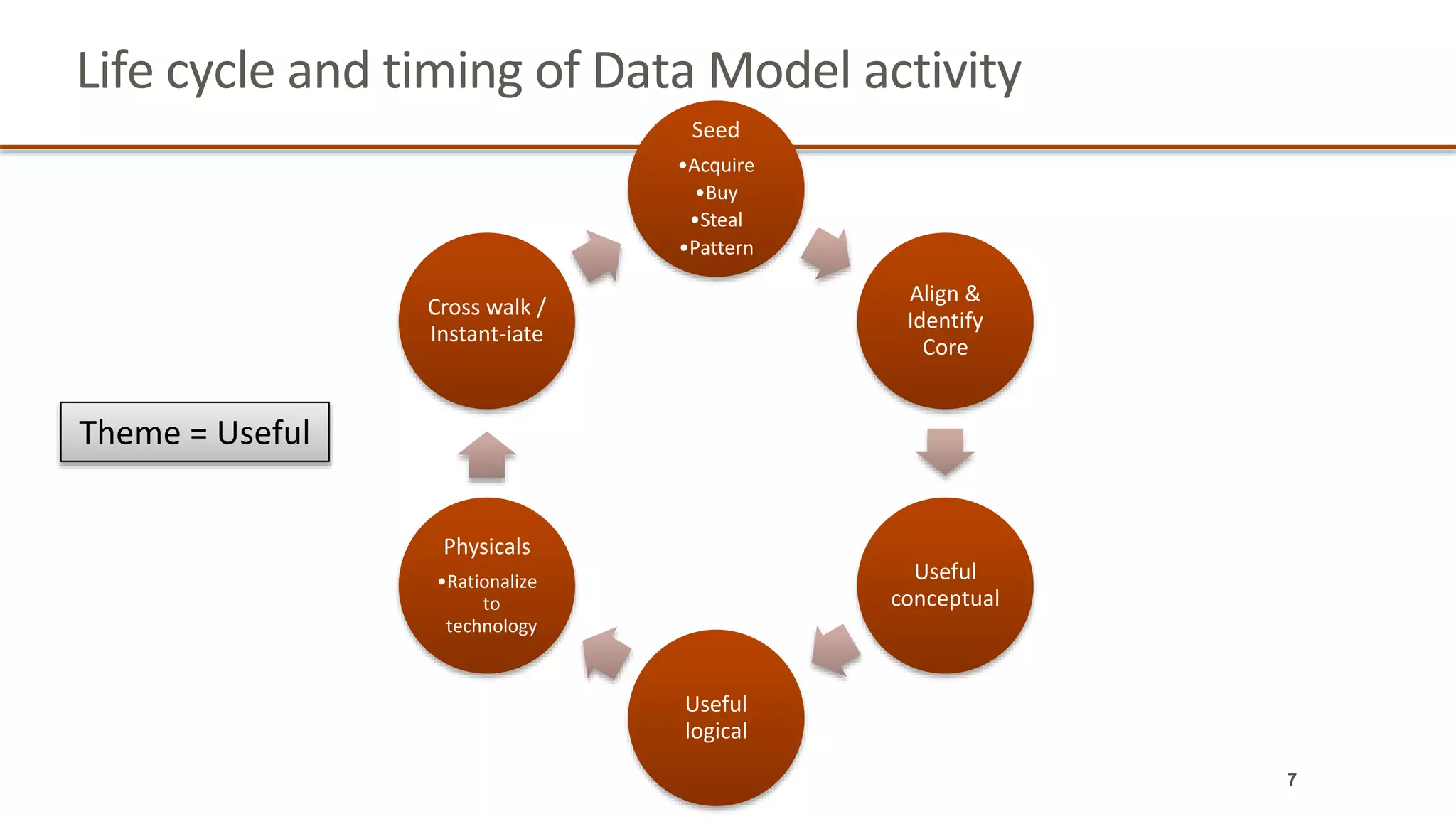
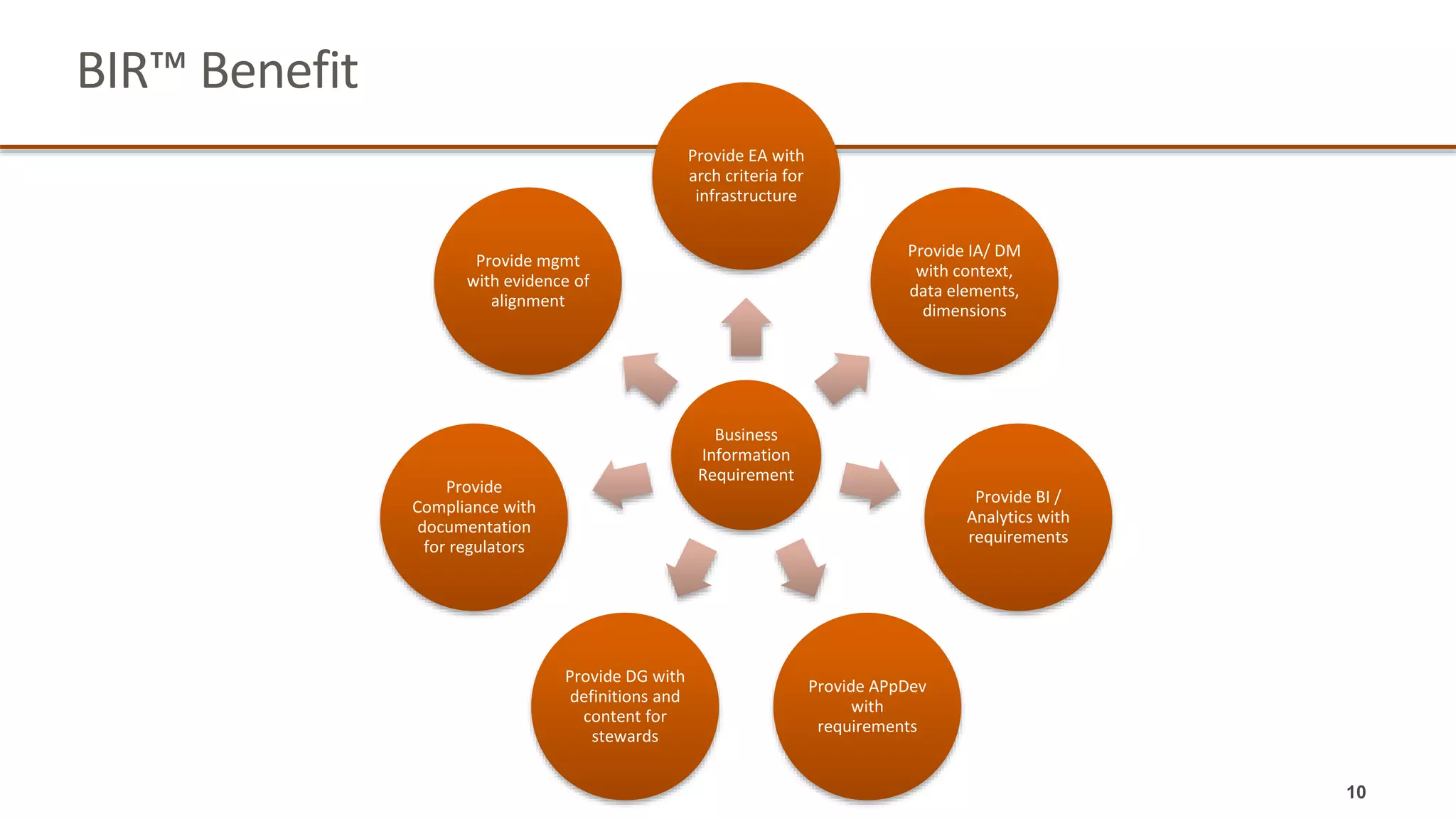
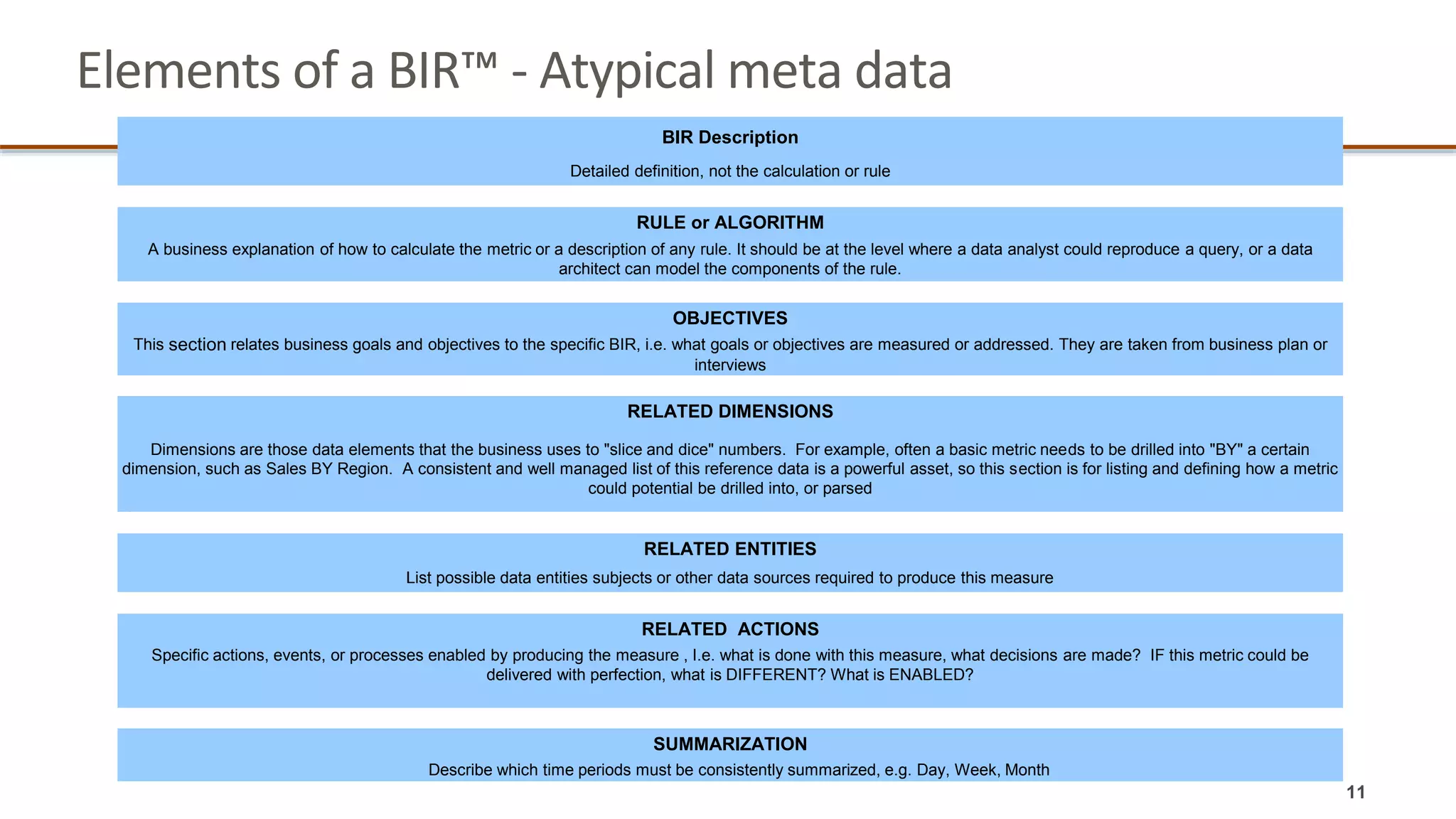
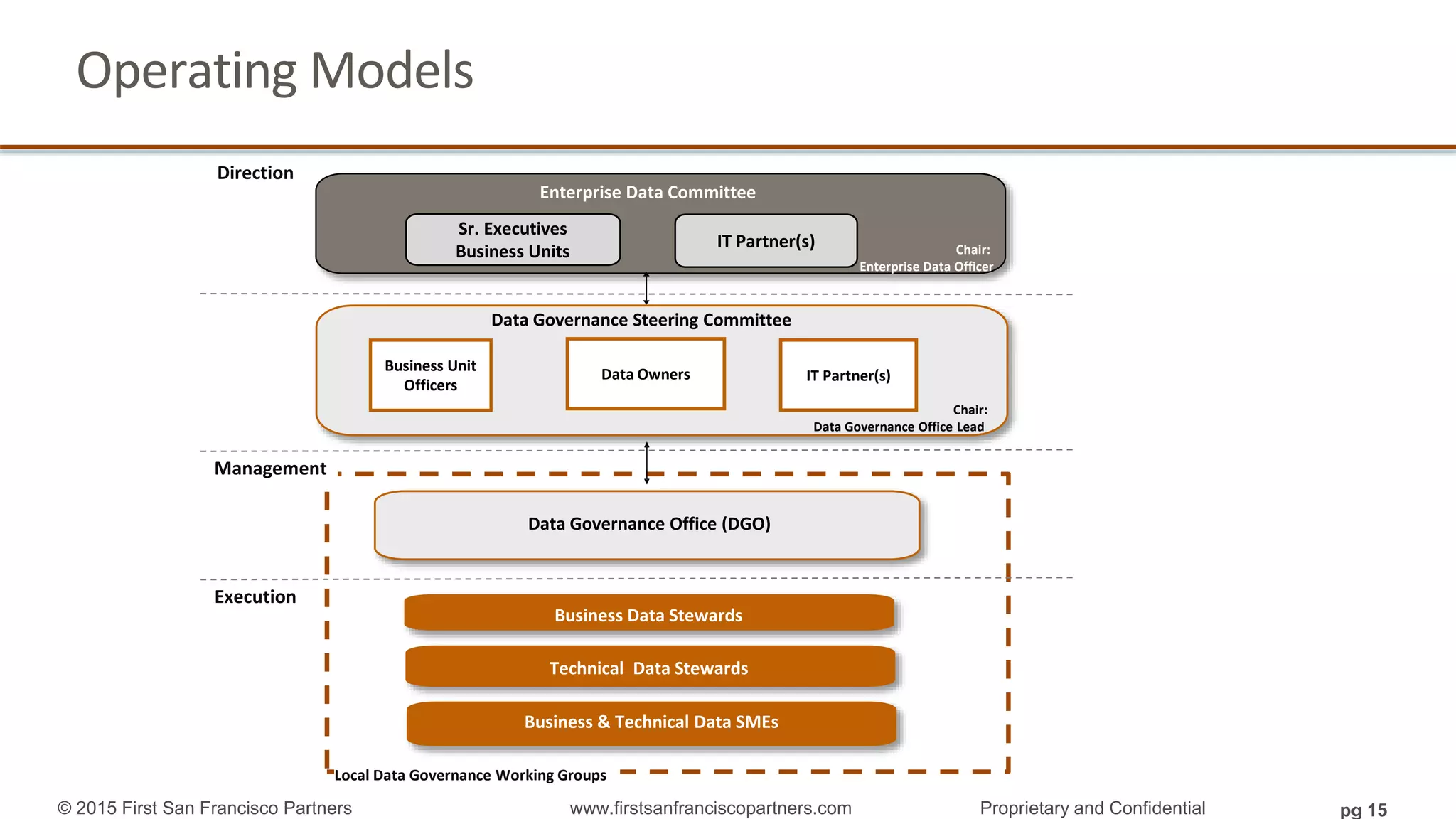
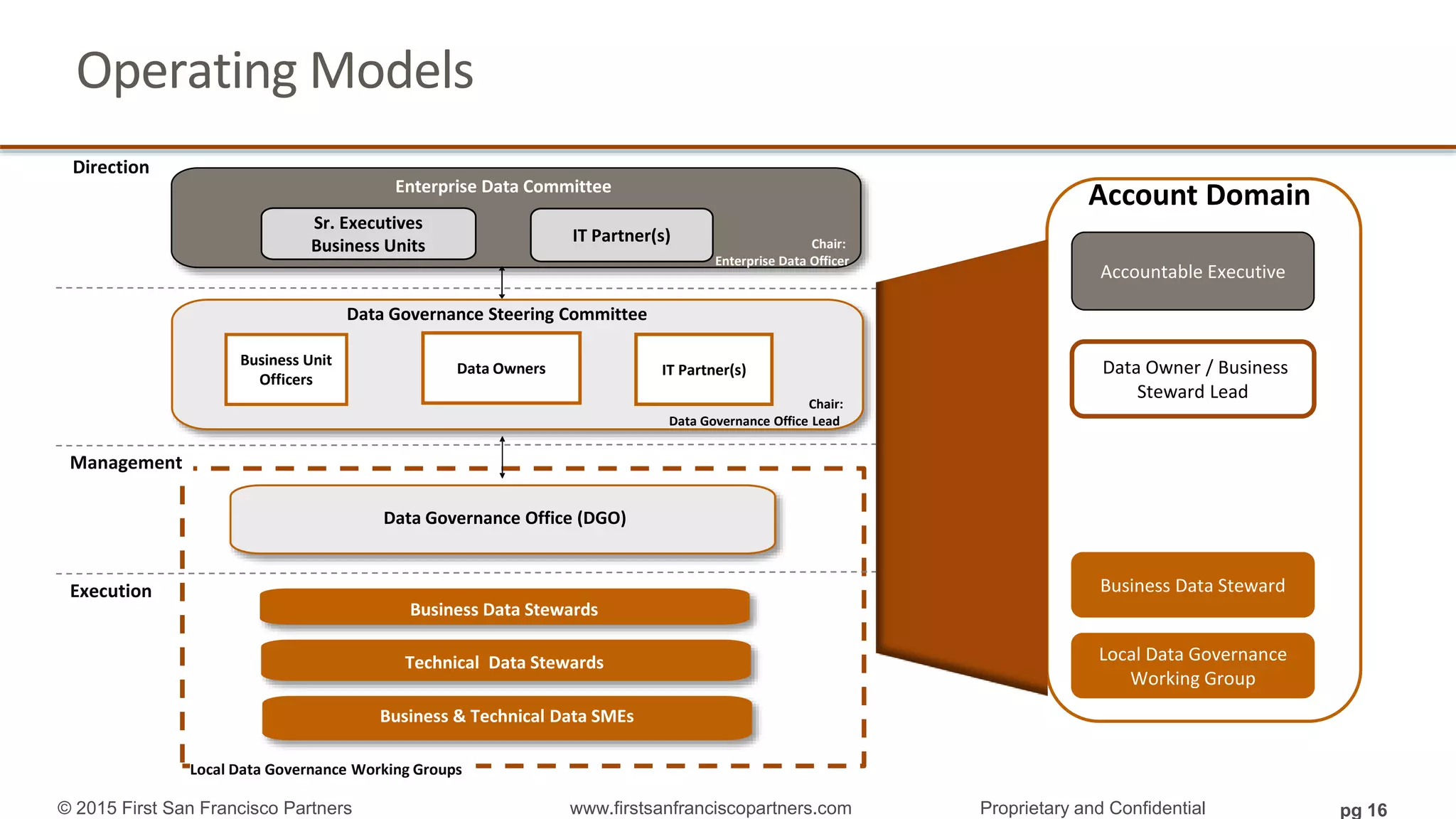
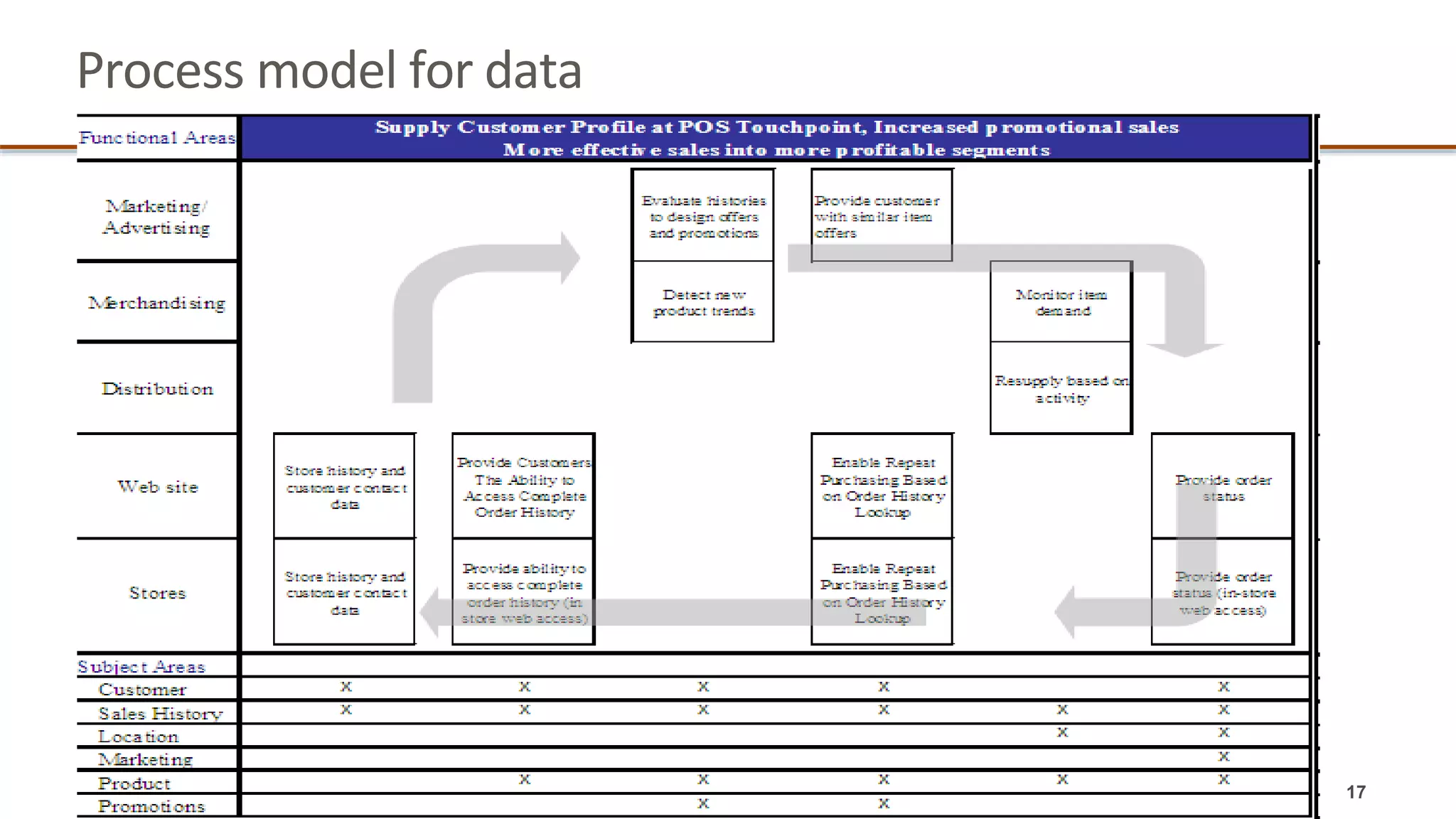
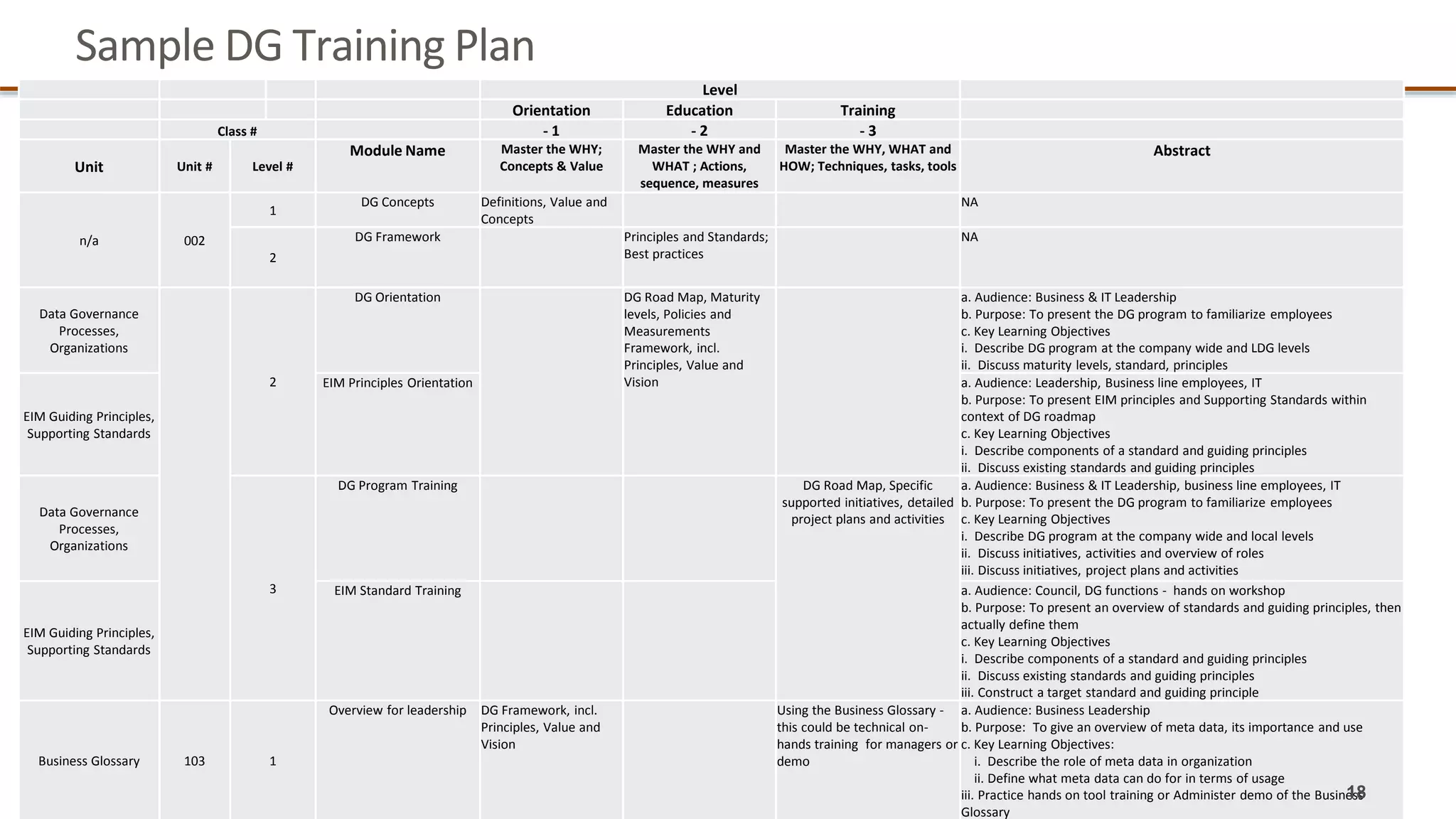
The document outlines a webinar series focused on information management, emphasizing the importance of data models and new tools for effective data governance. It discusses the role of Business Information Requirement Metrics (BIRTMs) and their significance in aligning business objectives with data management practices. The agenda includes upcoming sessions, the life cycle of data model activities, and the need for a comprehensive approach to capturing data context.