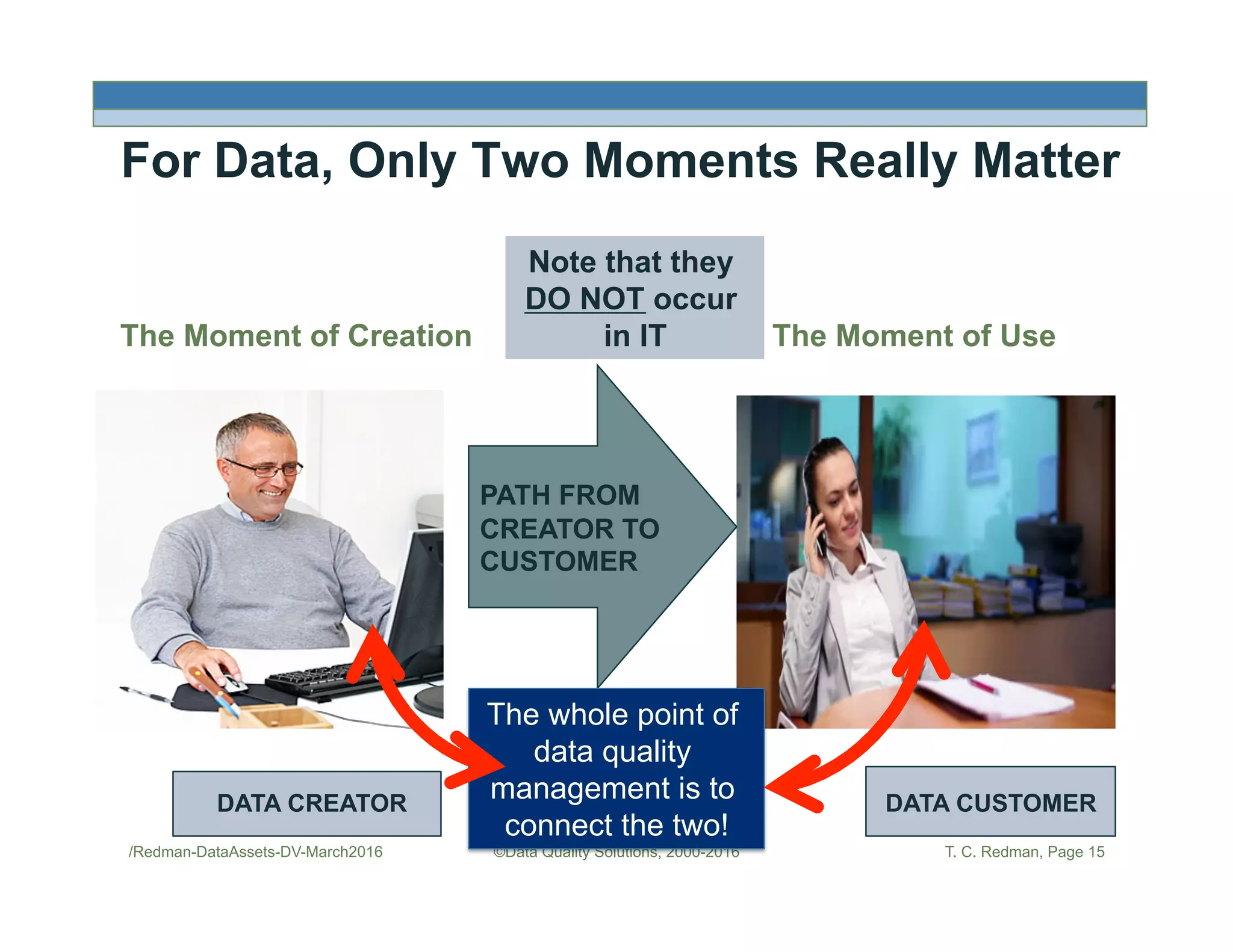
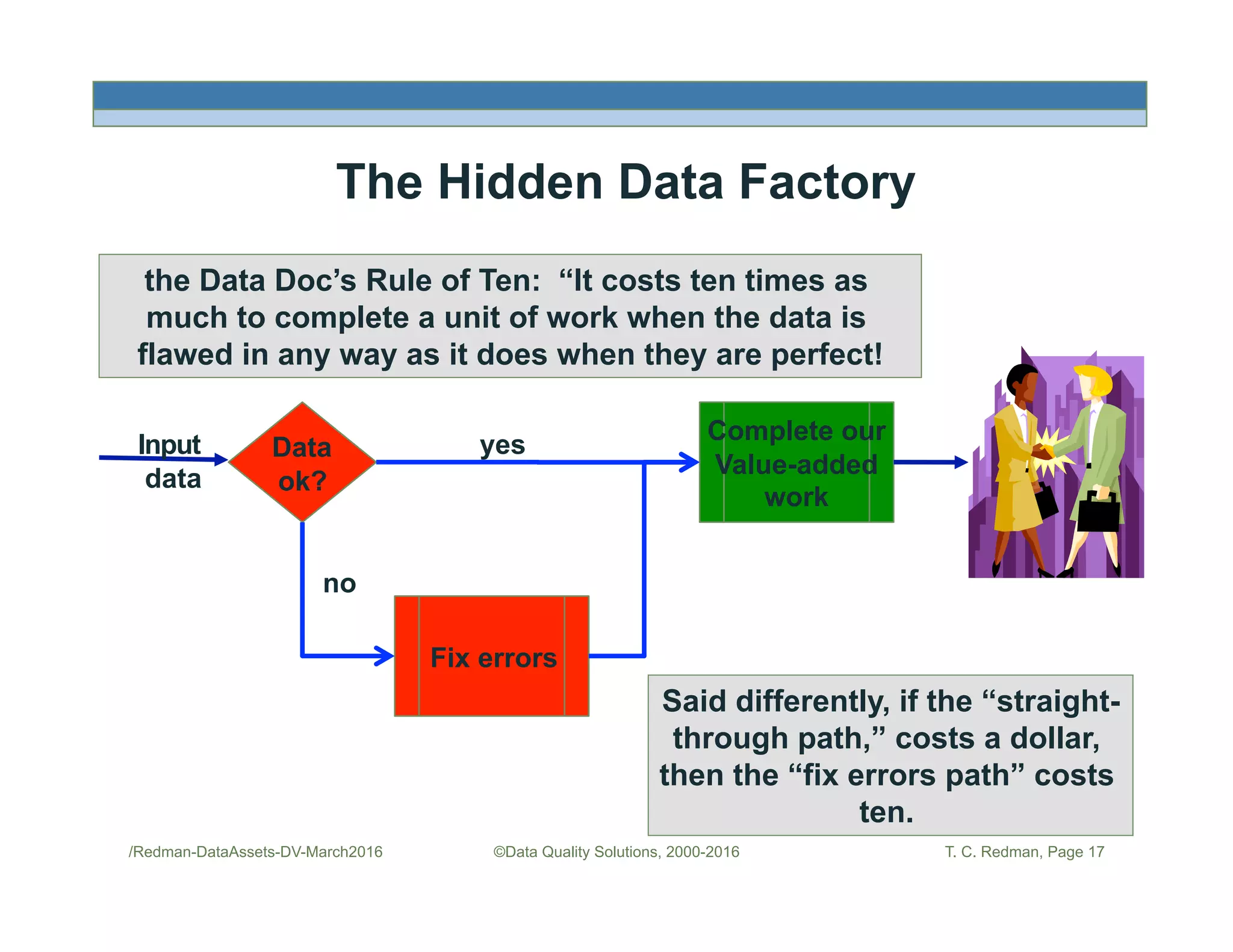
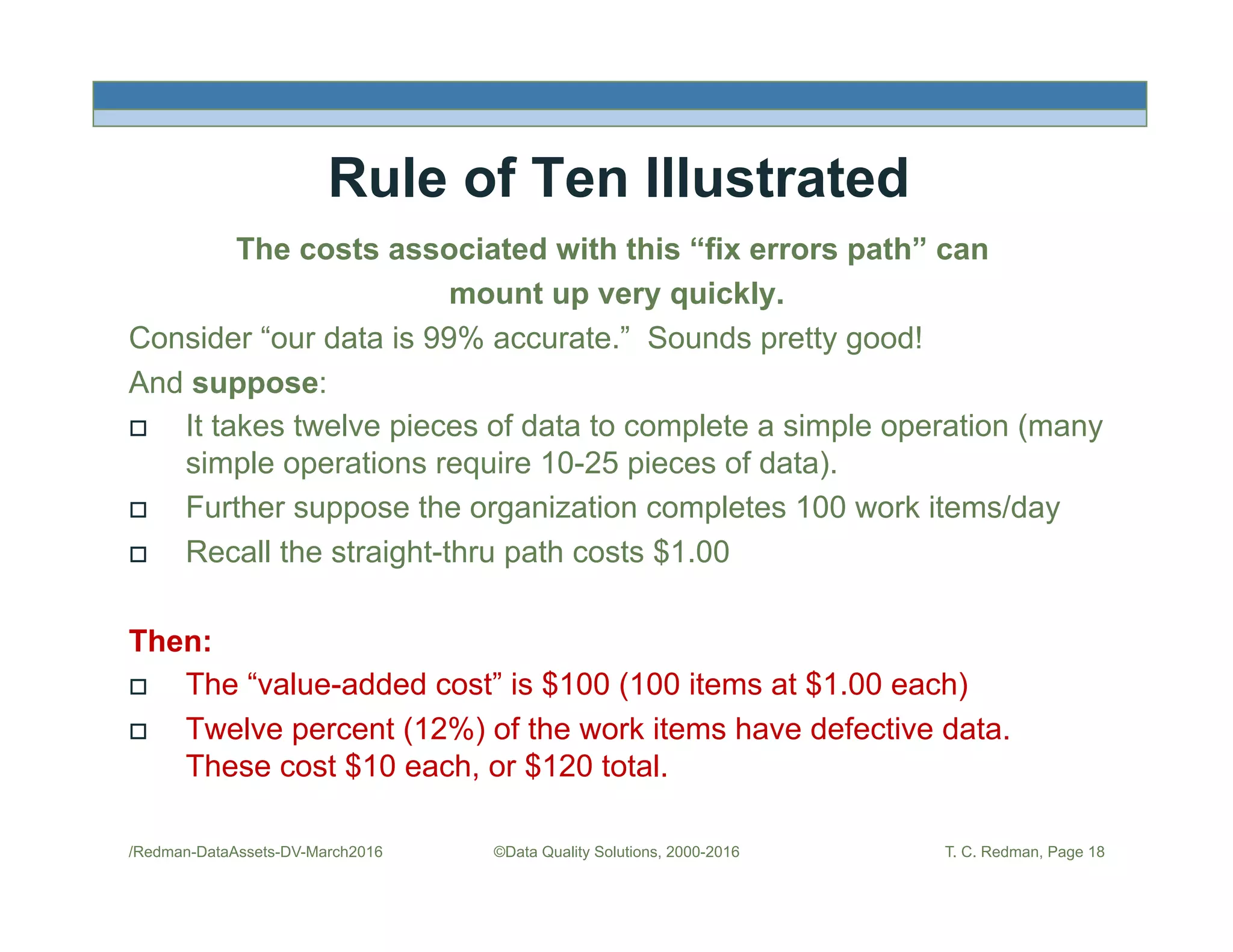
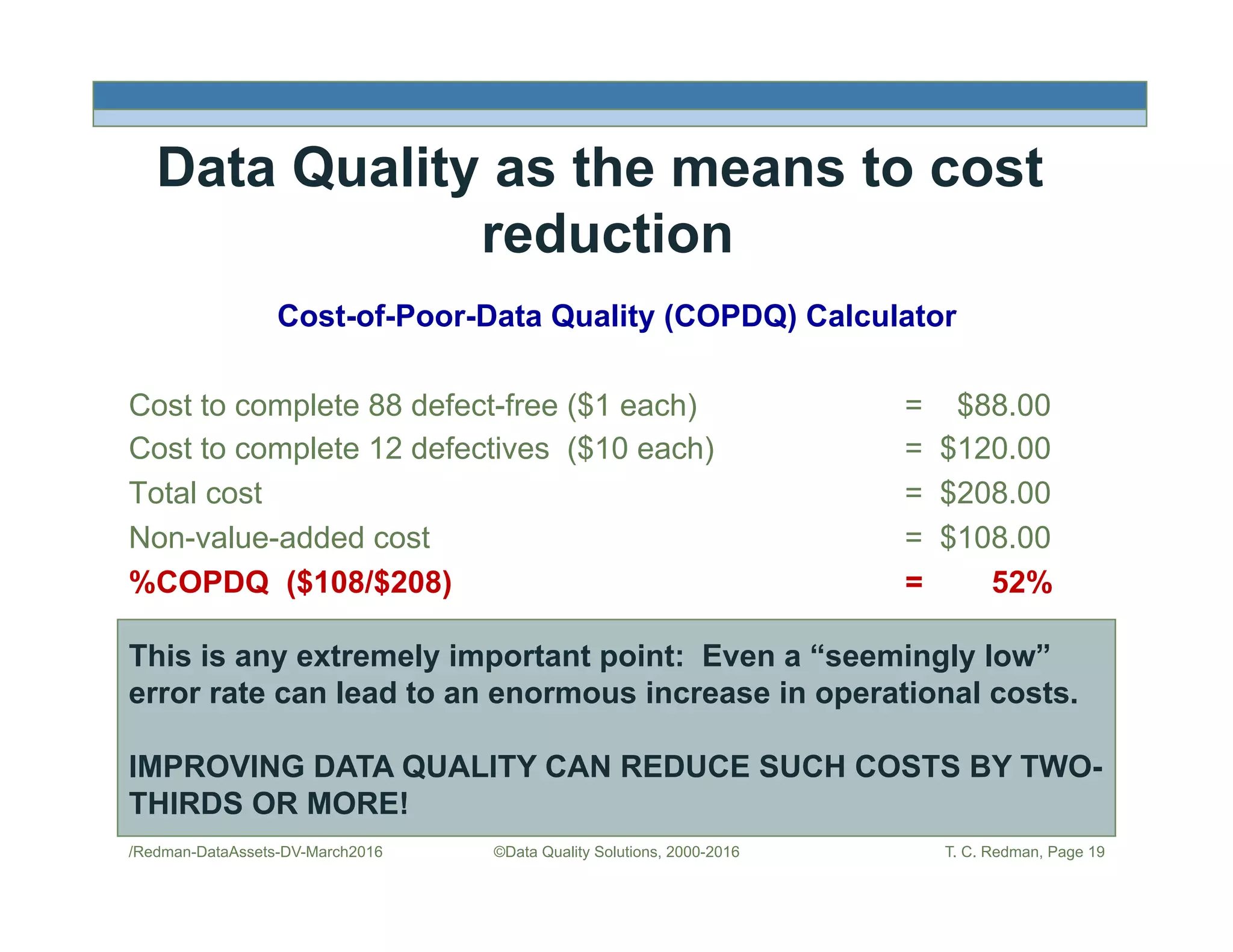
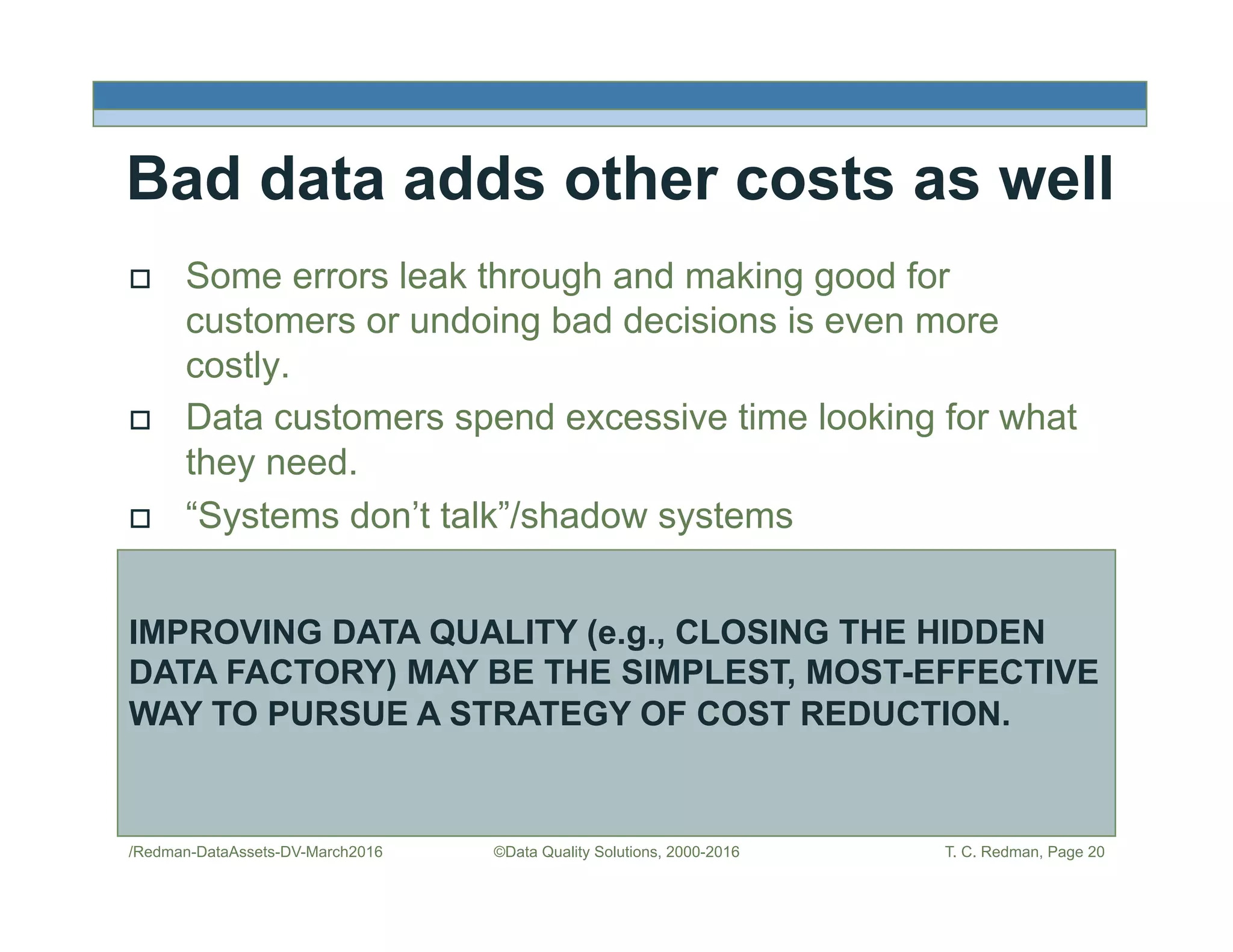
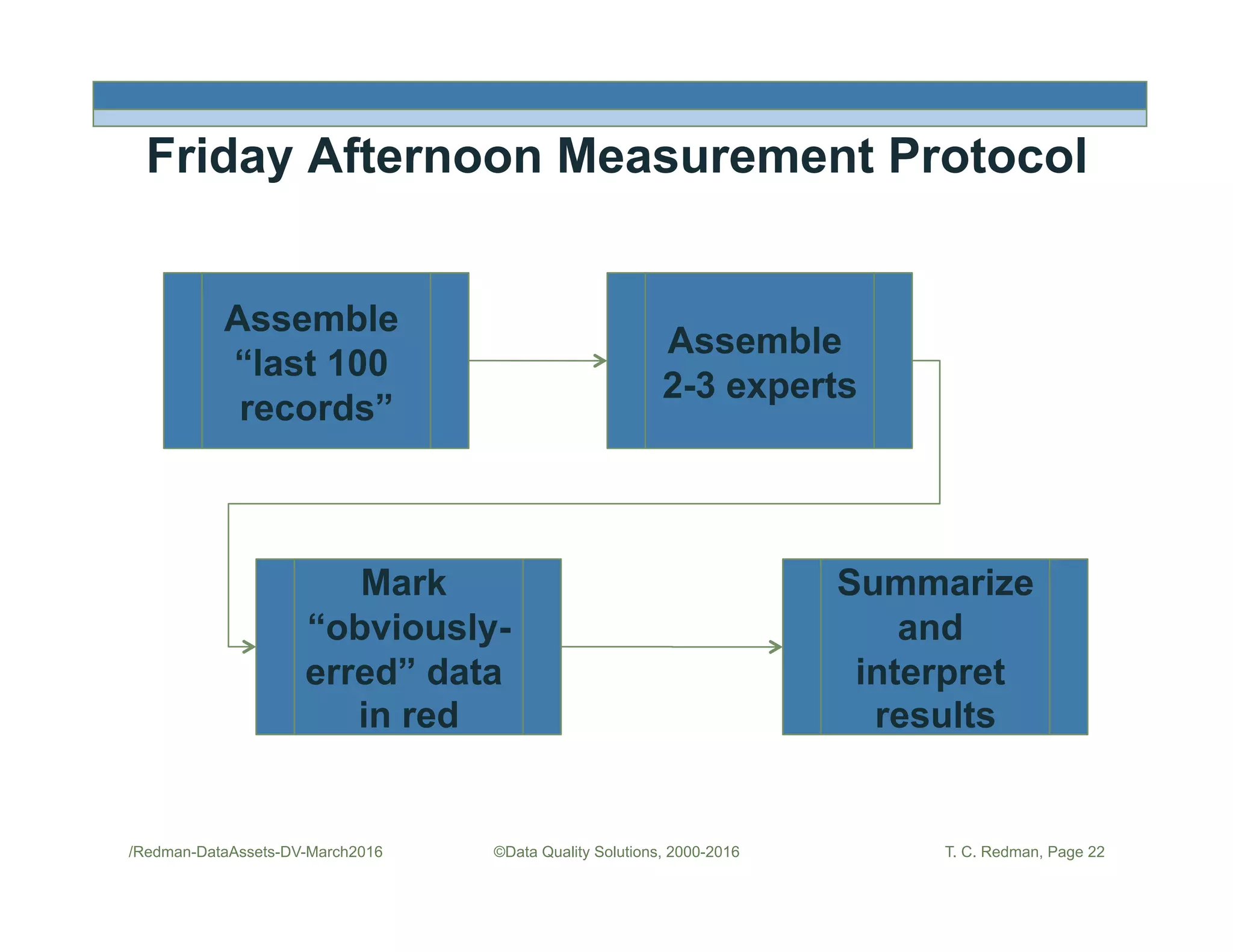
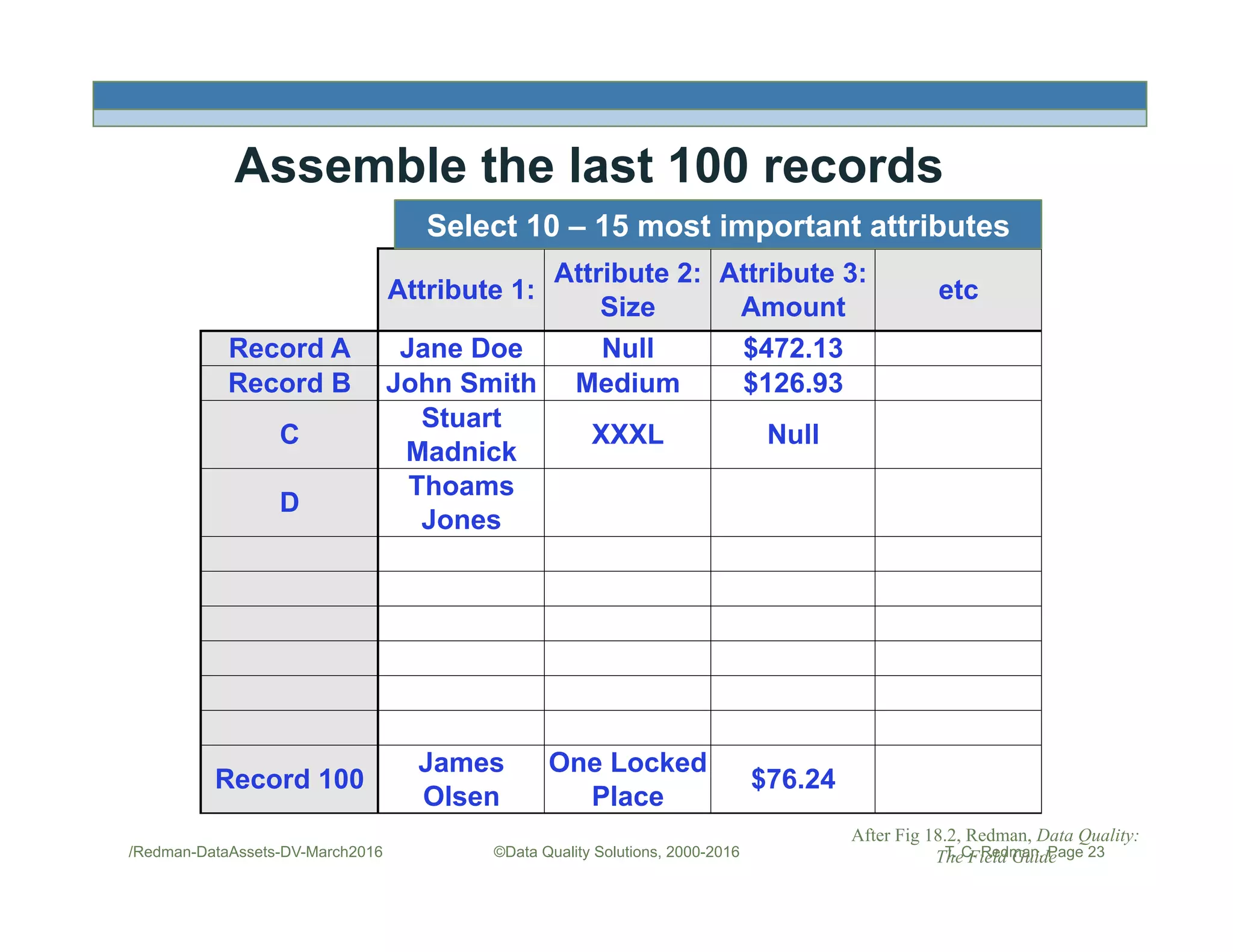
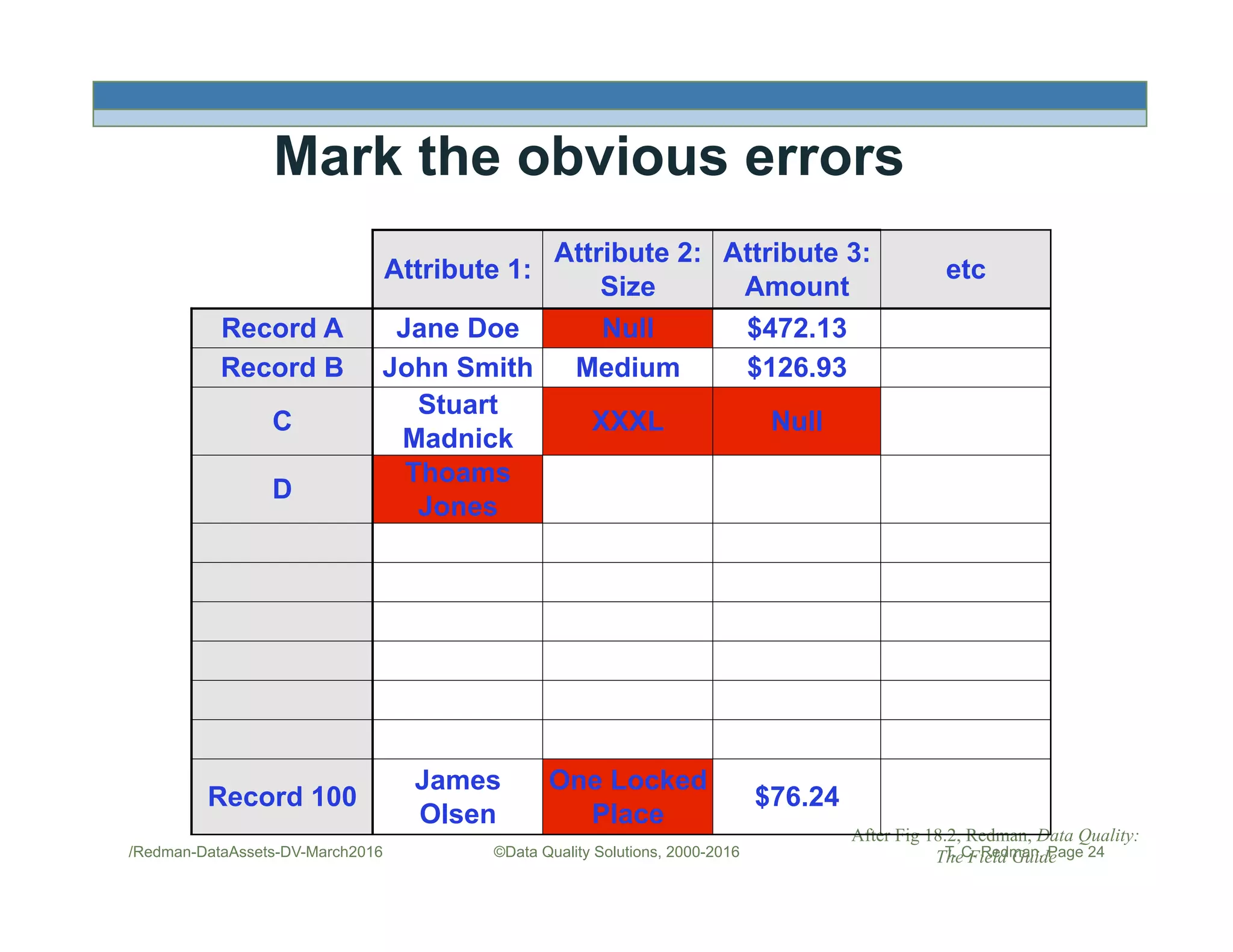
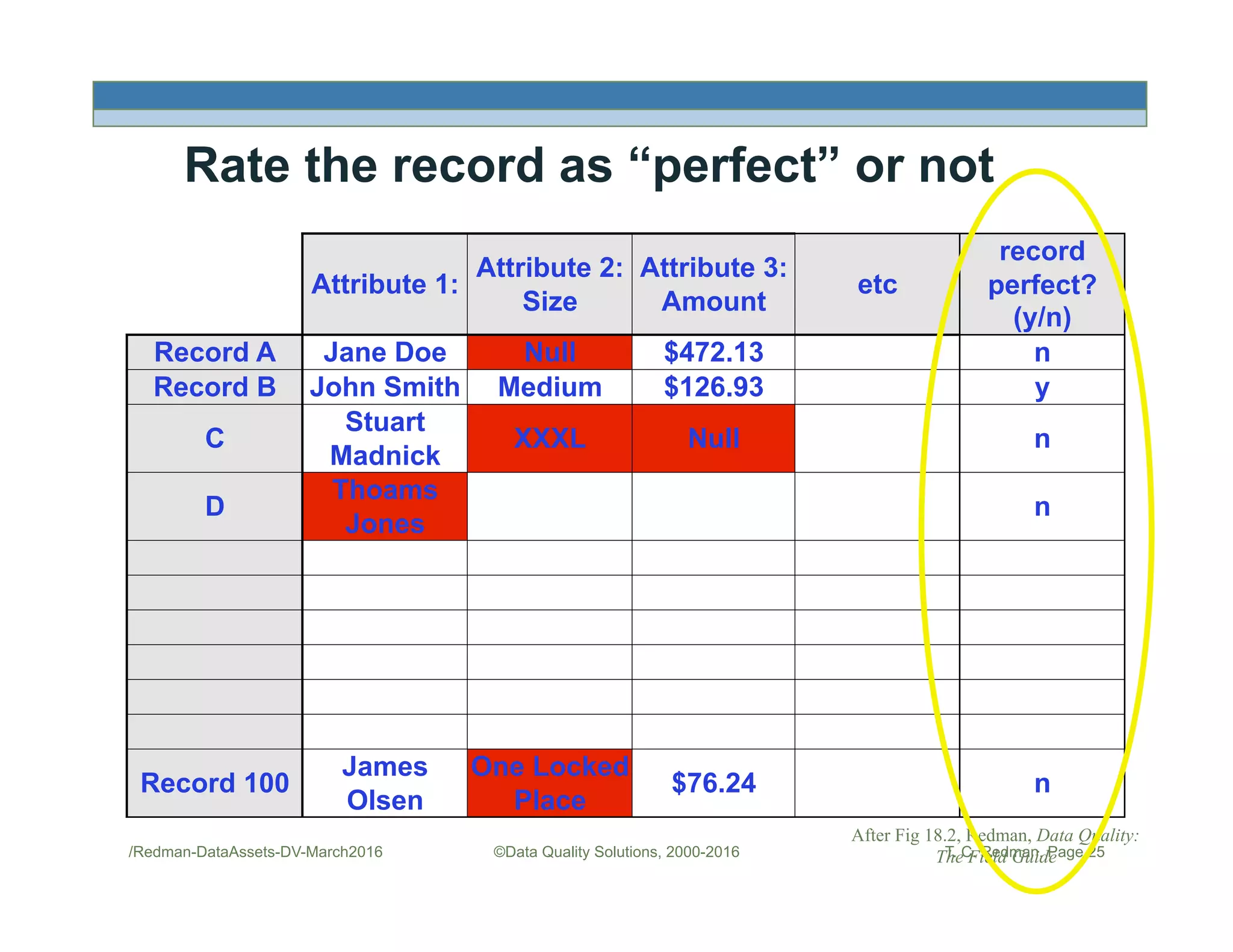
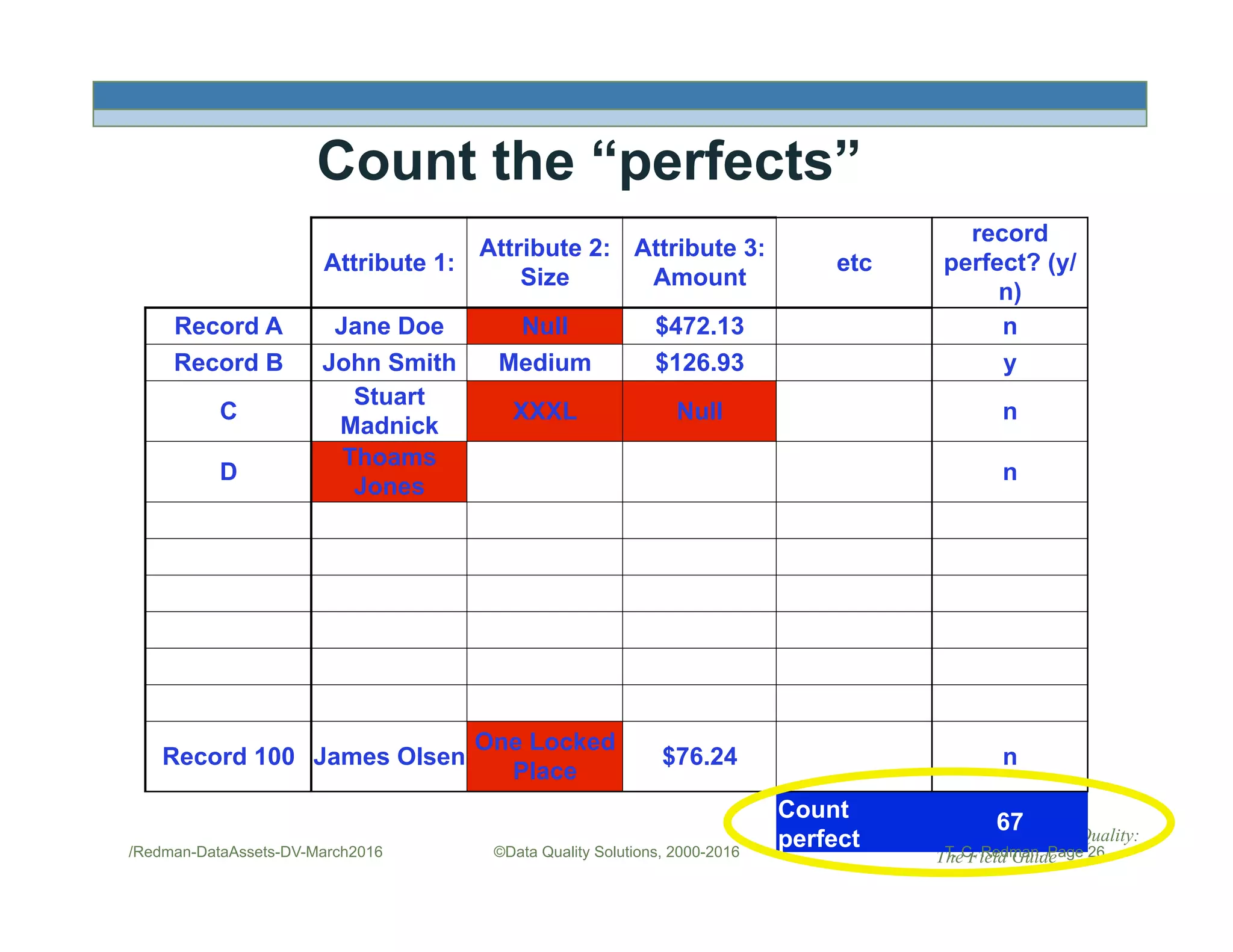
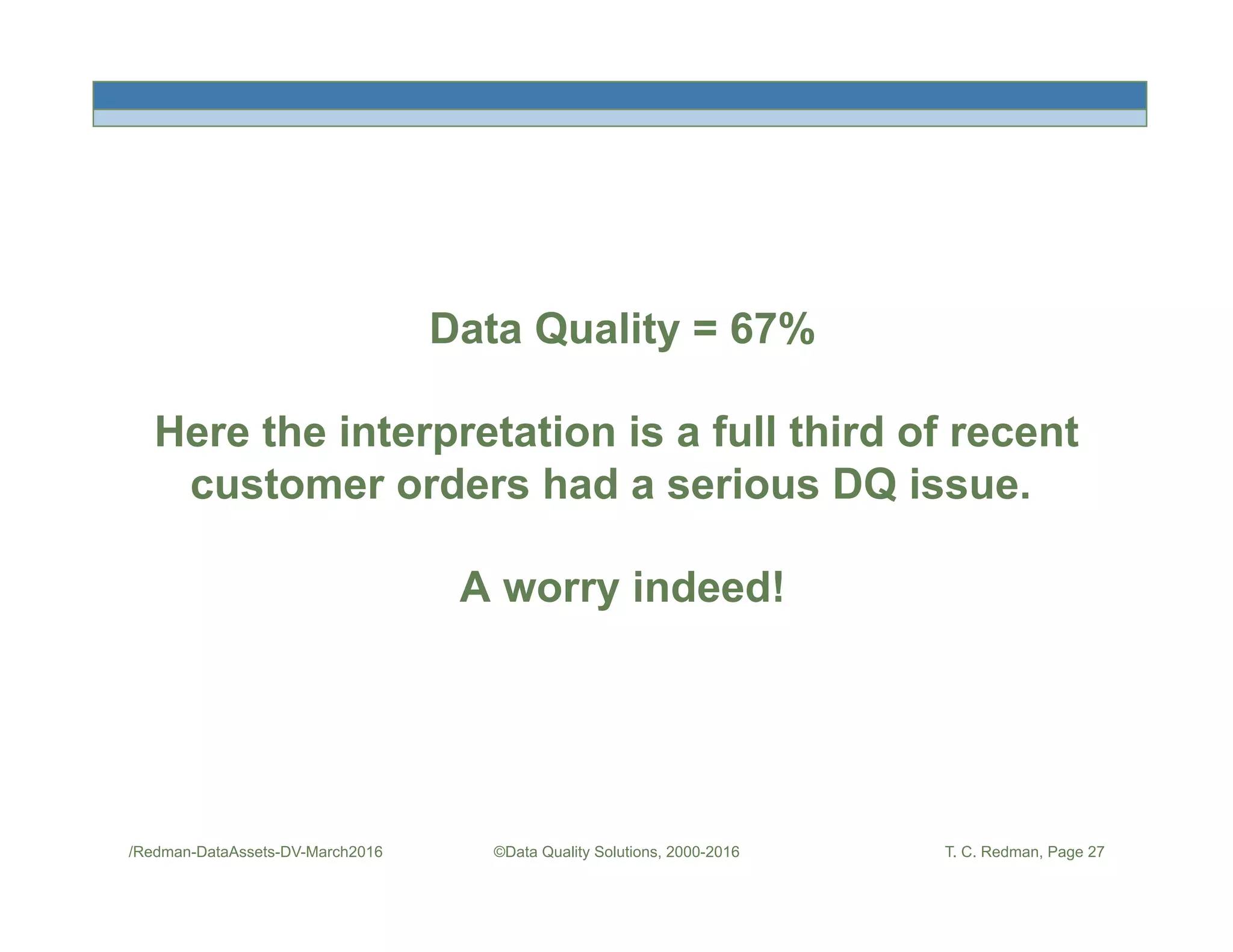
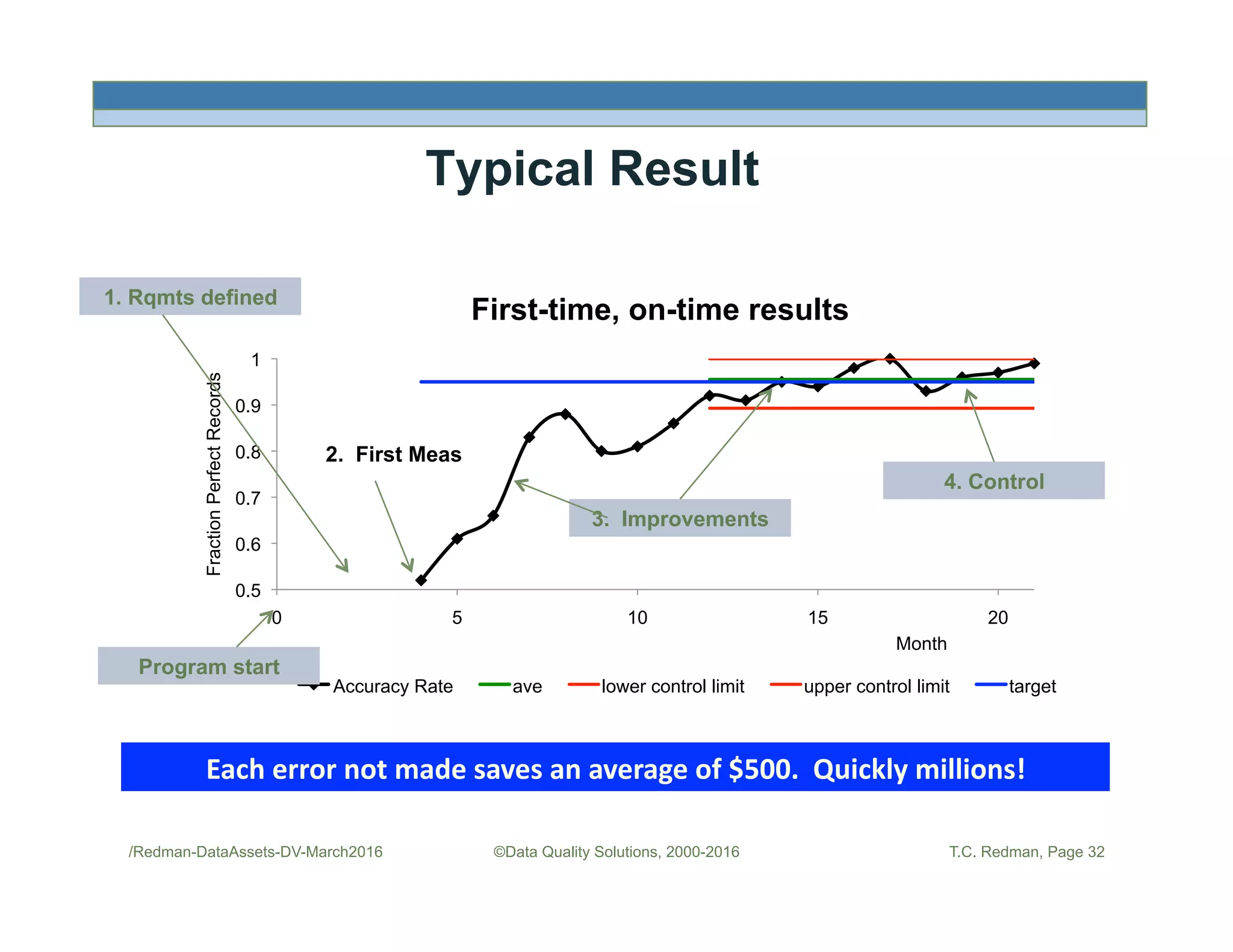
The document discusses managing data as assets and improving data quality. It defines what it means to manage data as assets by taking care of data, putting data to work, and advancing the management system. It emphasizes the roles of data creators and customers and how improving data quality can reduce costs. It recommends organizations perform a "Friday Afternoon Measurement" to assess data quality by reviewing recent records and identifying errors.