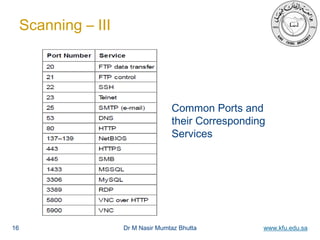
This document outlines an infrastructure penetration testing training workshop. It discusses the typical phases of a penetration test including reconnaissance, scanning, exploitation, post-exploitation, and reporting. During the reconnaissance phase, tools like ping, whois, and host are demonstrated to find the IP address and domain information of the target machine. Nmap and Nessus are shown for port scanning and vulnerability scanning. Exploitation involves using tools like telnet and rlogin to exploit known vulnerabilities like rlogin and gaining access. Netcat is demonstrated for maintaining backdoor access. The document emphasizes learning additional tools and techniques for deeper understanding.