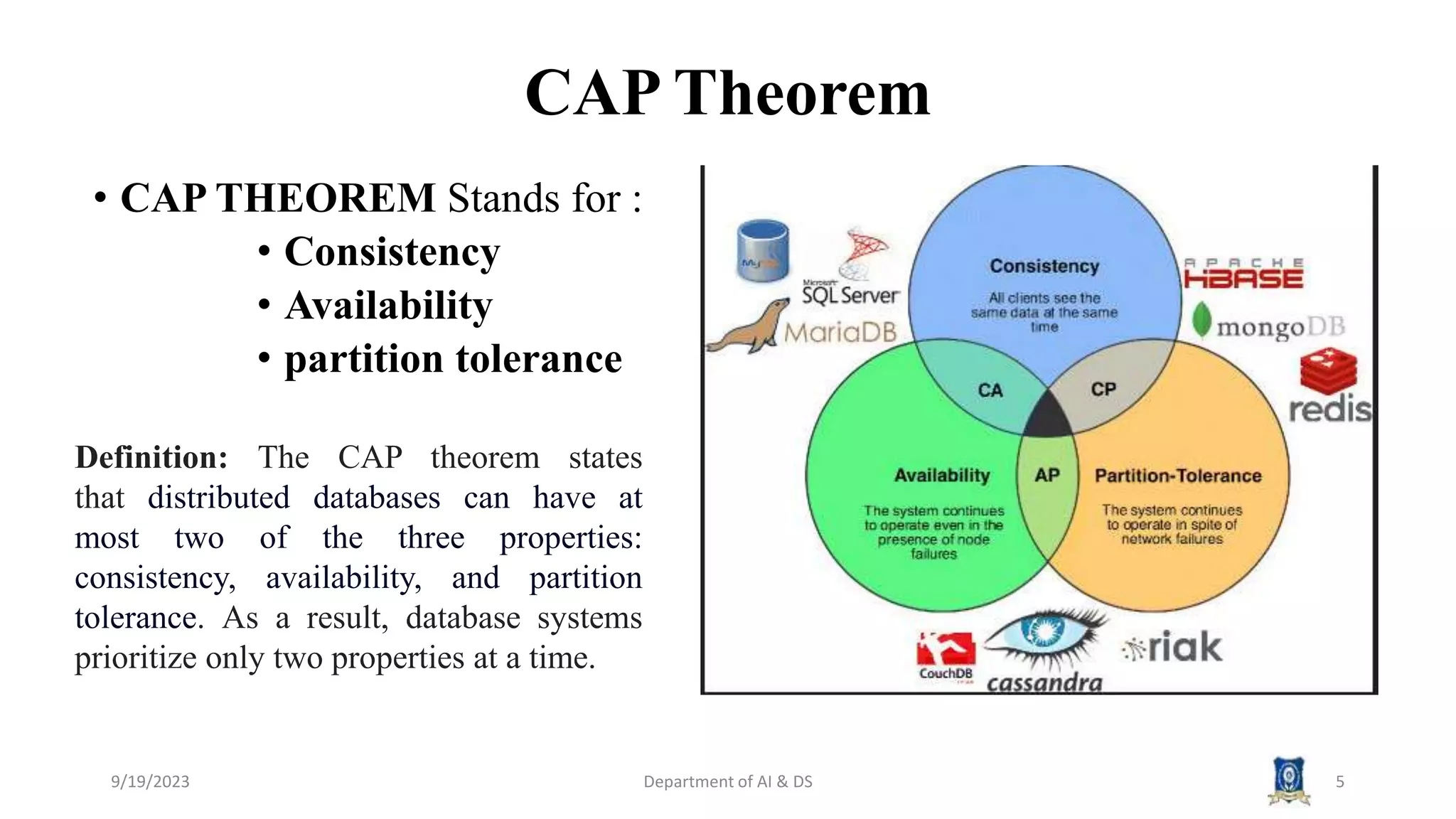
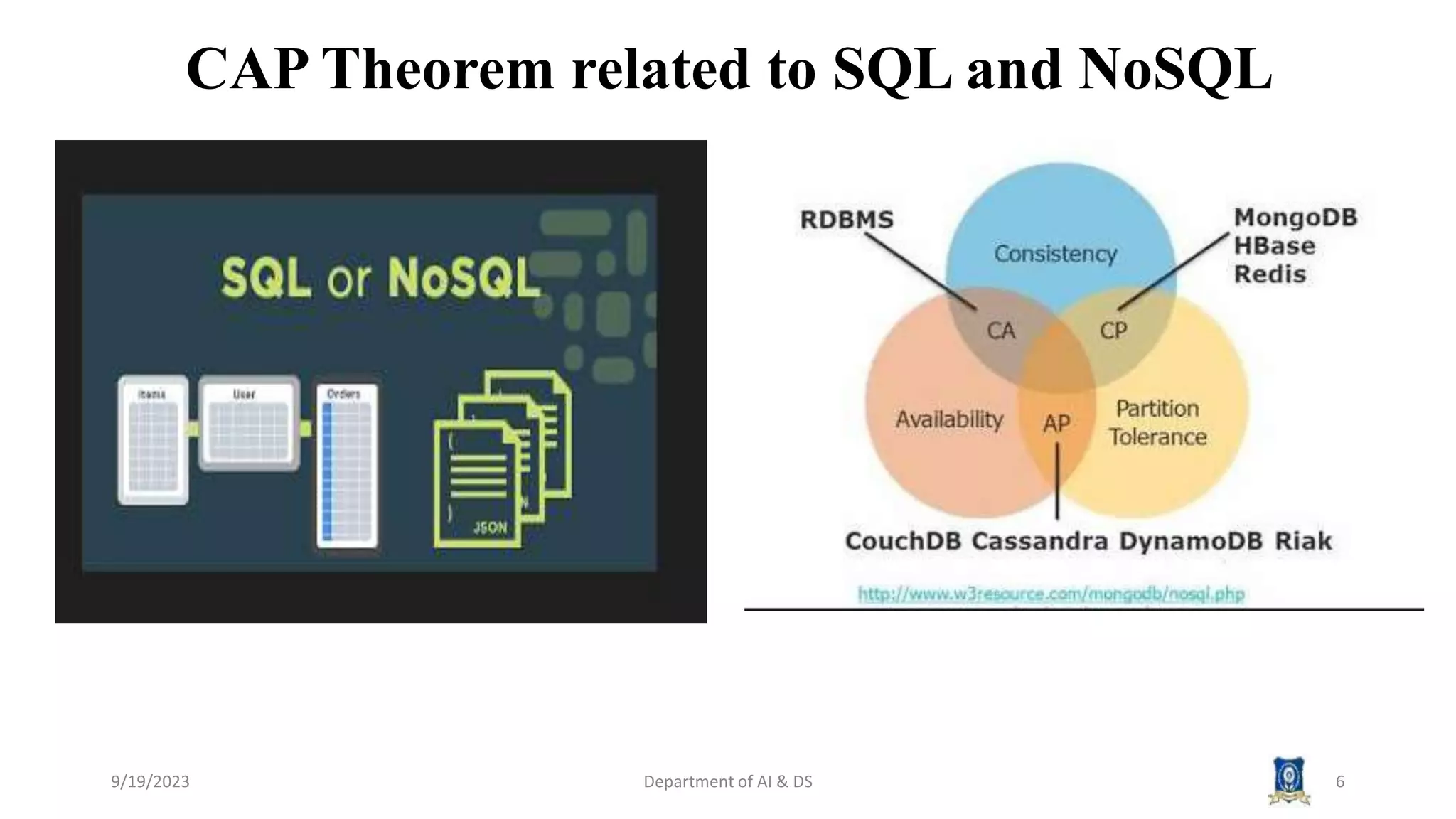
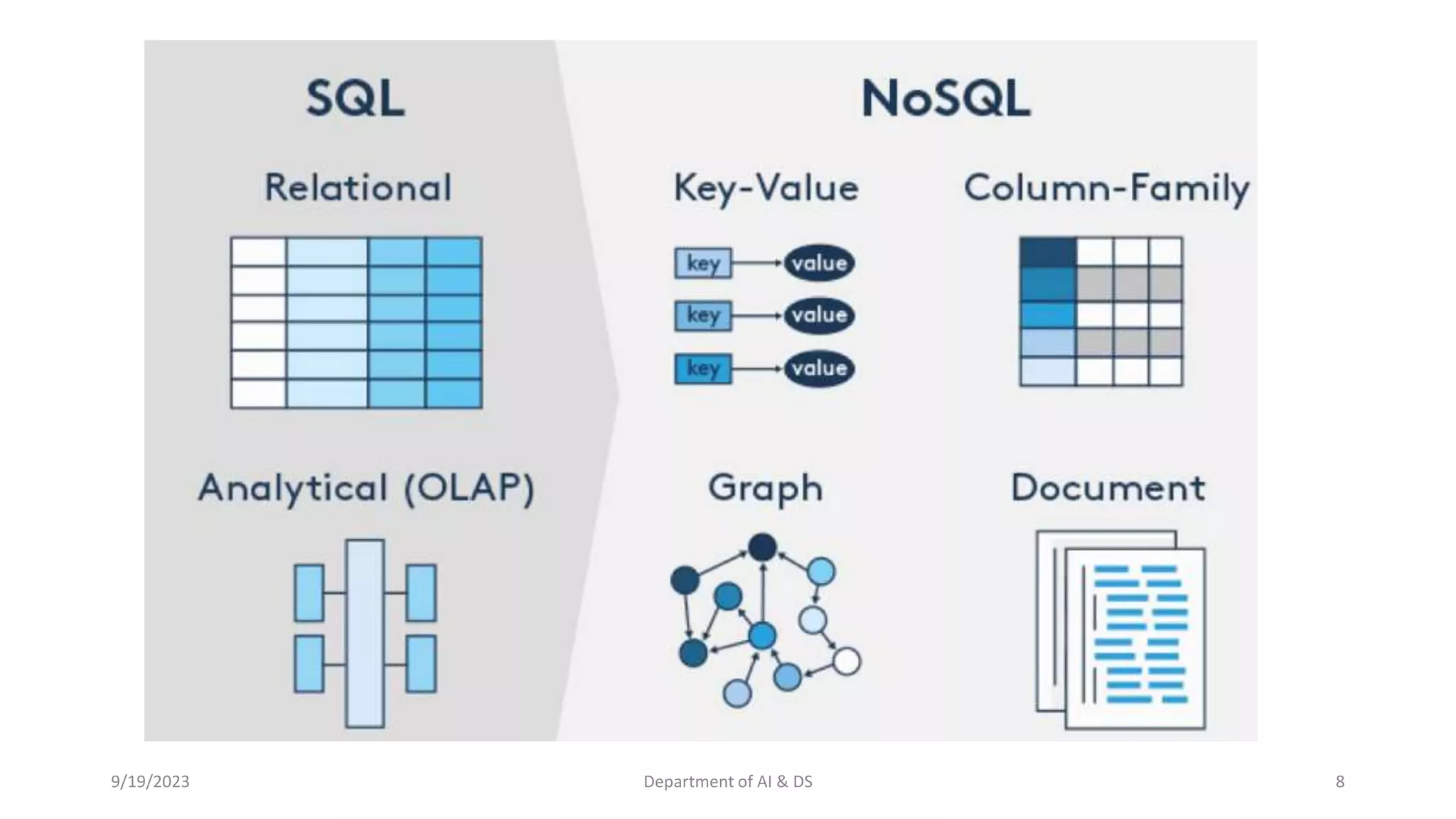
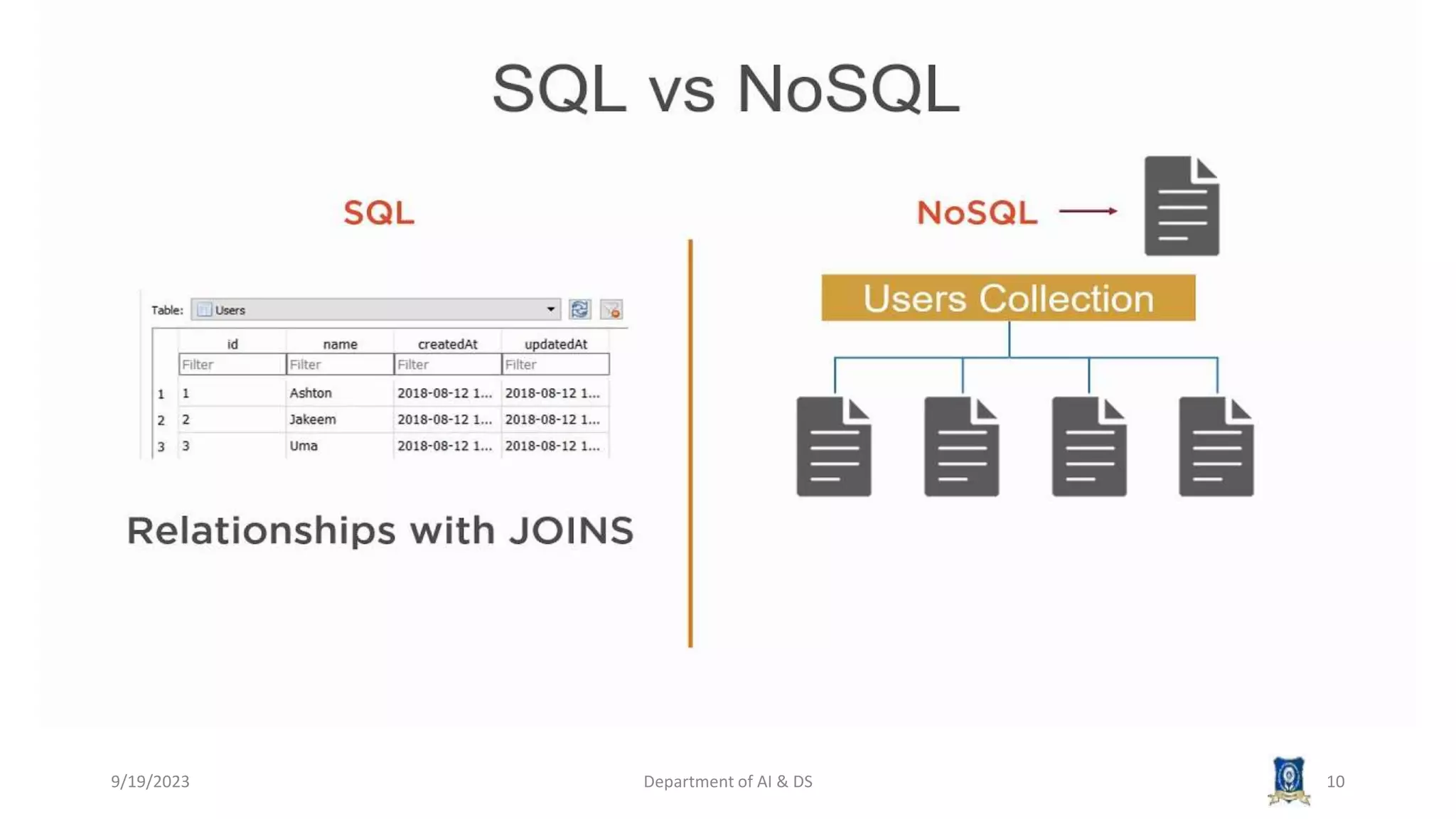
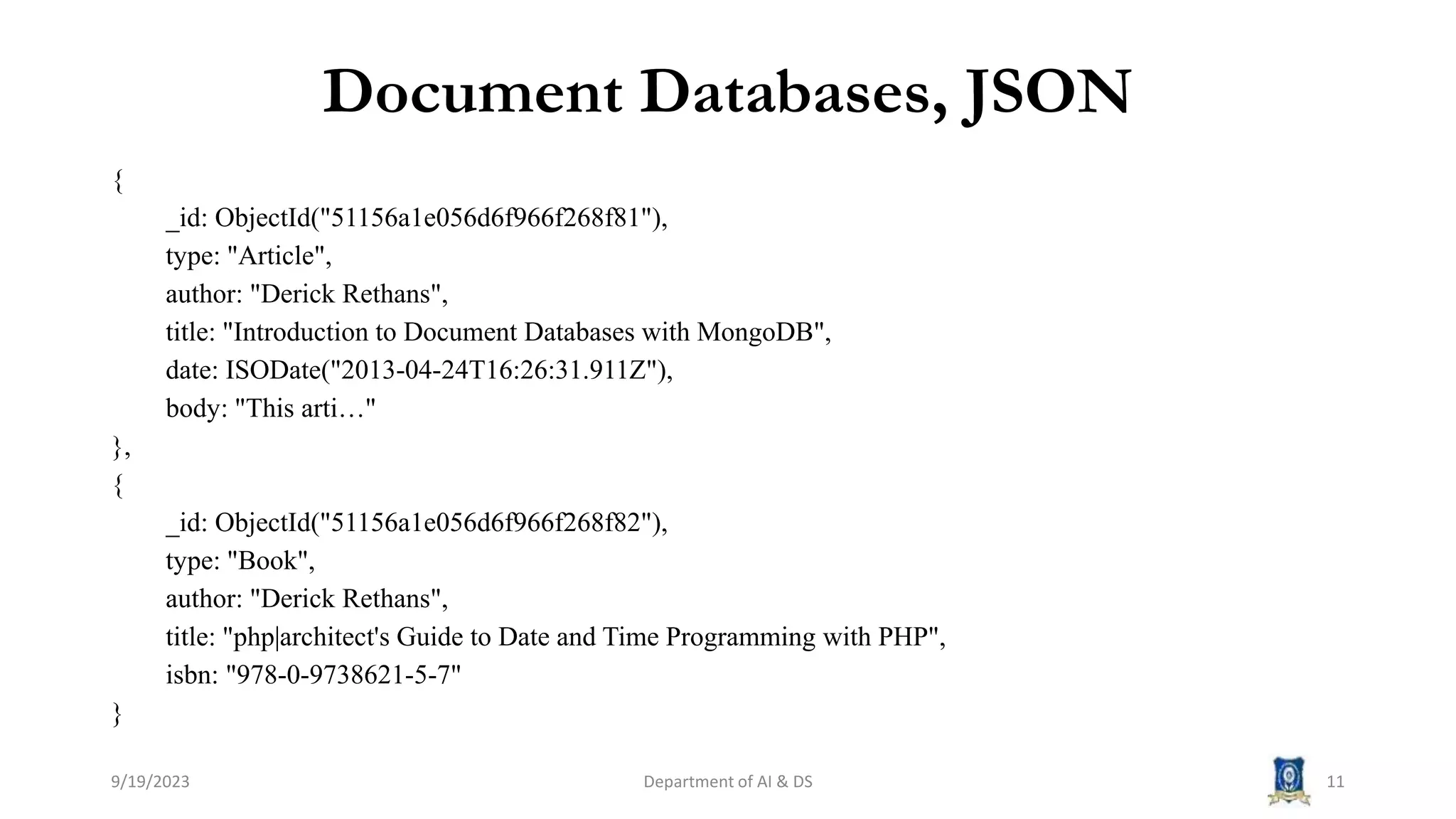
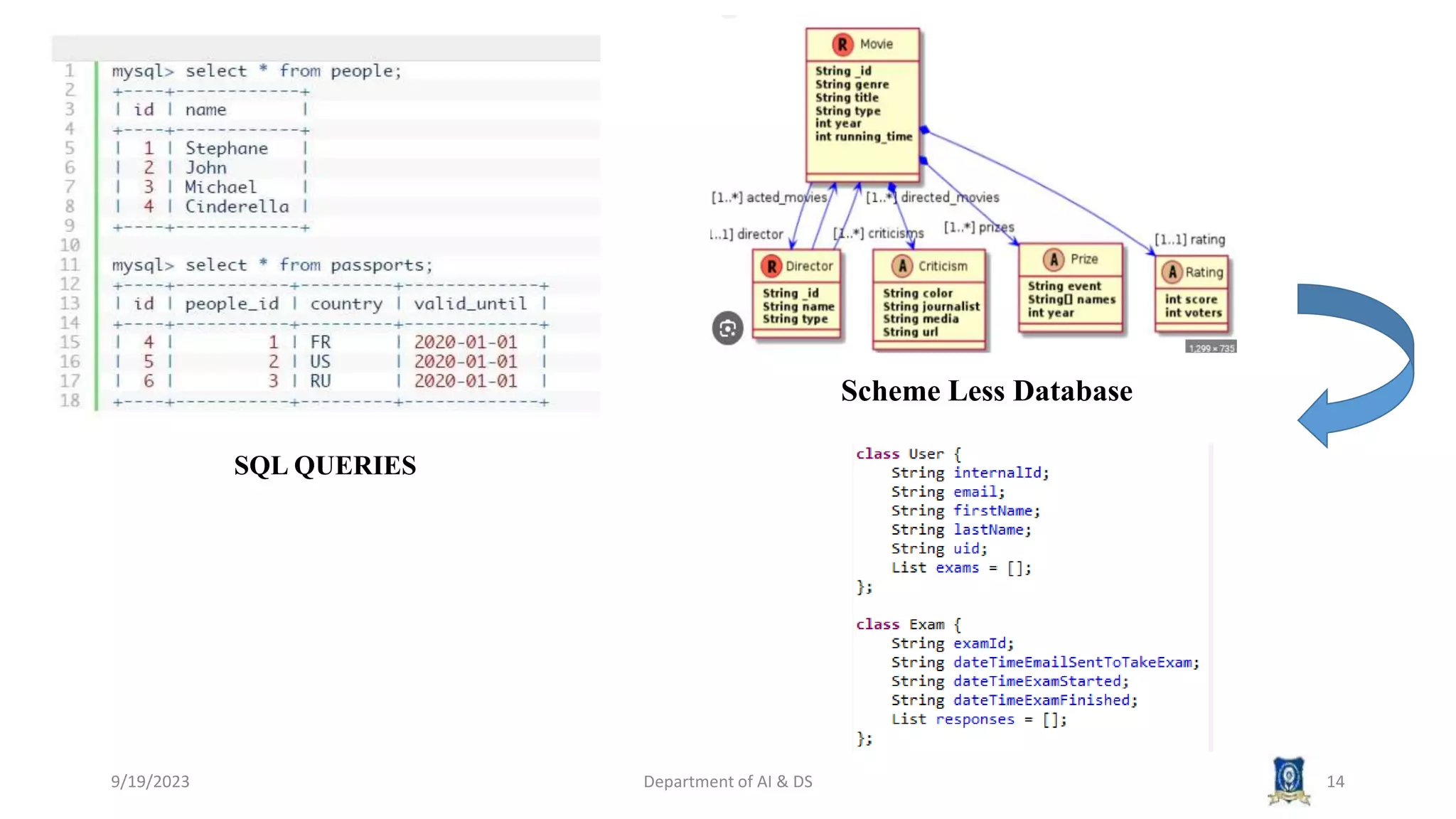
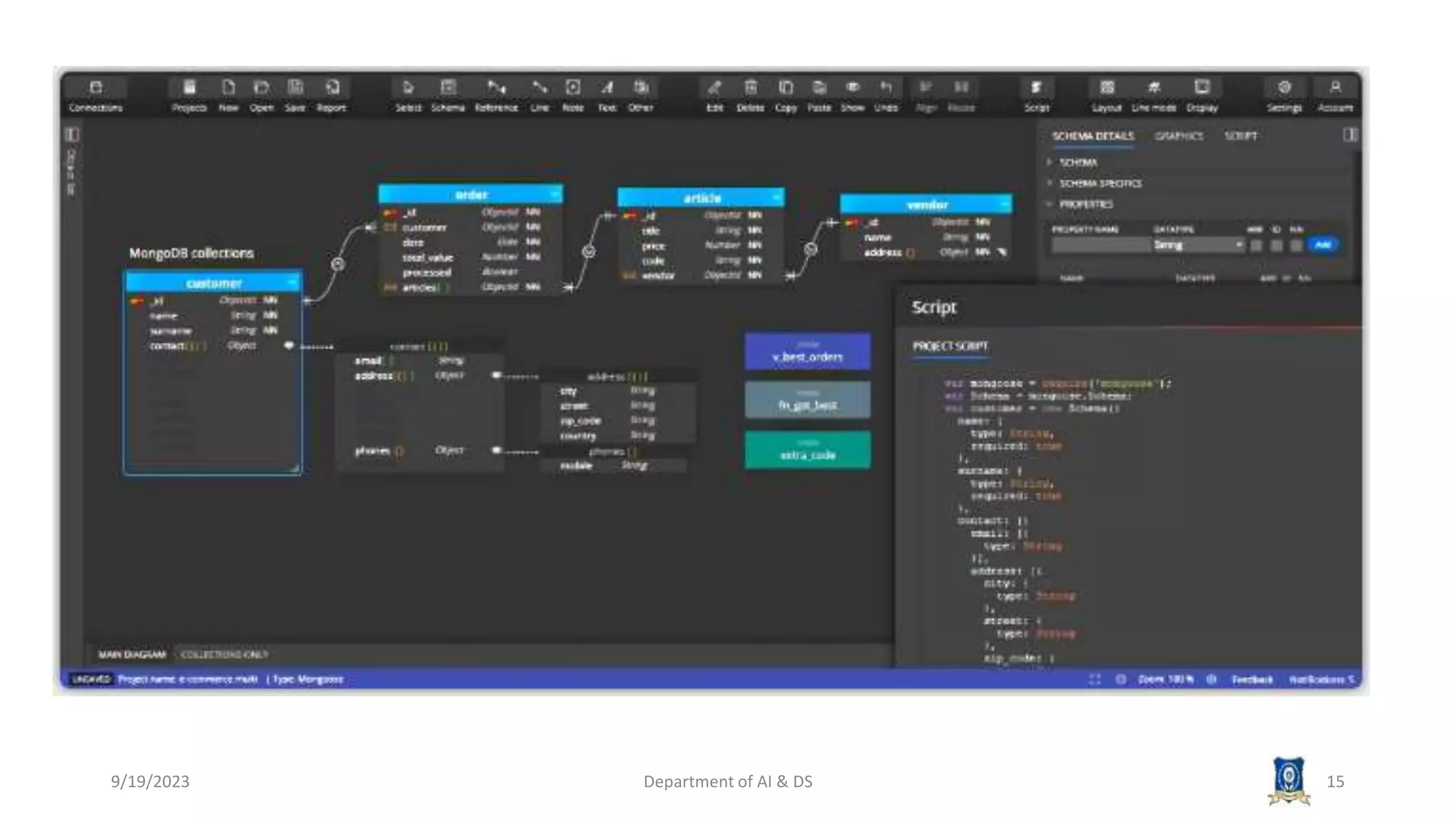
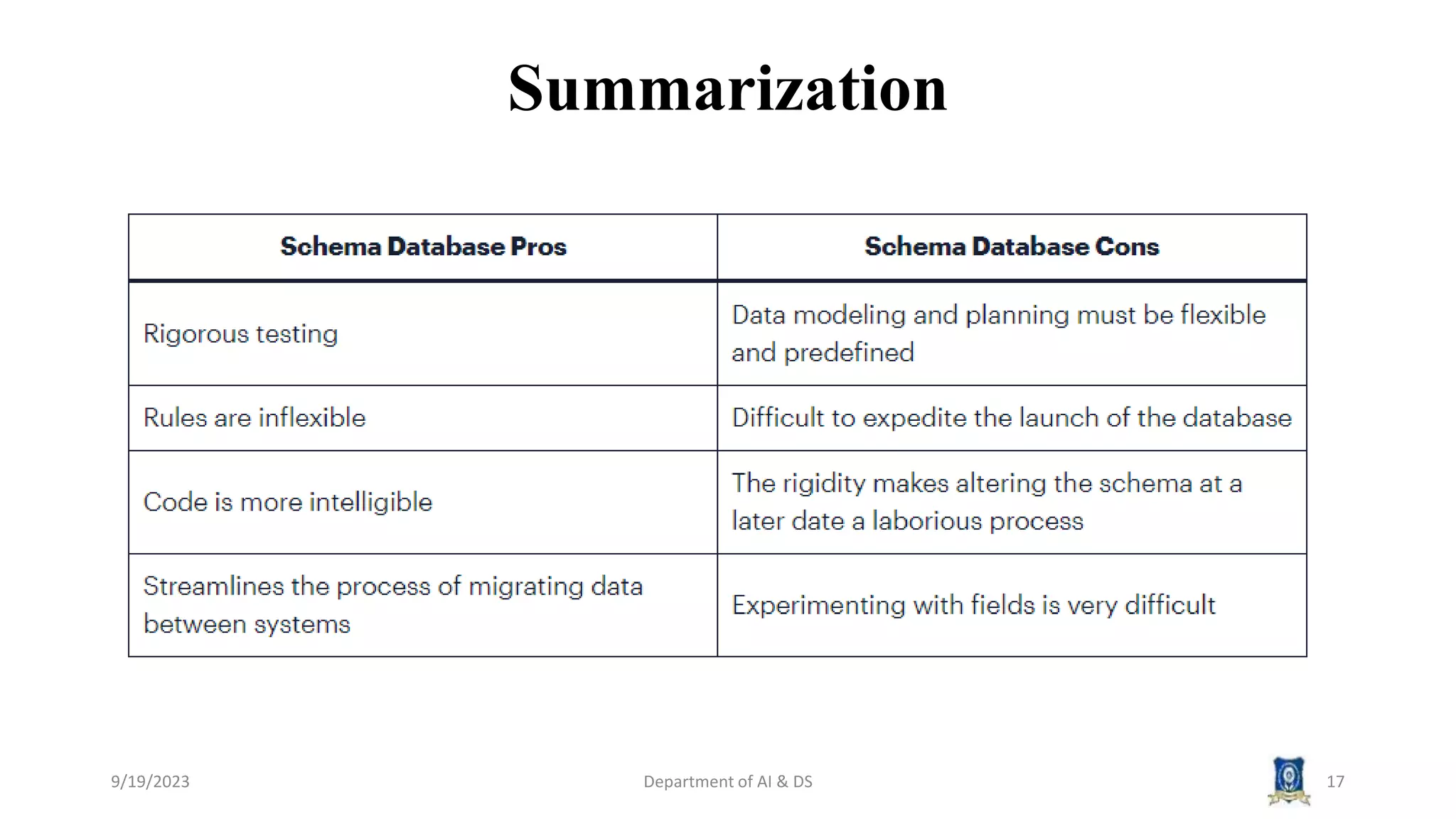
The document summarizes key topics from a session on NoSQL data management. It introduced document, key-value, and graph databases. It described MongoDB and Cassandra, explaining their data models. The CAP theorem was defined as stating distributed databases can only prioritize two of consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. Materialized views were defined as pre-computed views that are stored physically. The next session will cover distributed models.