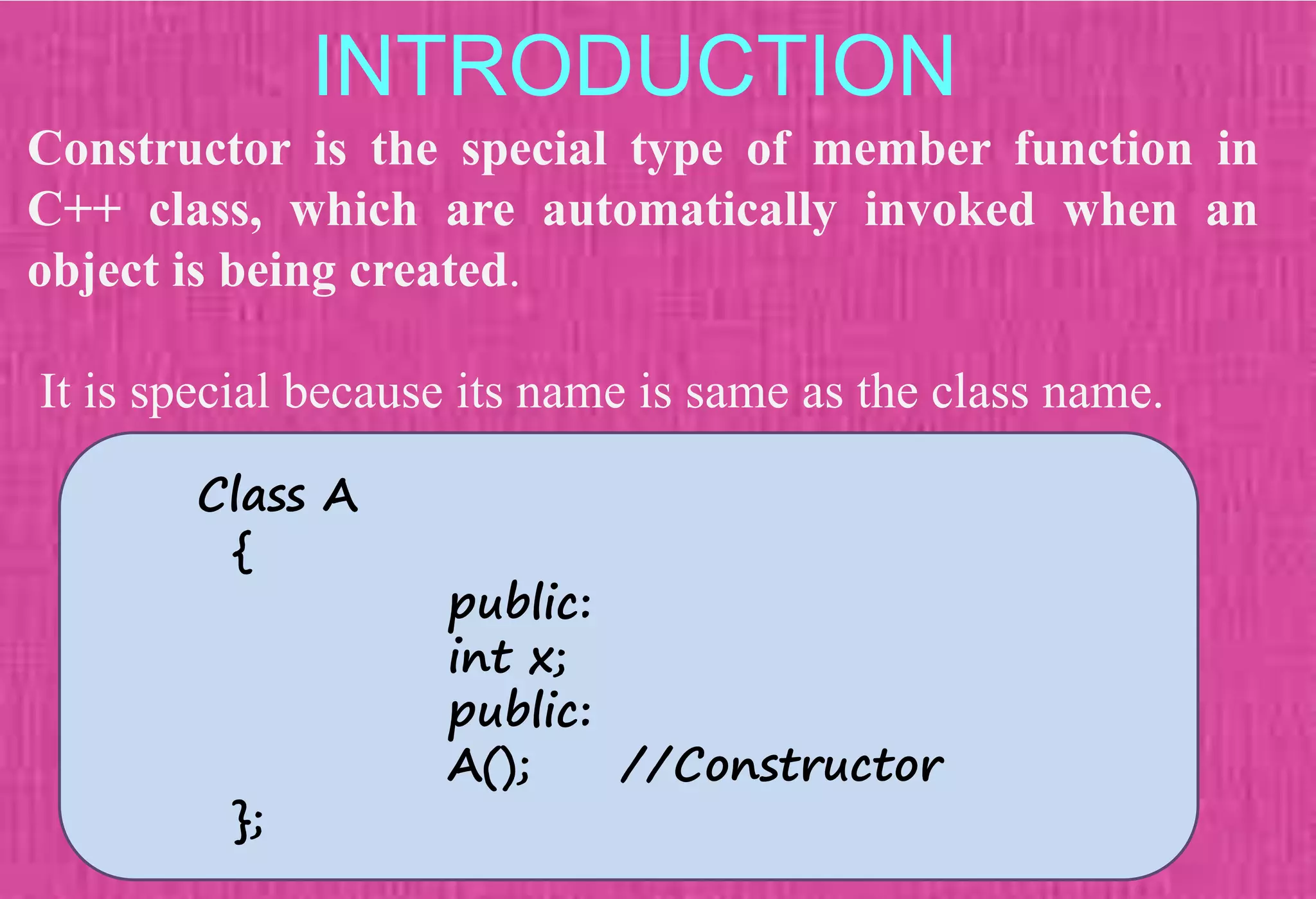
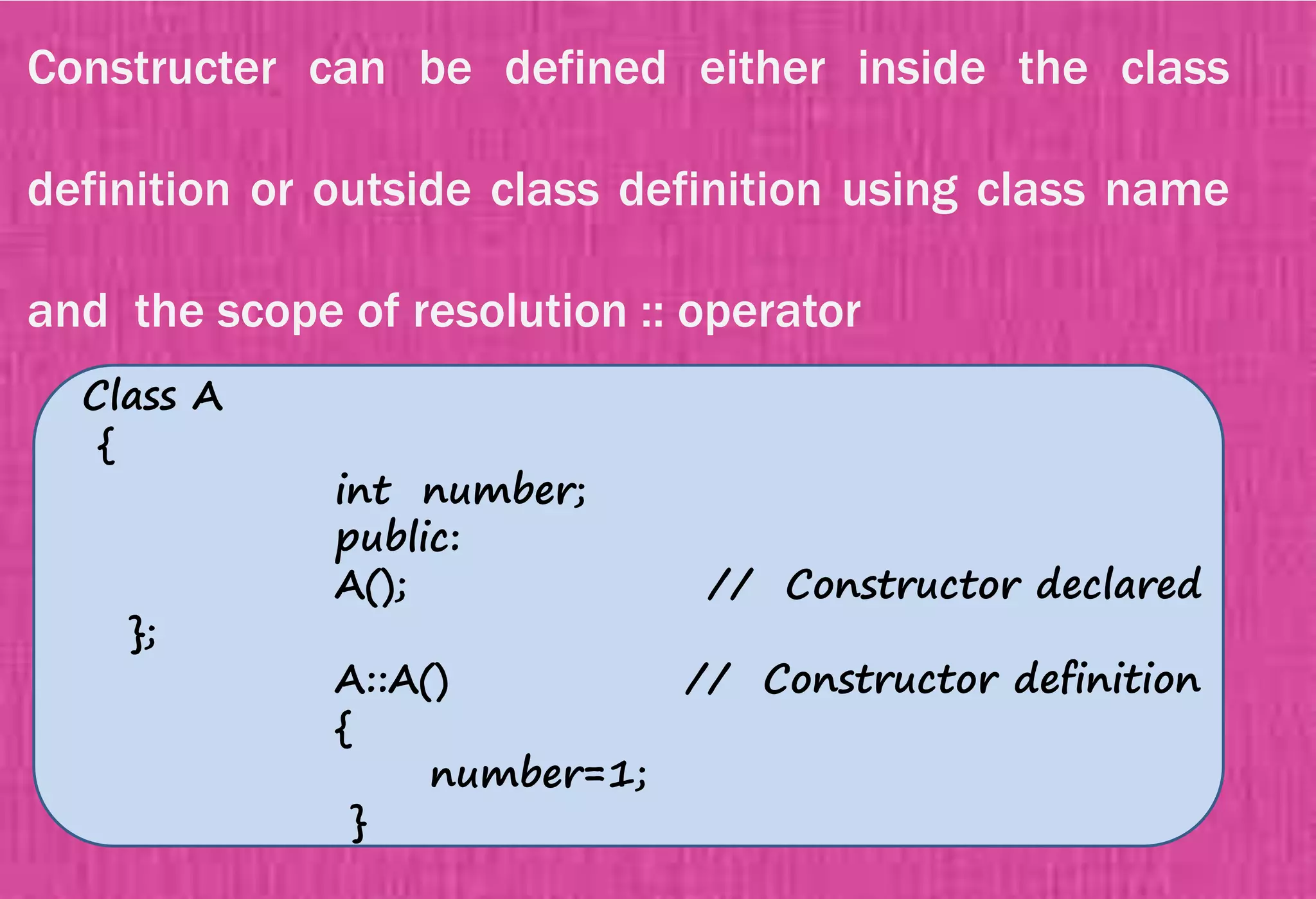
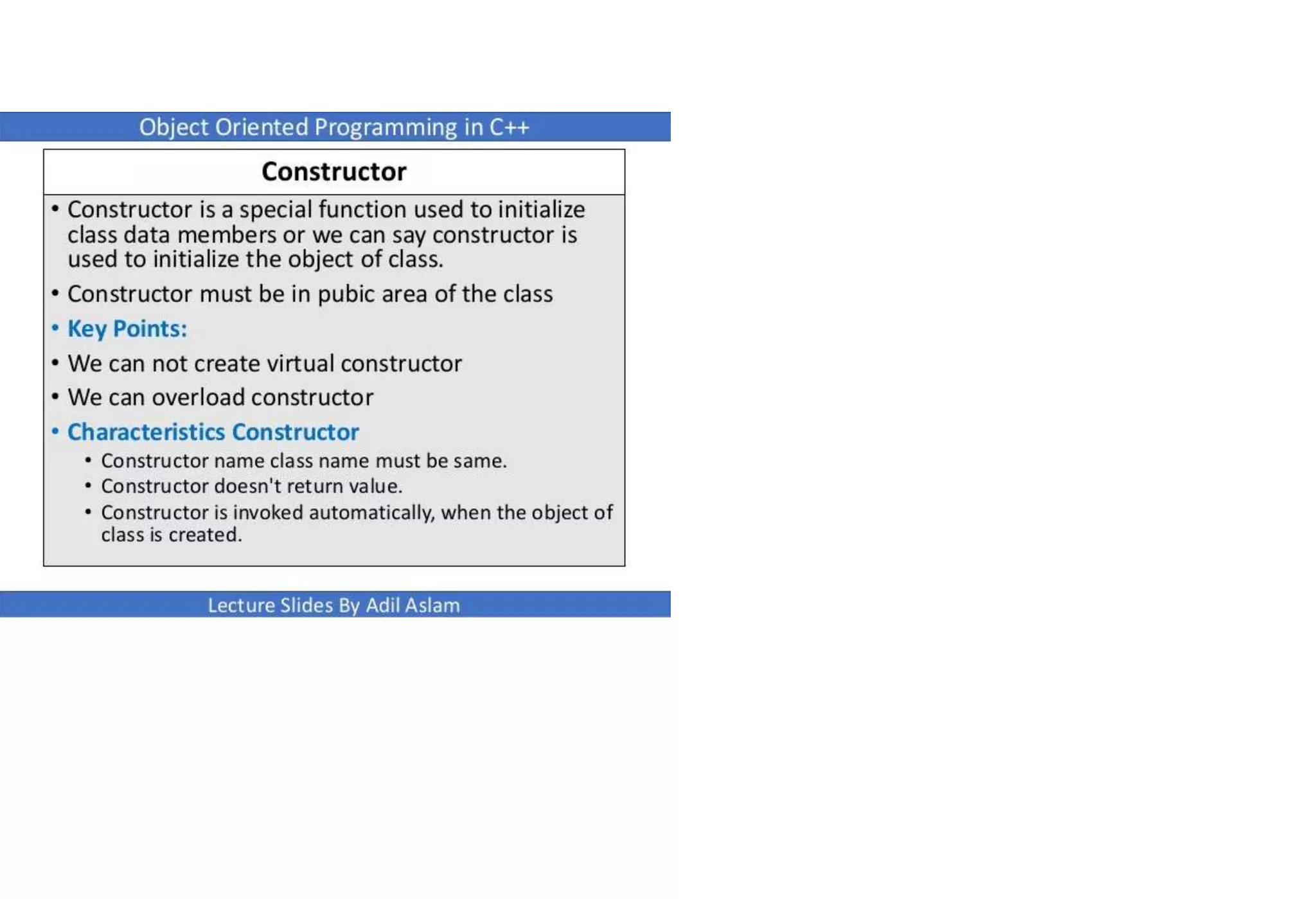
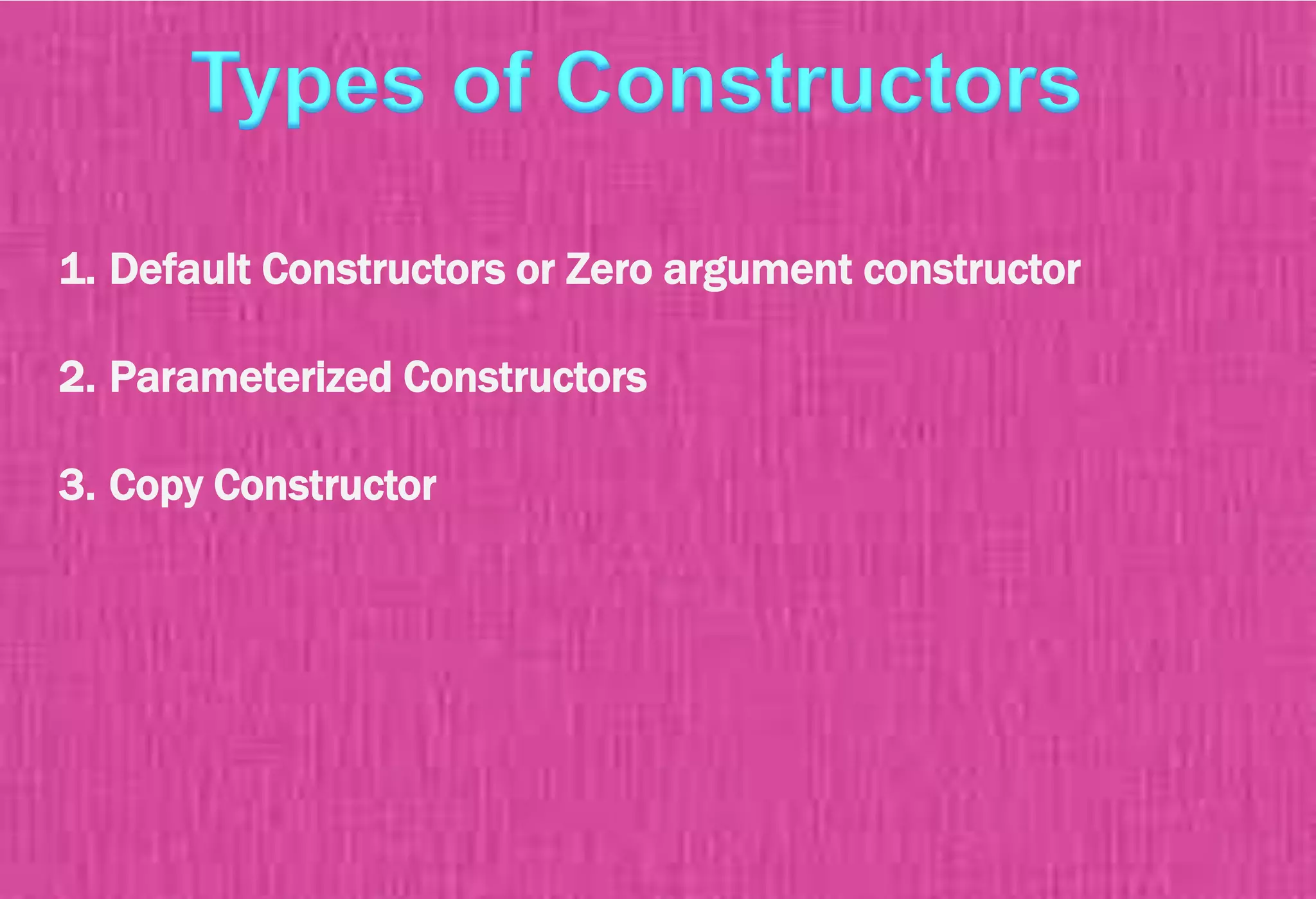
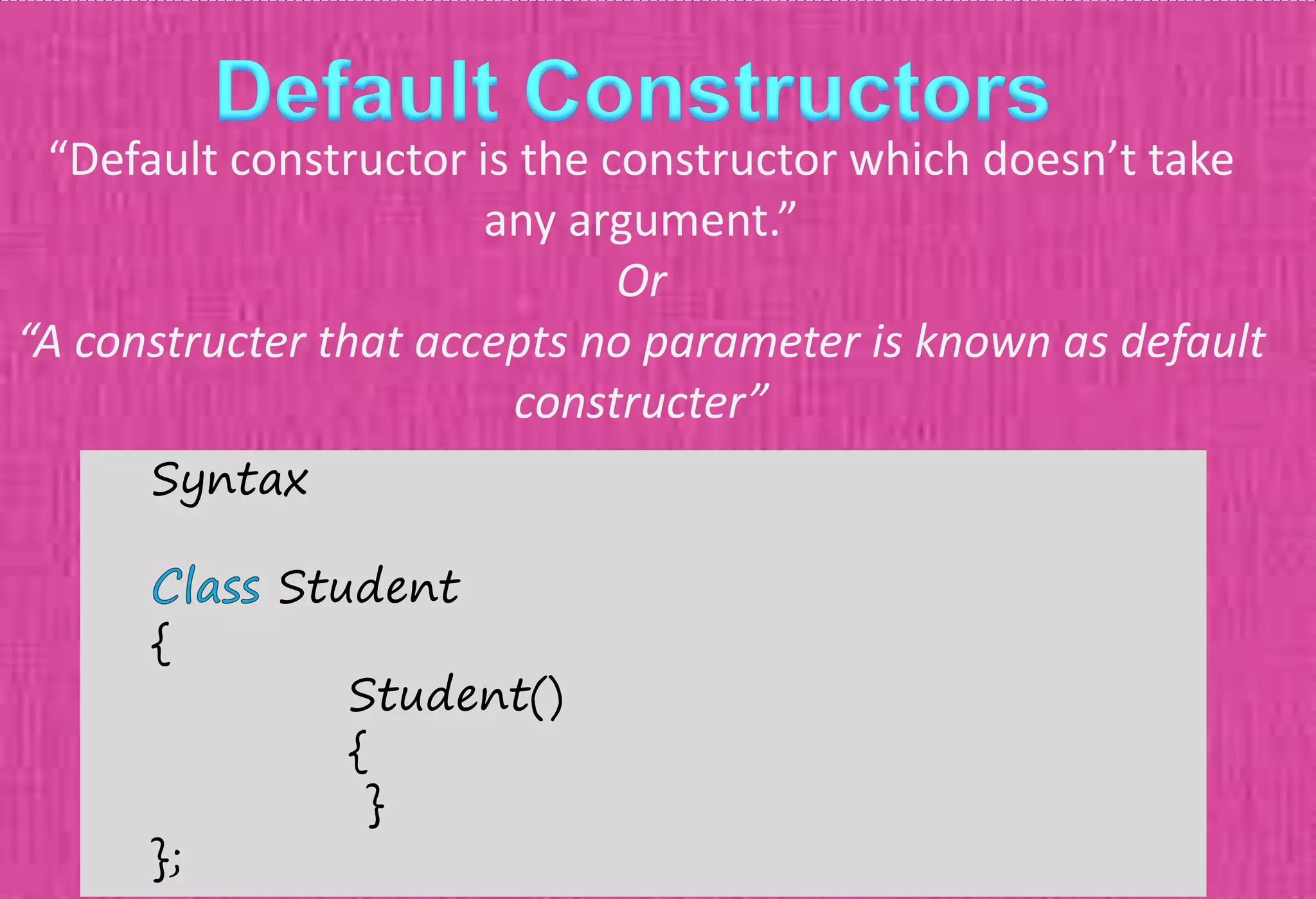
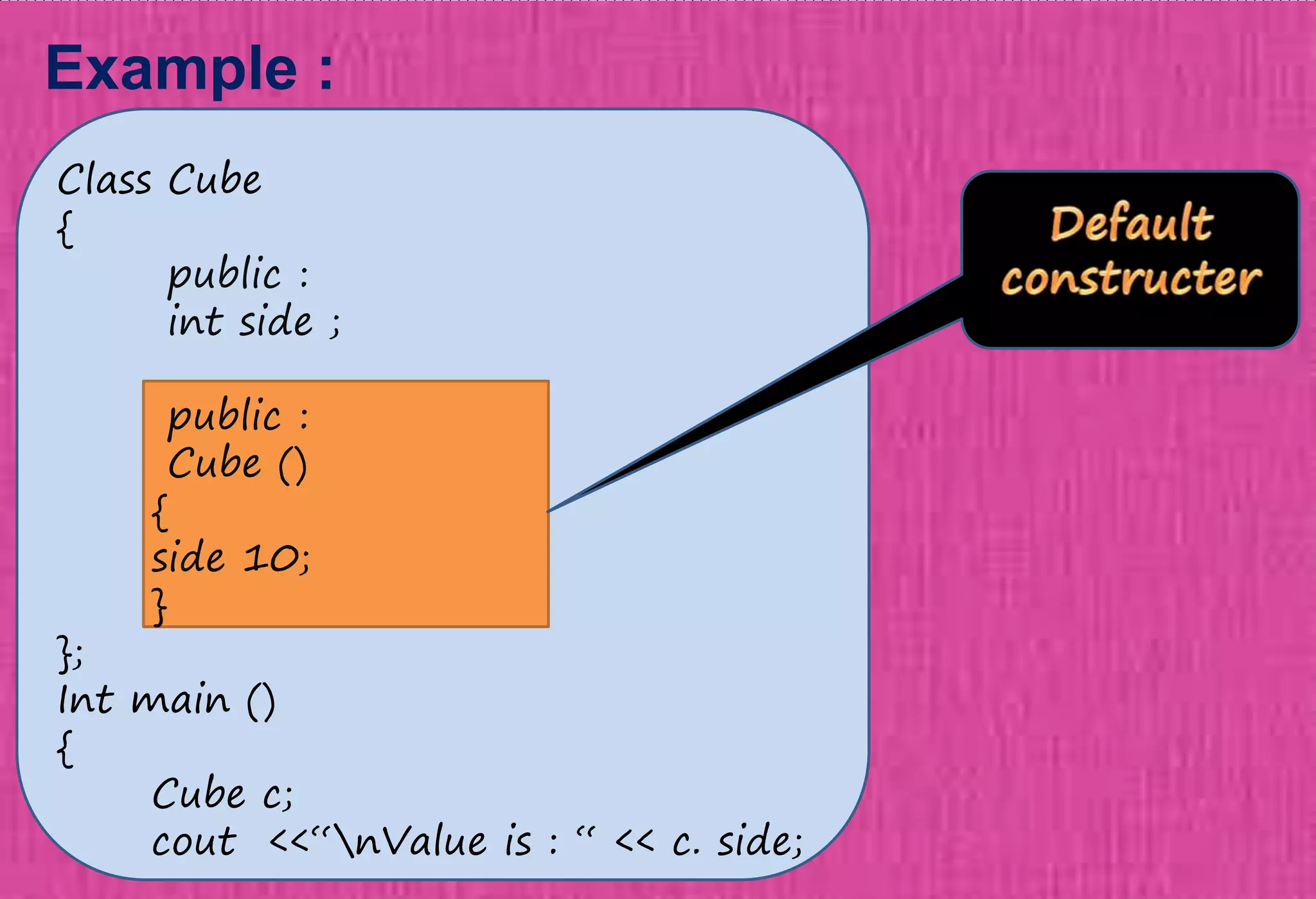
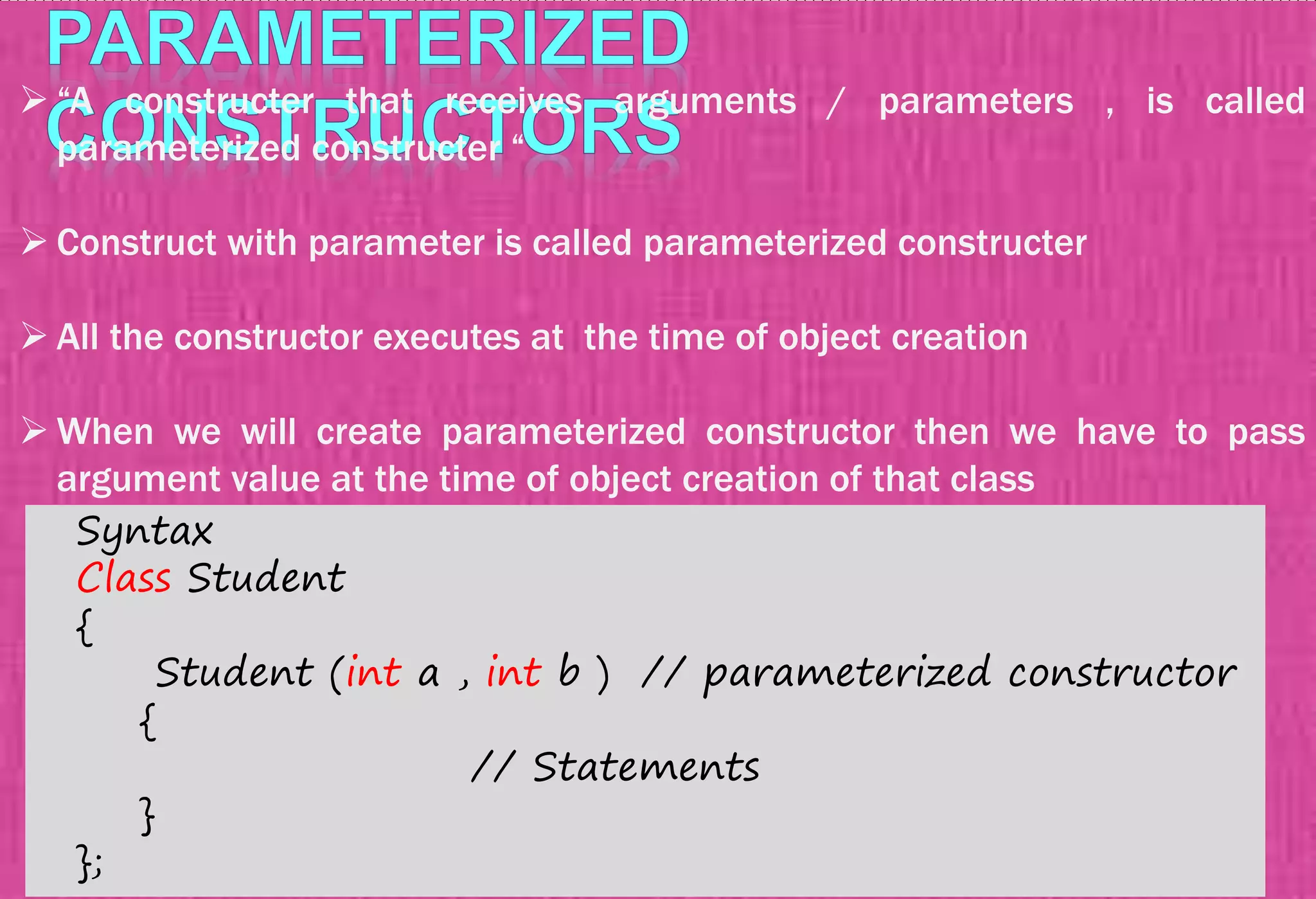
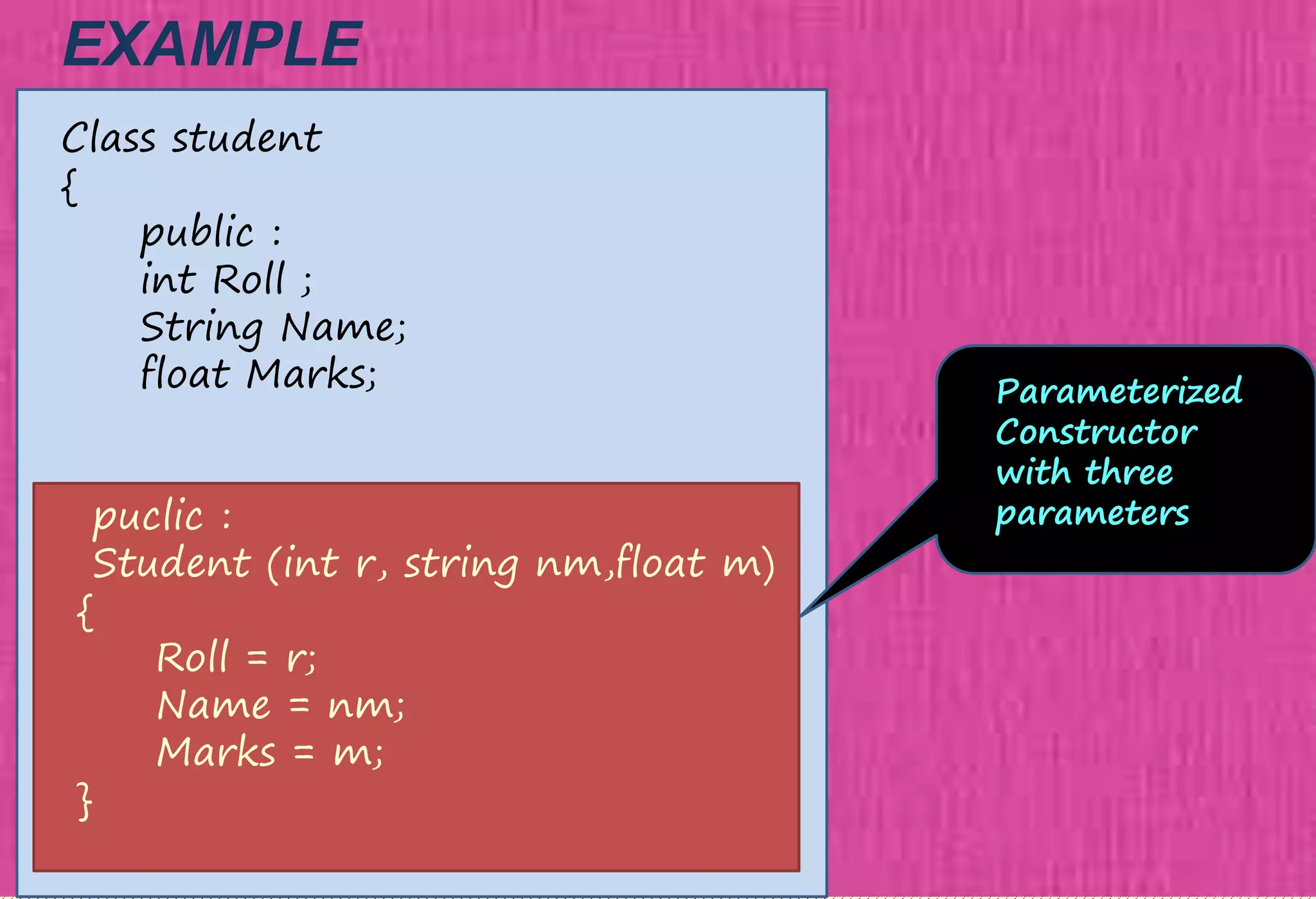
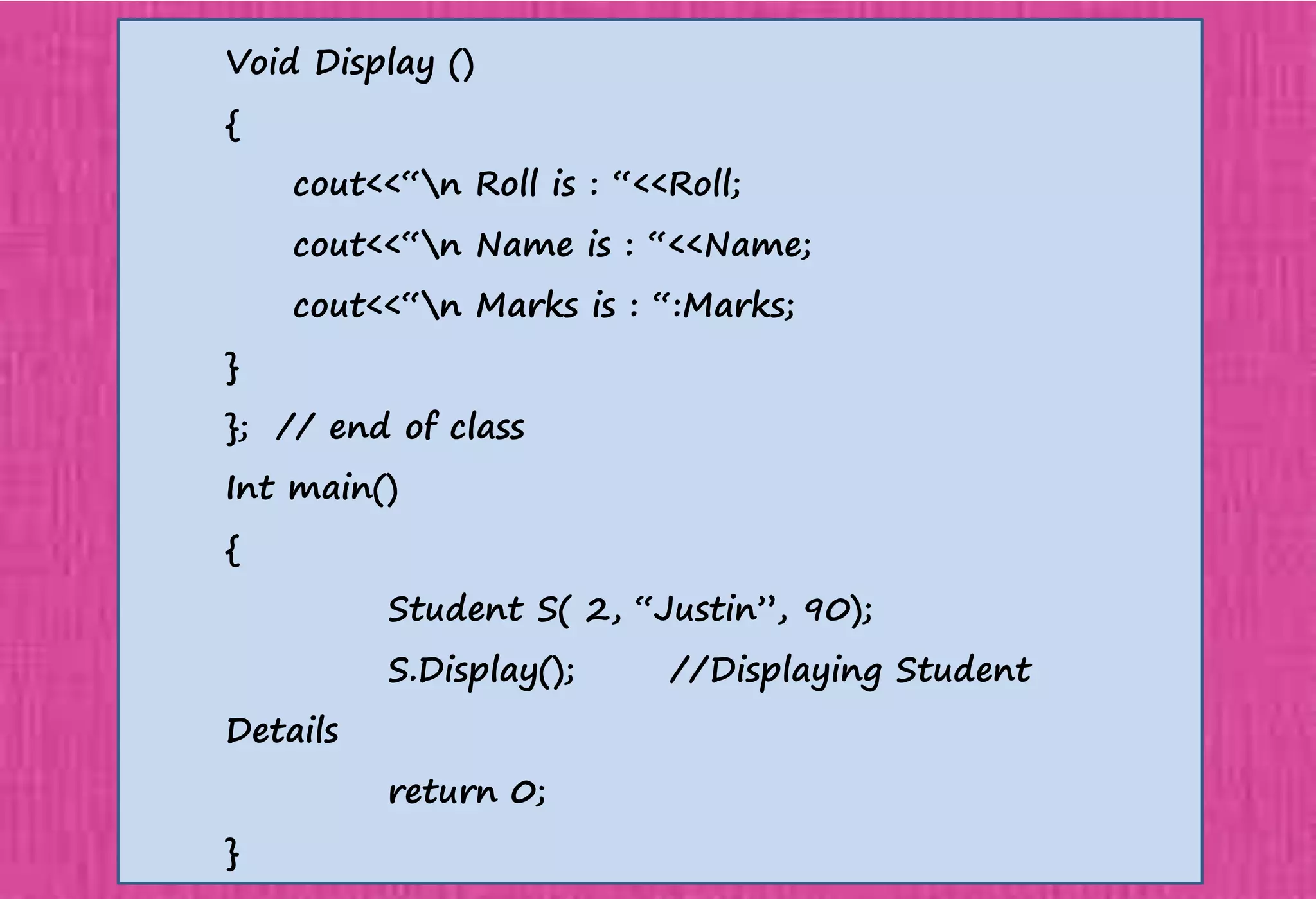
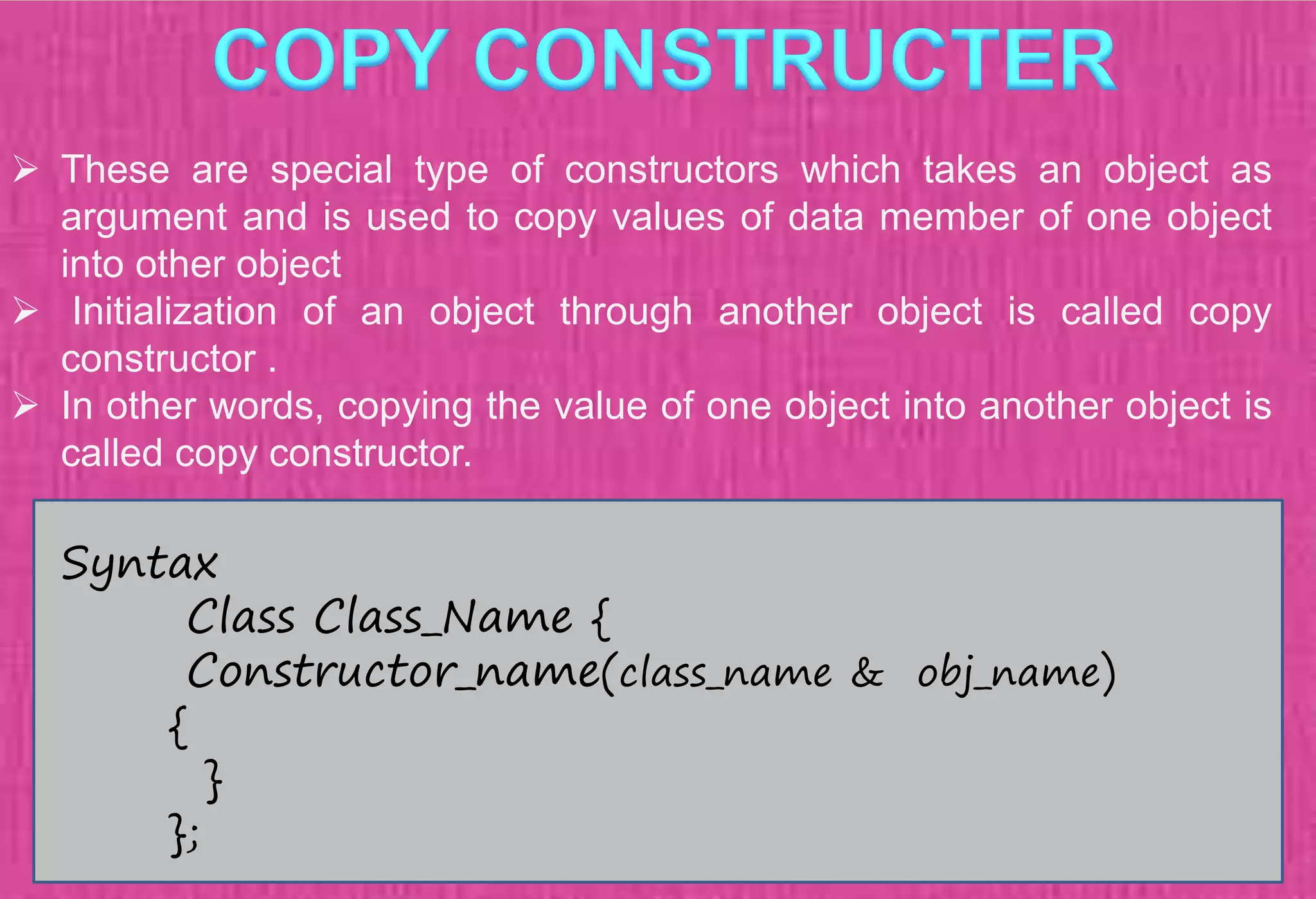
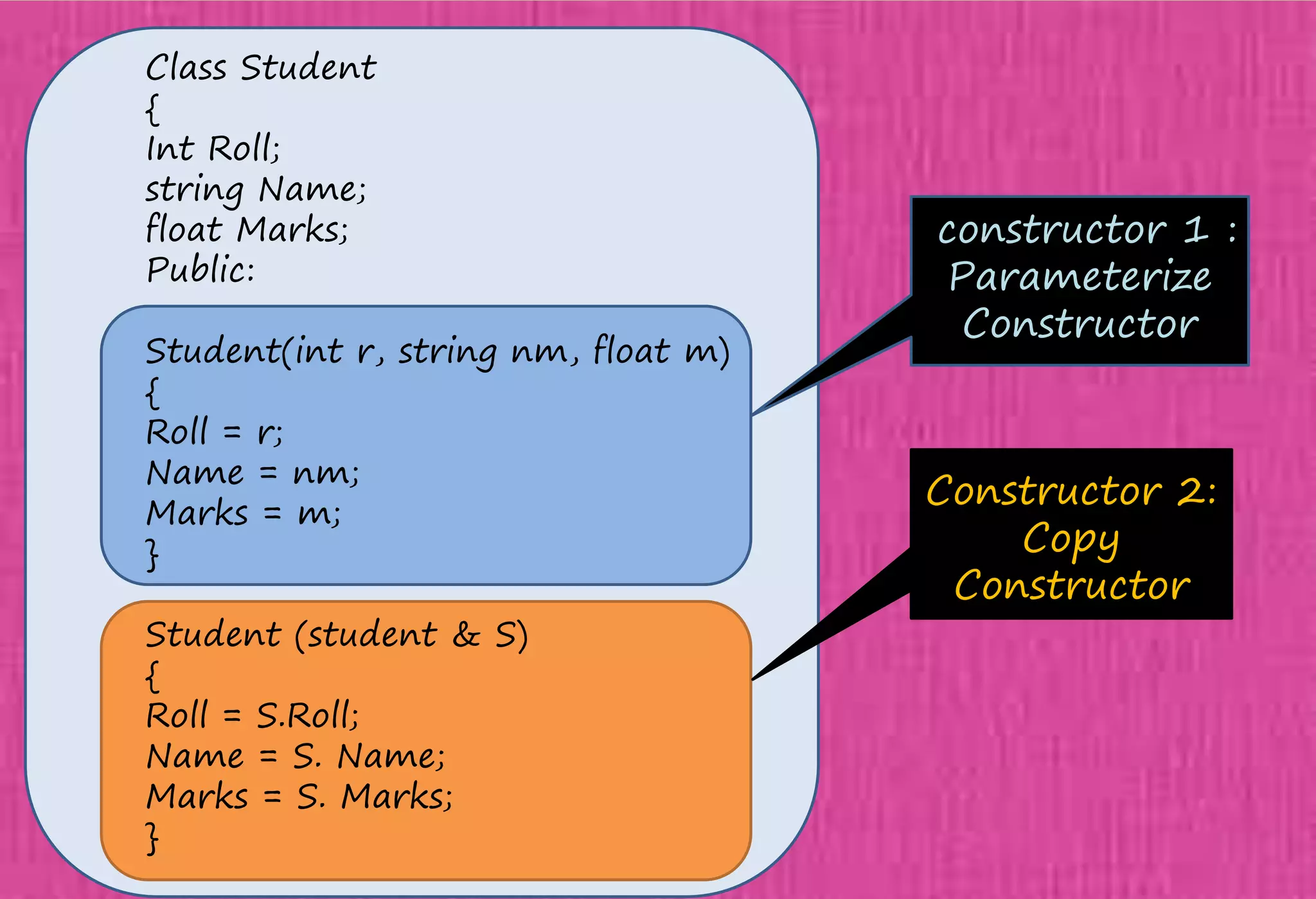
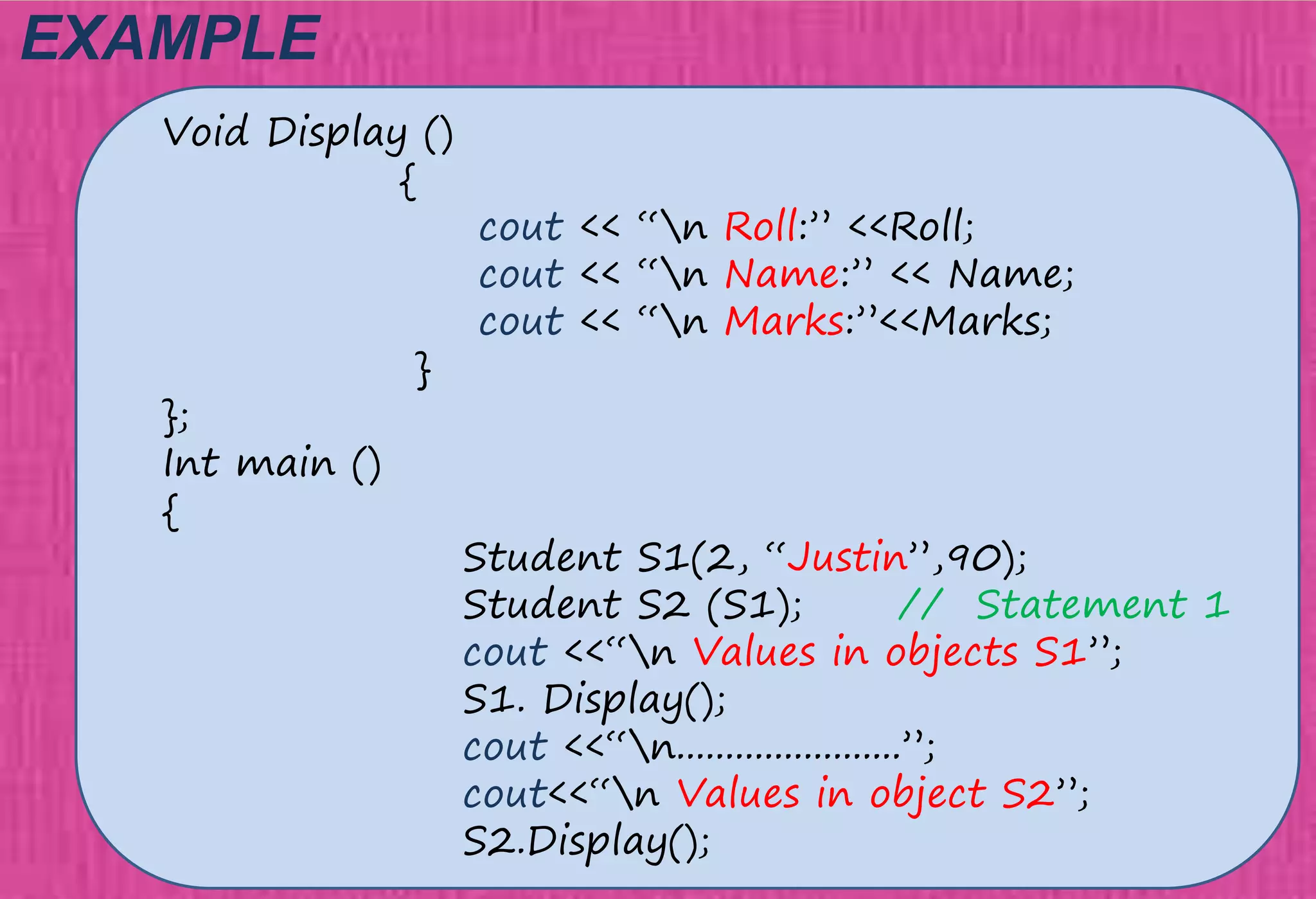
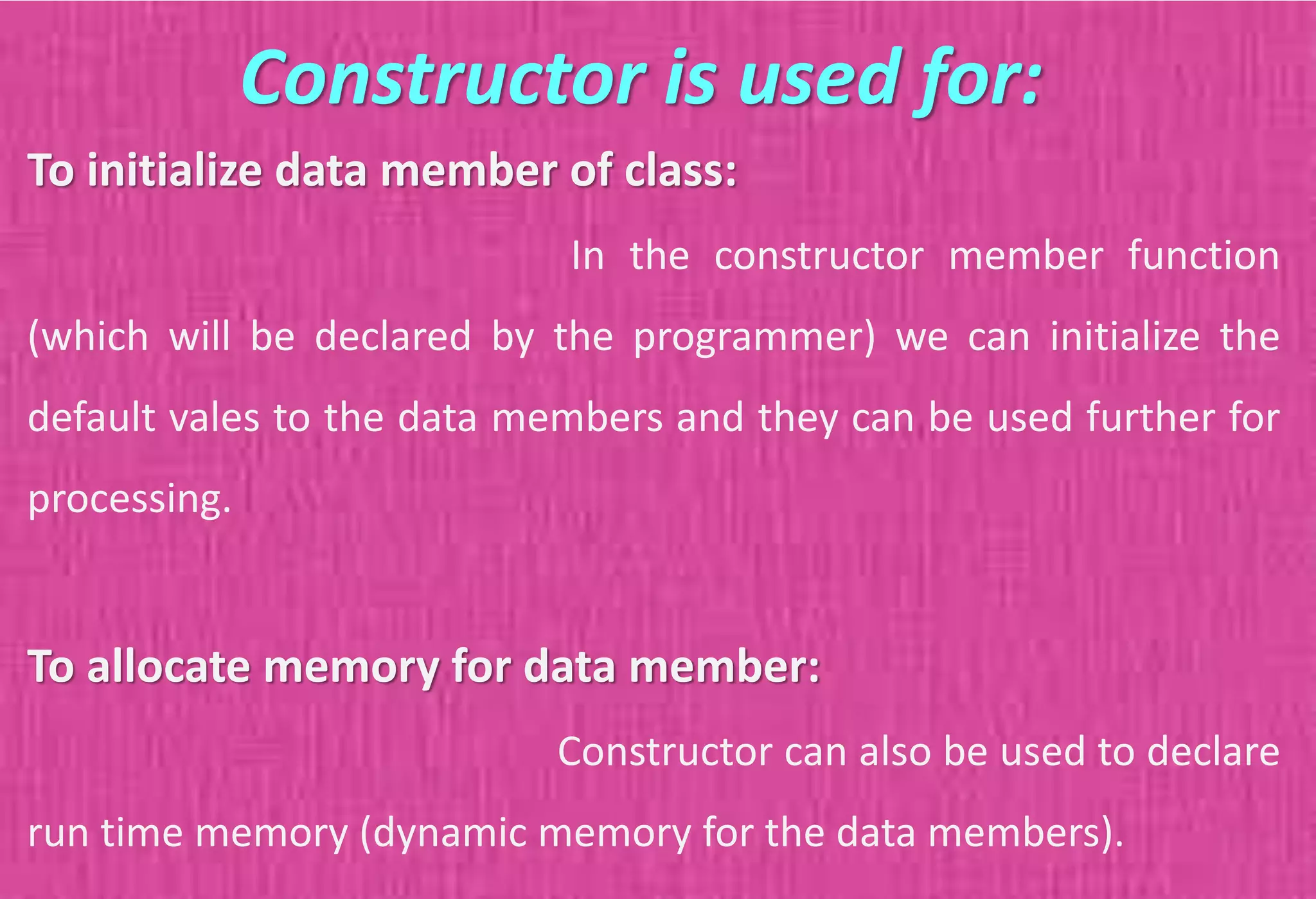
The document provides an overview of constructors in C++, explaining their types: default constructors, parameterized constructors, and copy constructors. It details their definitions, syntax, and provides examples demonstrating their usage within classes. Additionally, it highlights the role of constructors in initializing data members and managing dynamic memory allocation.