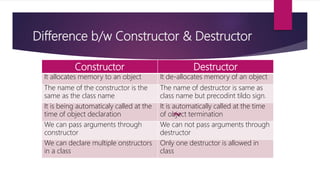
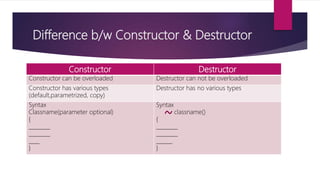
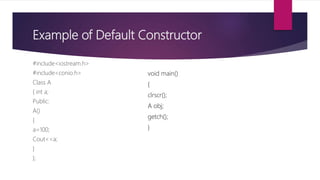
The document explains constructors and destructors in C++, highlighting their definitions, types, and usage. Constructors are special functions that initialize objects automatically when declared, while destructors deallocate memory when objects are destroyed. Various types of constructors include default, parametric, and copy constructors, each serving distinct purposes in object-oriented programming.