This document provides an overview of networking fundamentals, focusing on small network creation, security measures, and performance optimization. It covers device selection, IP addressing, redundancy, and the importance of securing network devices against various vulnerabilities. Additionally, it discusses managing IOS configuration files, integrated routing services, and essential commands for network performance verification.






















![Presentation_ID 36© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential
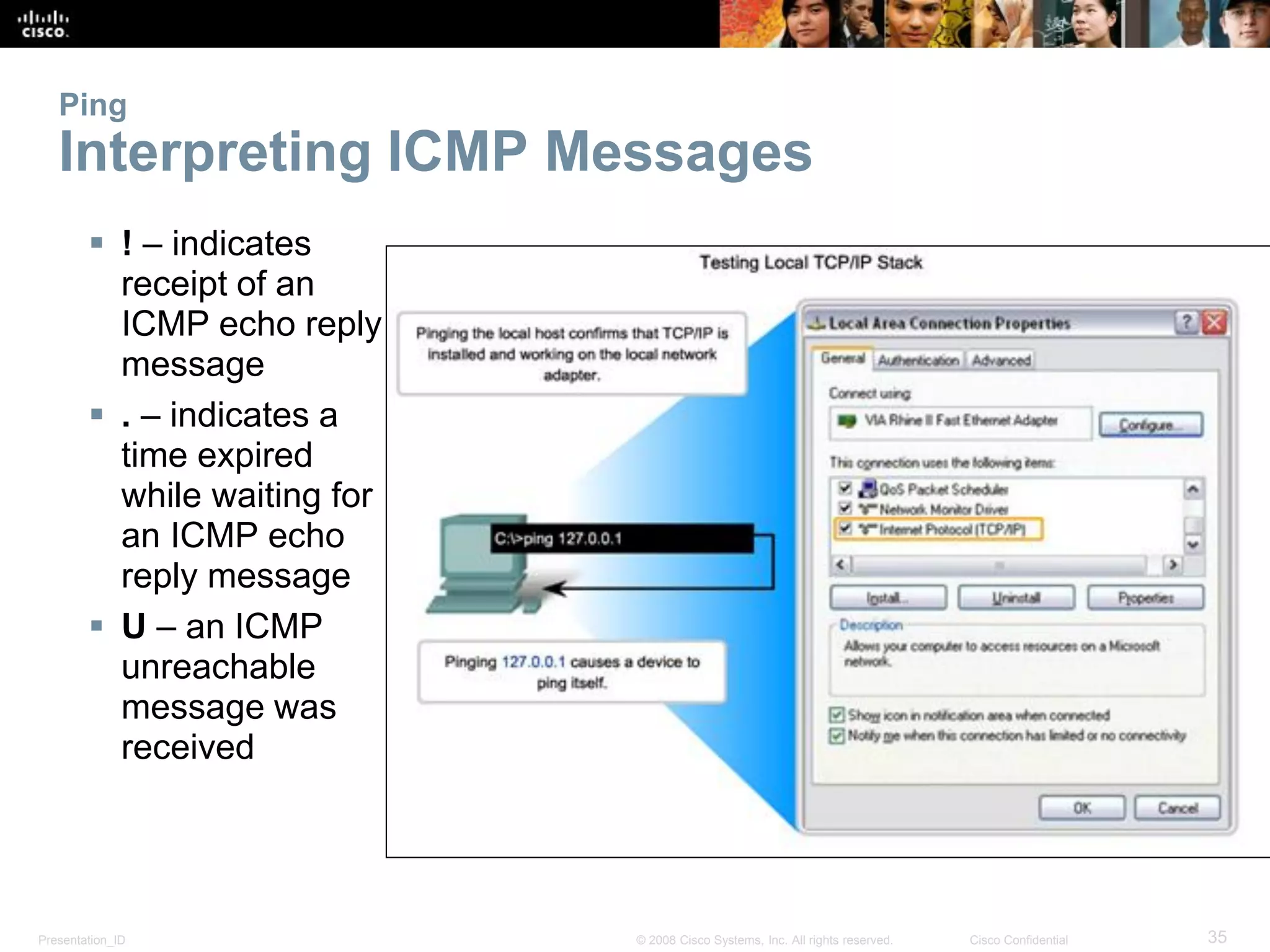
Ping
Leveraging Extended Ping
The Cisco IOS offers an "extended" mode of the ping command:
• R2# ping
• Protocol [ip]:
• Target IP address: 192.168.10.1
• Repeat count [5]:
• Datagram size [100]:
• Timeout in seconds [2]:
• Extended commands [n]: y
• Source address or interface: 10.1.1.1
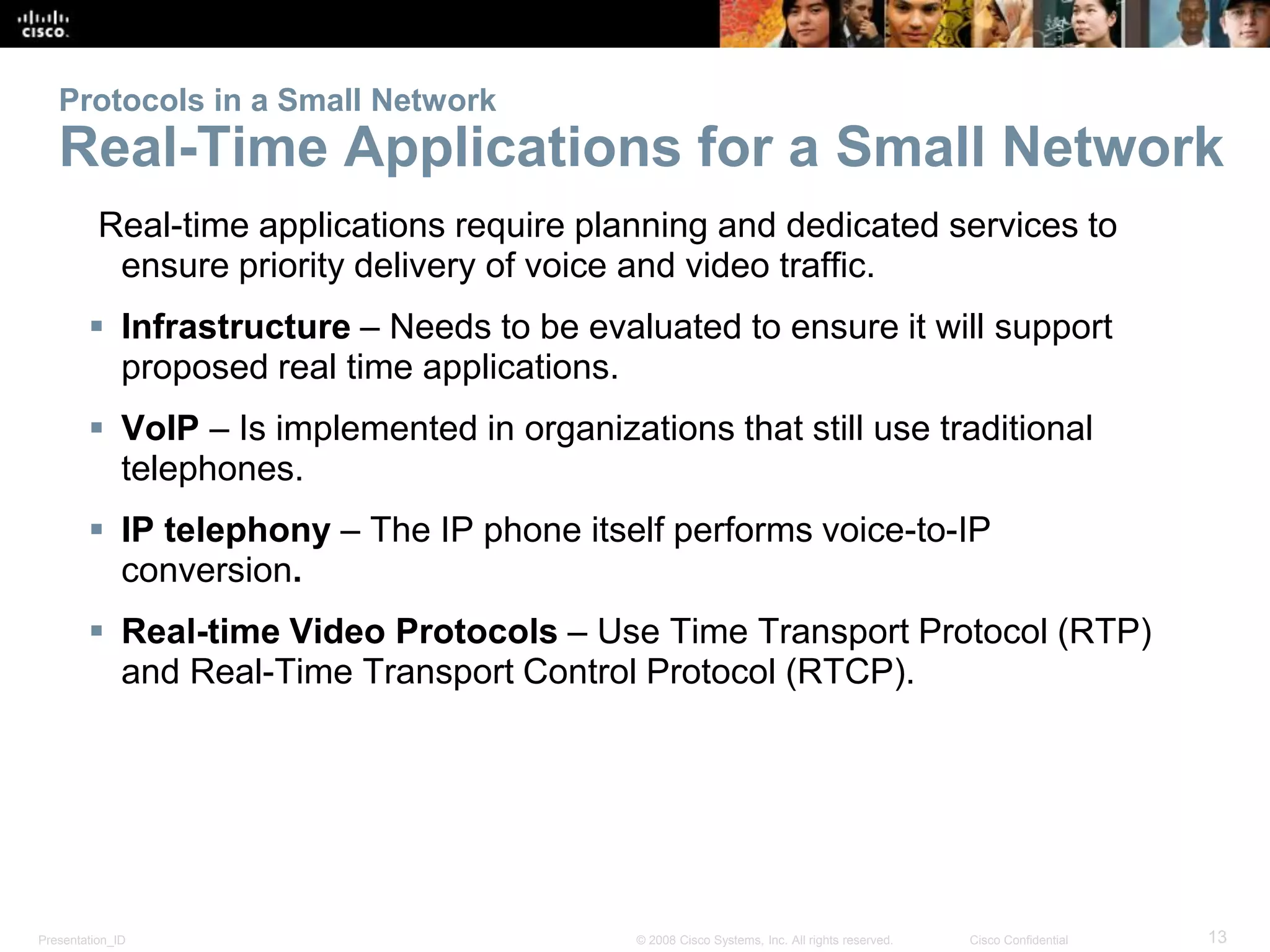
• Type of service [0]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11itsanetwork-150206083633-conversion-gate01/75/CCNAv5-S1-Chapter11-It-s-A-Network-36-2048.jpg)