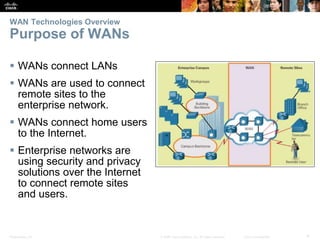
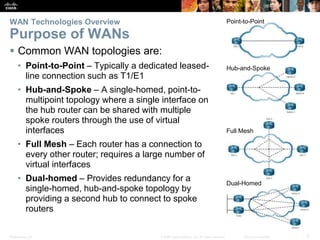
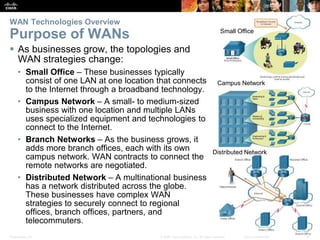
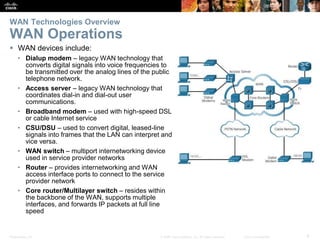
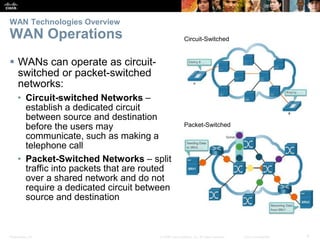
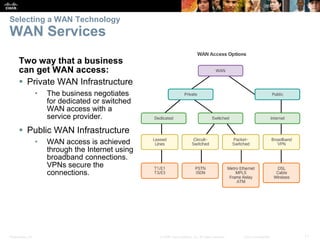
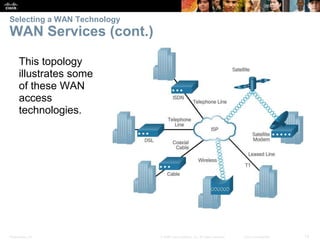
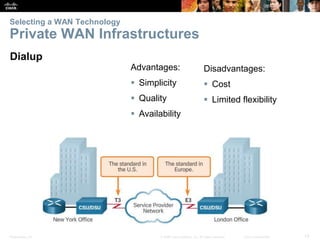
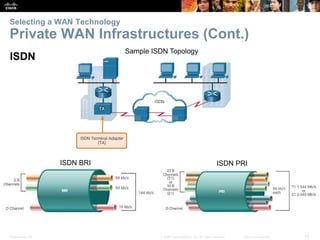
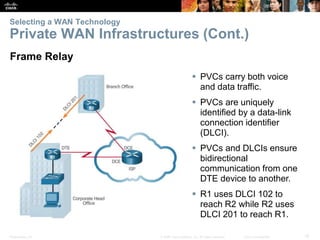
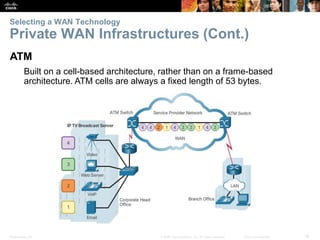
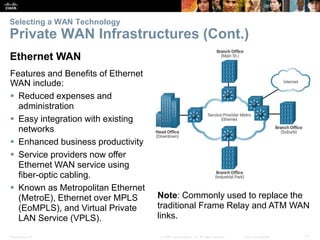
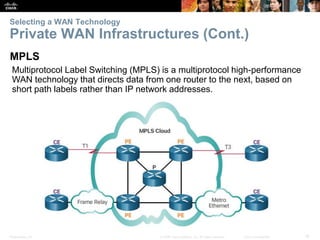
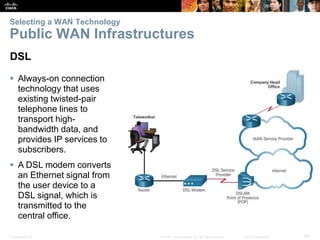
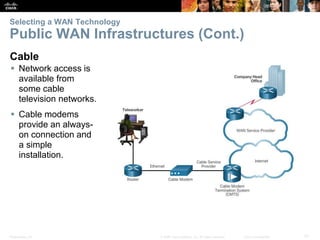
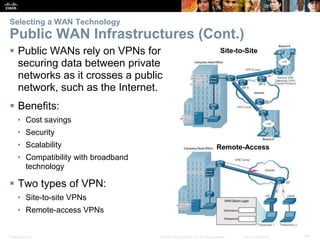
The document covers WAN (Wide Area Network) technologies, highlighting their purpose in connecting remote sites, home users to the internet, and enterprise networks. It outlines various WAN topologies and operations, as well as offers insights into selecting appropriate WAN technologies for businesses, including private and public infrastructures. Additionally, it addresses the importance of security solutions such as VPNs for safeguarding data over public WAN connections.