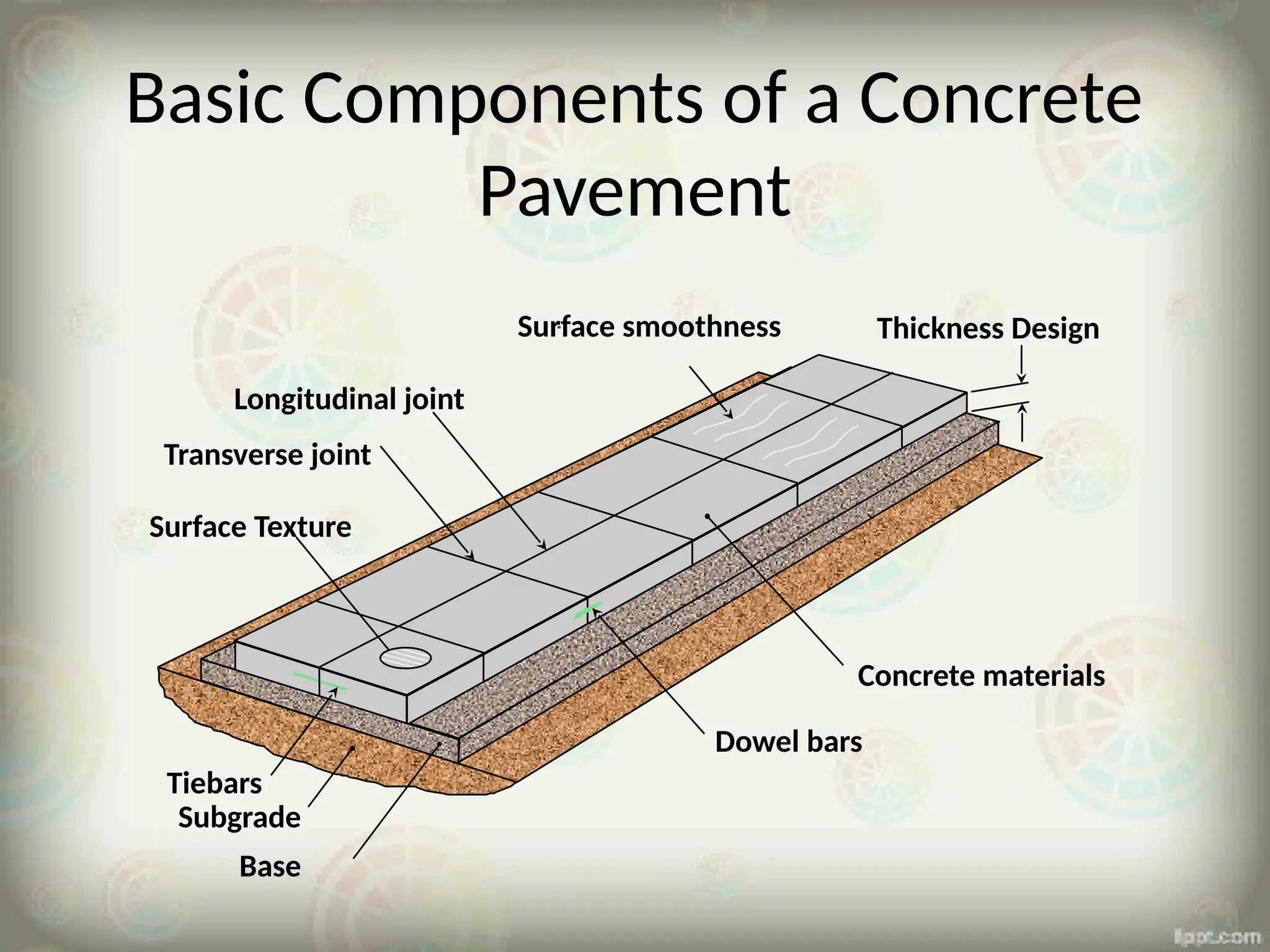
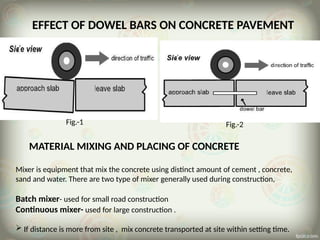
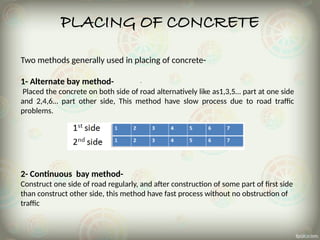
The document outlines the essential components and processes involved in concrete pavement construction, focusing on materials, equipment, and methods used. It discusses the types of cement and aggregates, site preparation, joint construction, concrete mixing and placing techniques, as well as curing and the timeline for traffic opening. The advantages of concrete roads include durability, reduced fuel consumption, and environmental benefits.