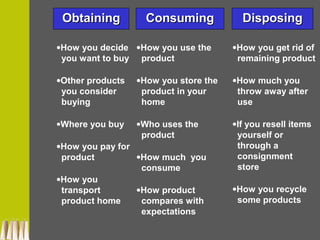
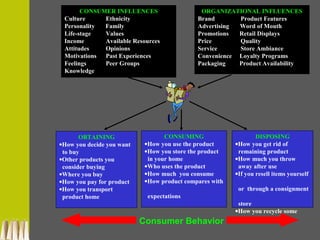
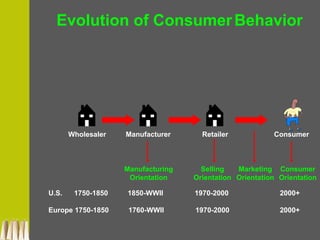
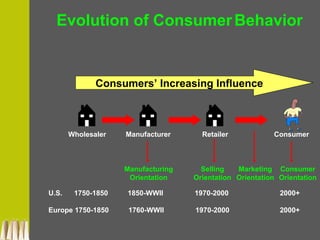
The document provides an in-depth exploration of consumer behavior, detailing the activities involved in obtaining, consuming, and disposing of products and services. It highlights the importance of understanding consumer influences, such as culture and personal values, and discusses the evolution of consumer roles in the marketplace. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of studying consumer behavior for economic health and effective marketing strategies.