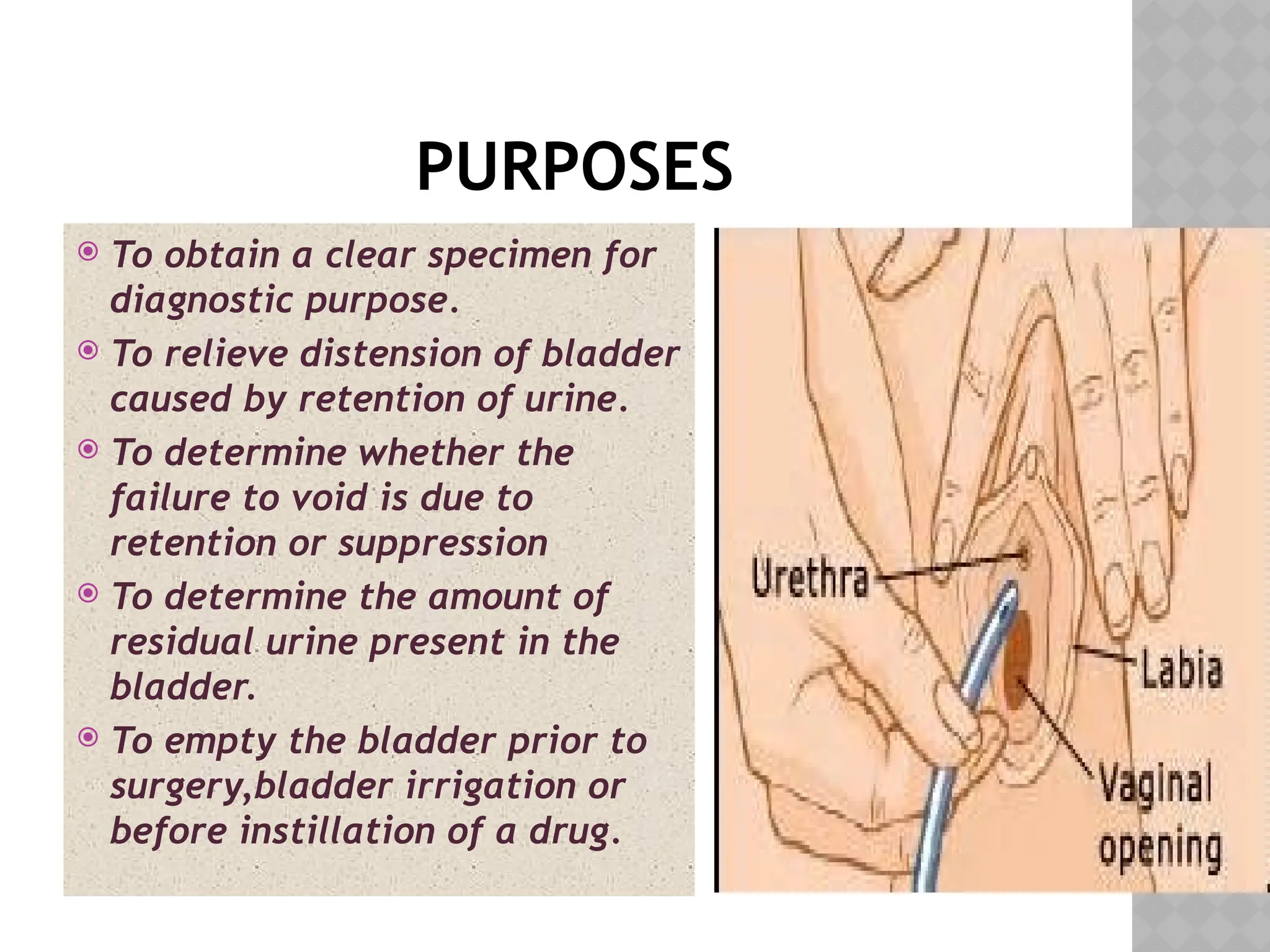
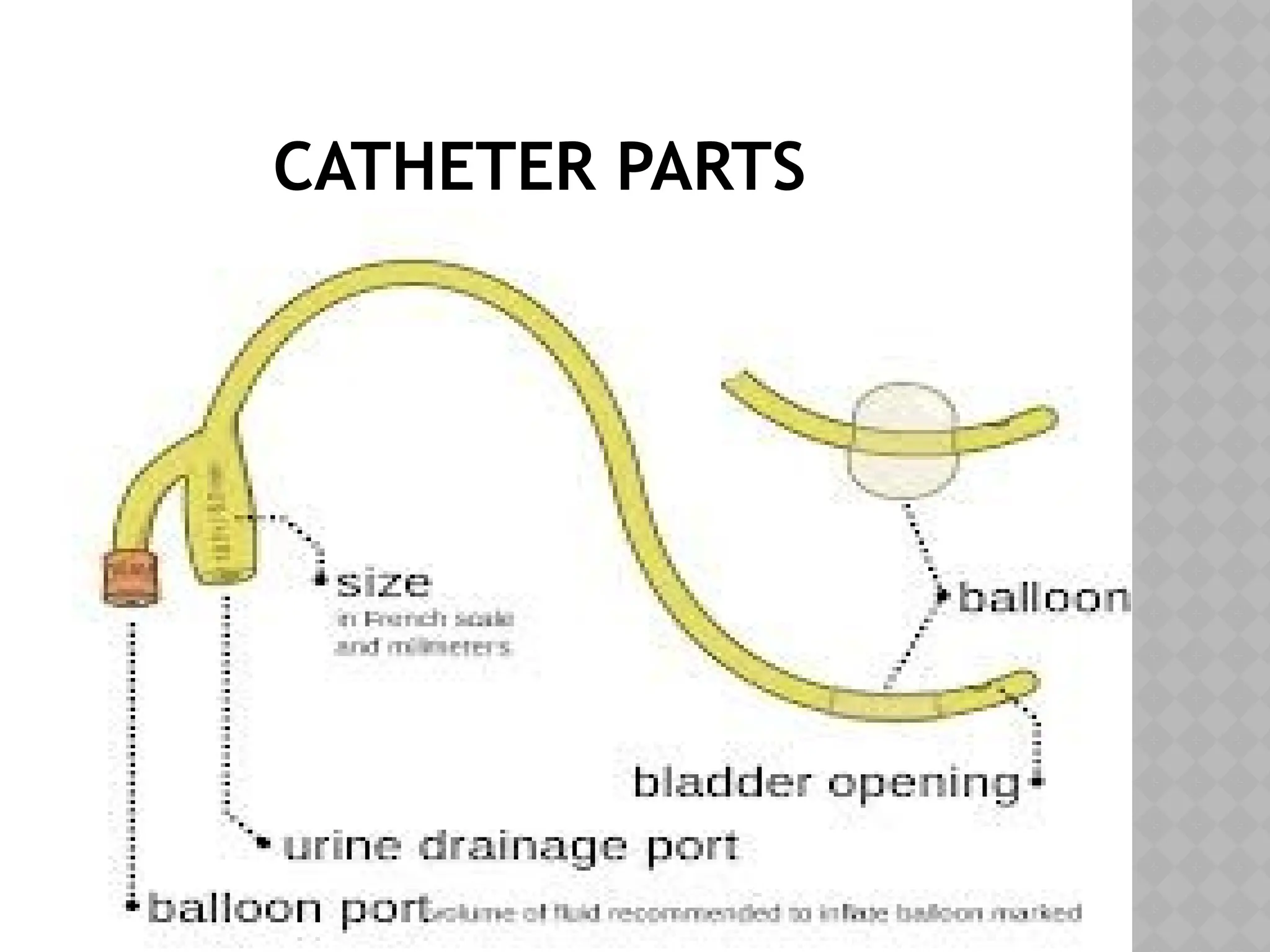
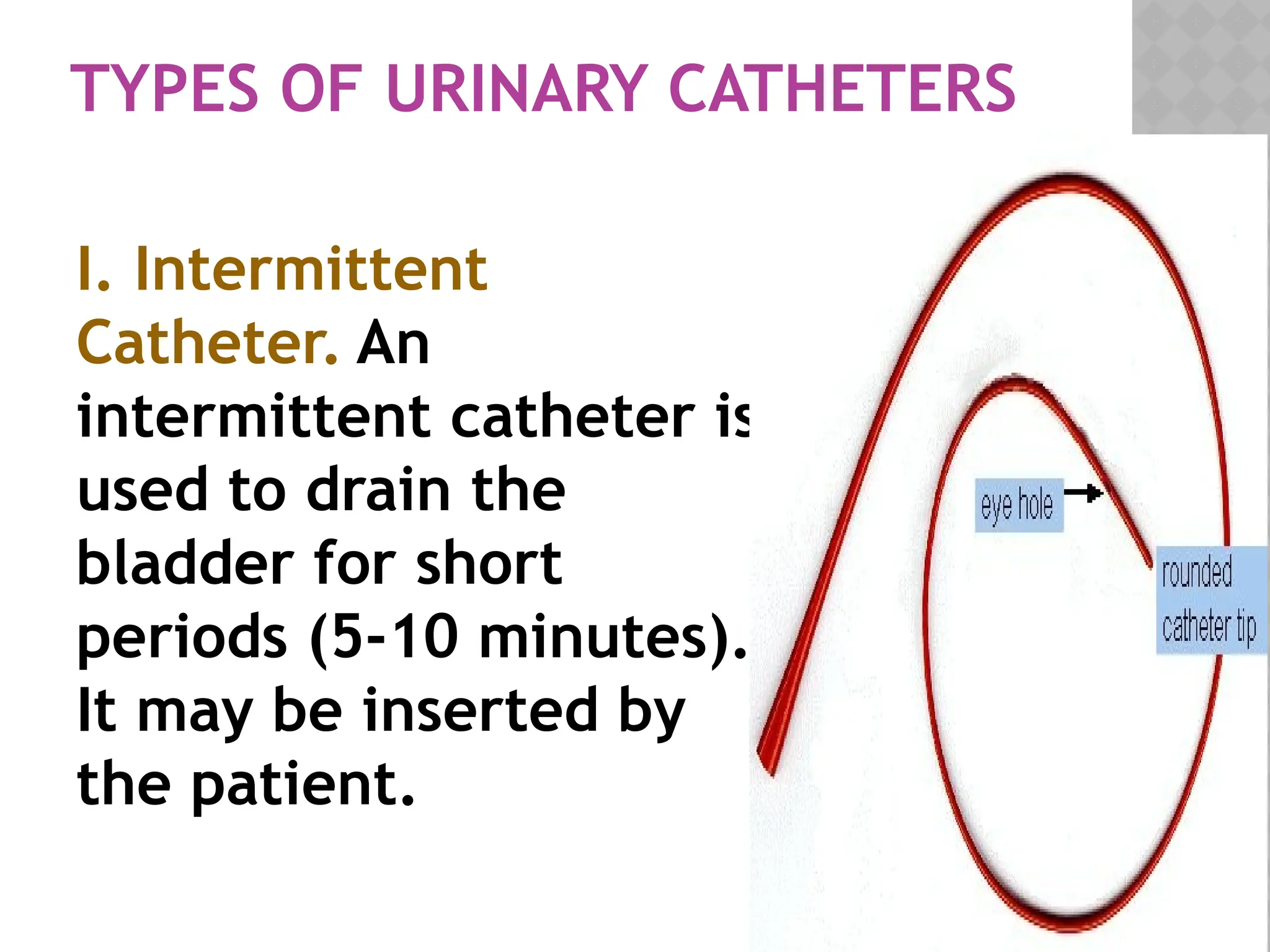
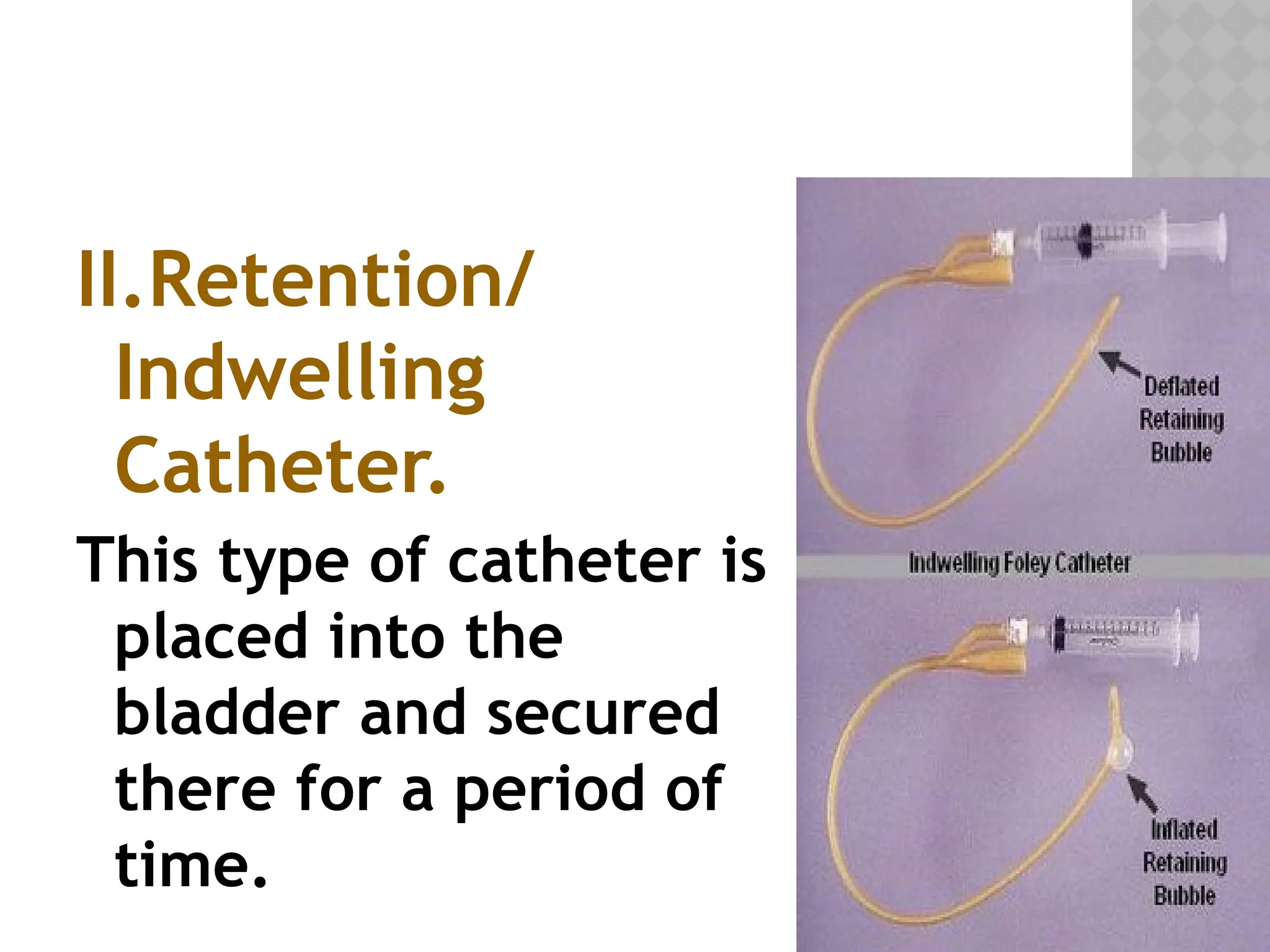
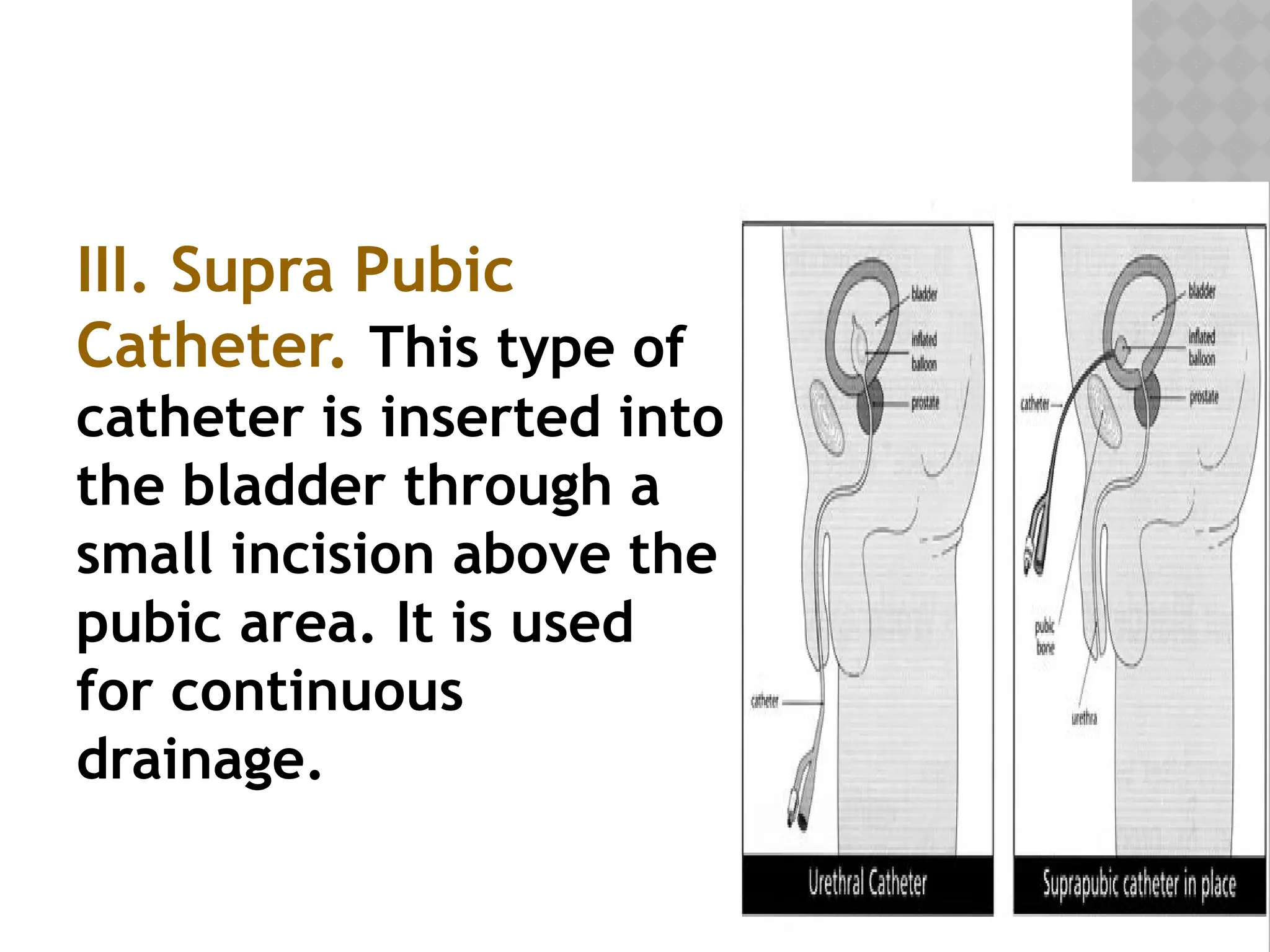
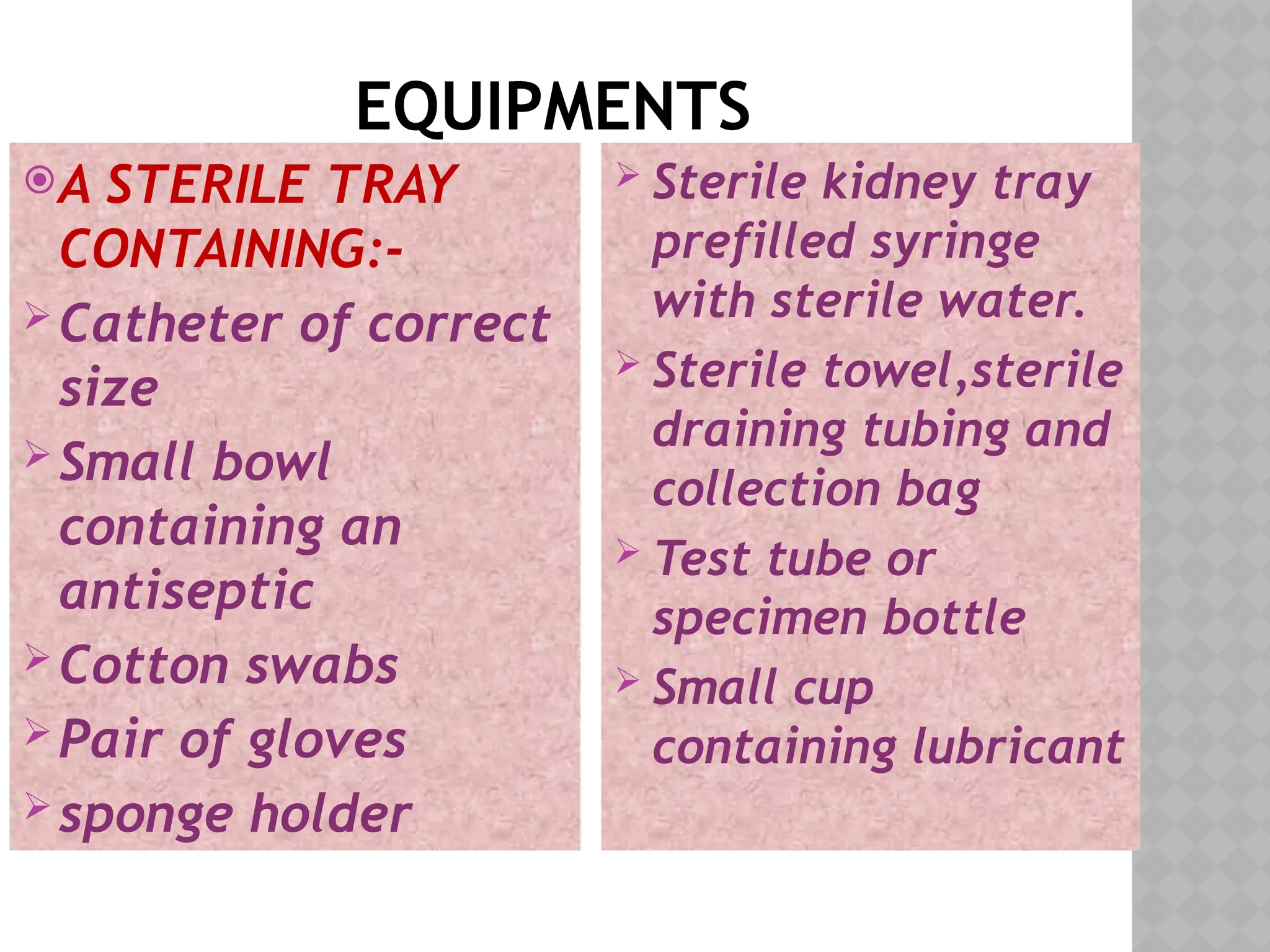
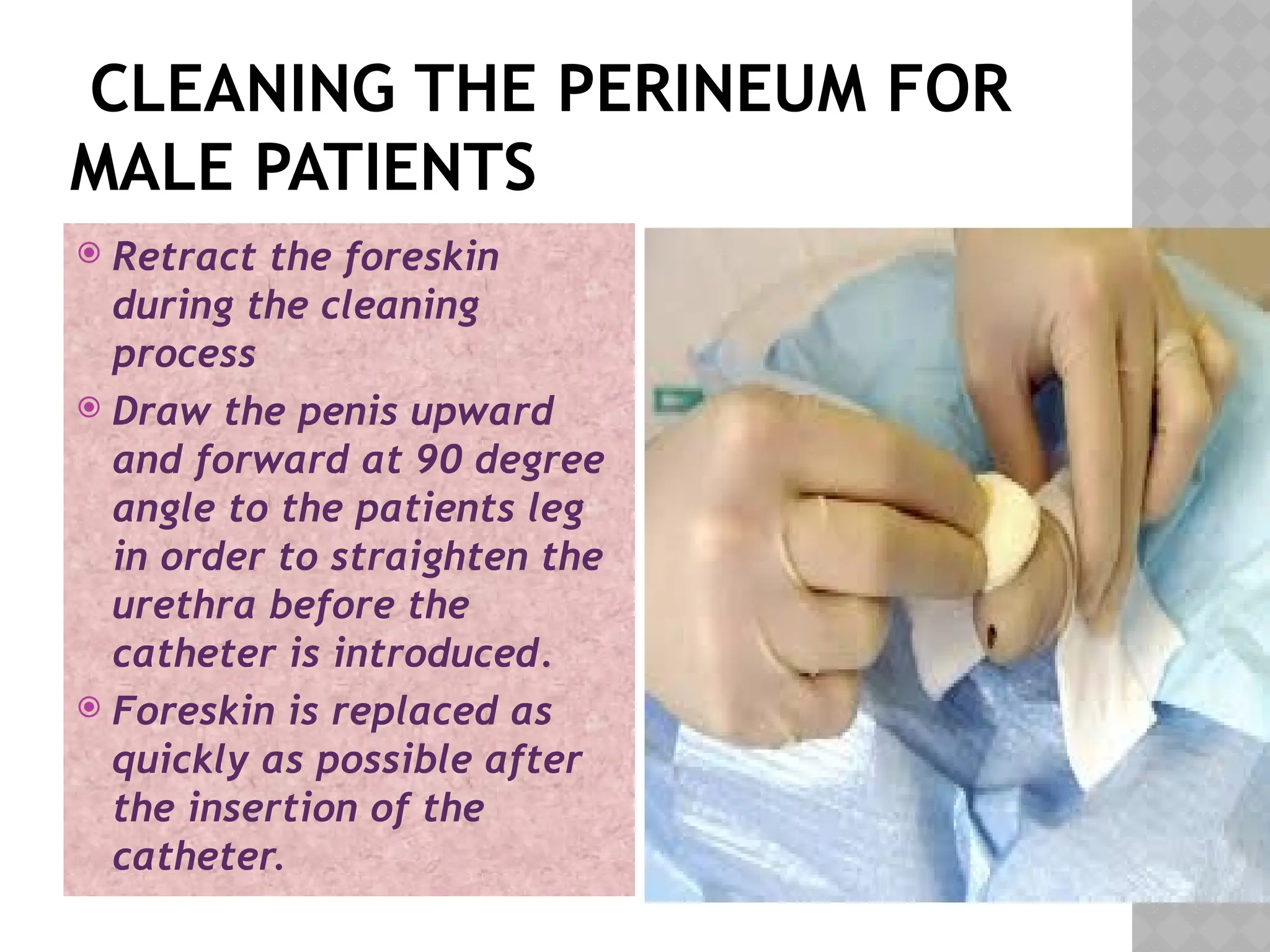
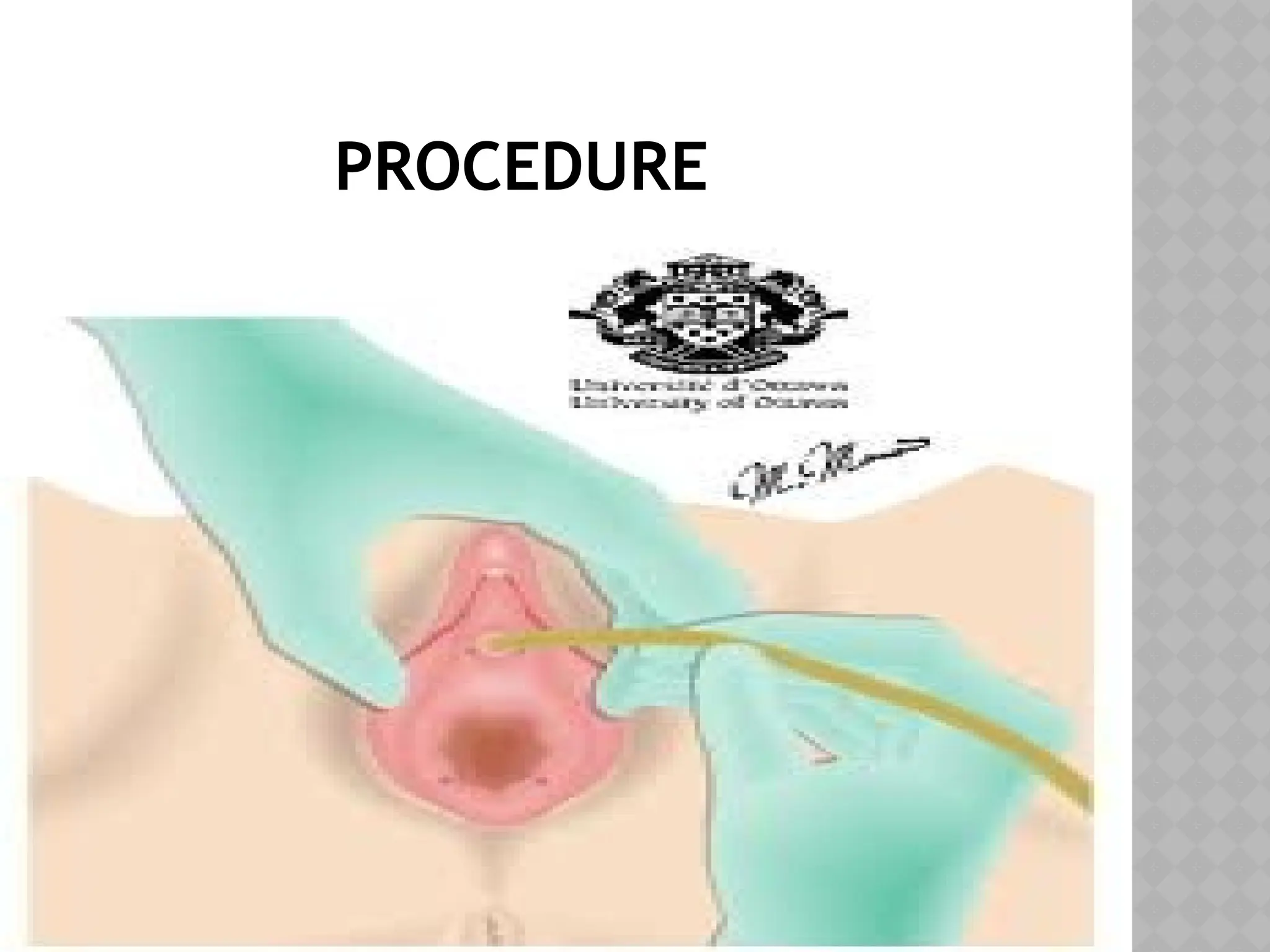
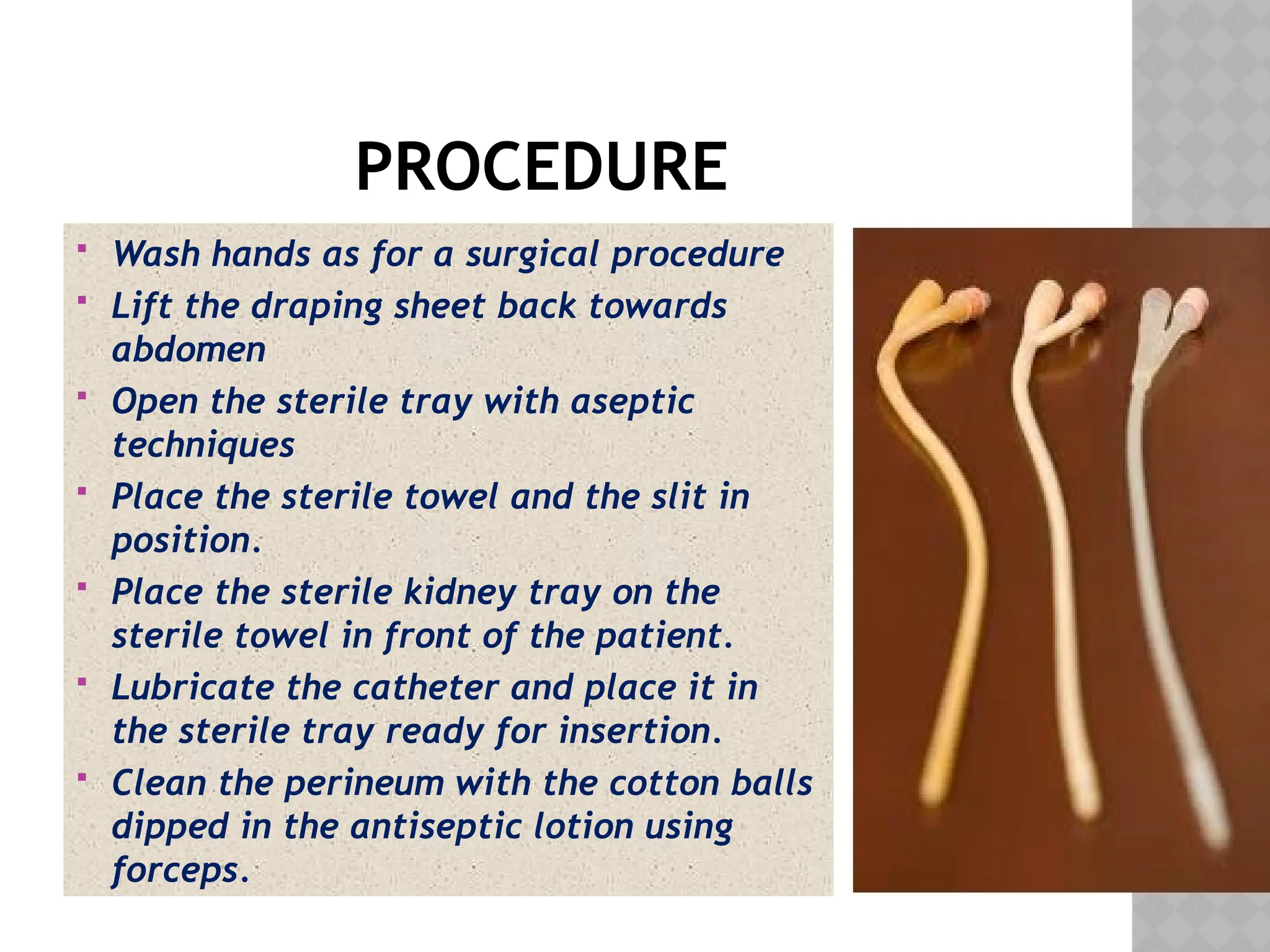
This document provides a comprehensive overview of urinary catheterization, including its definition, purposes, types, and procedures for insertion and care. It outlines the importance of aseptic technique, equipment needed, and steps for both male and female patients during catheterization. Additionally, it emphasizes preliminary assessments and aftercare following the procedure.