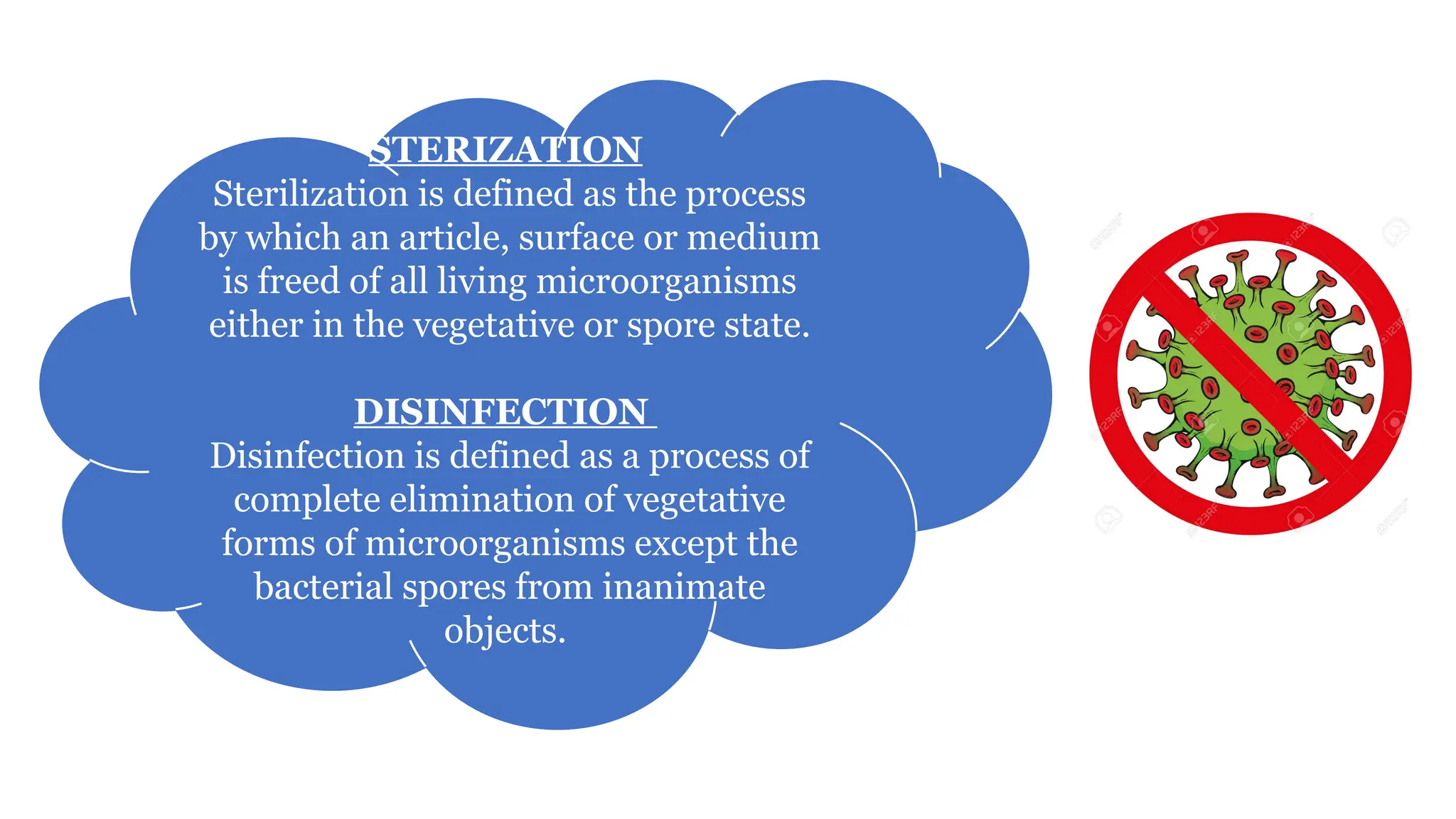
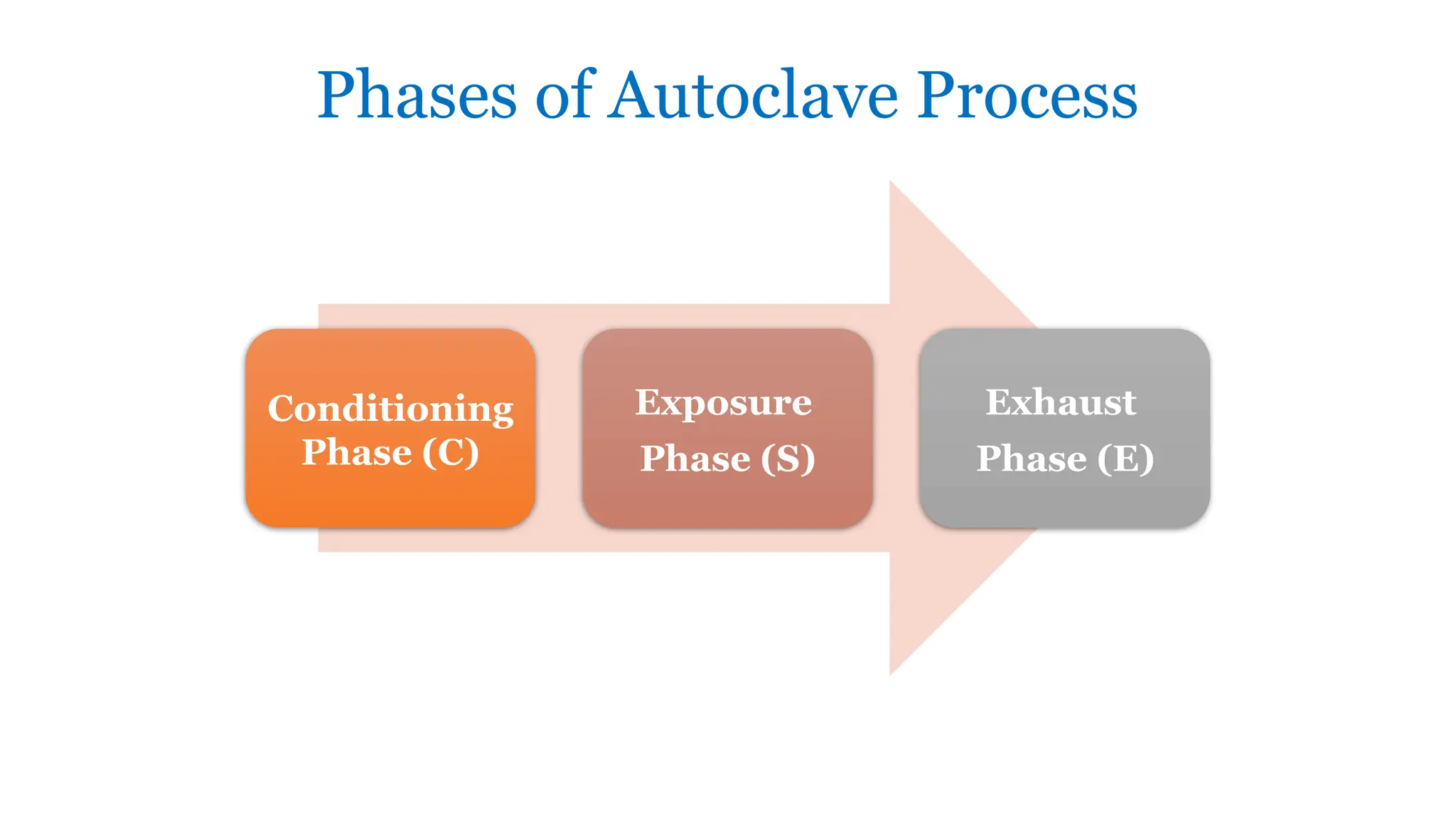
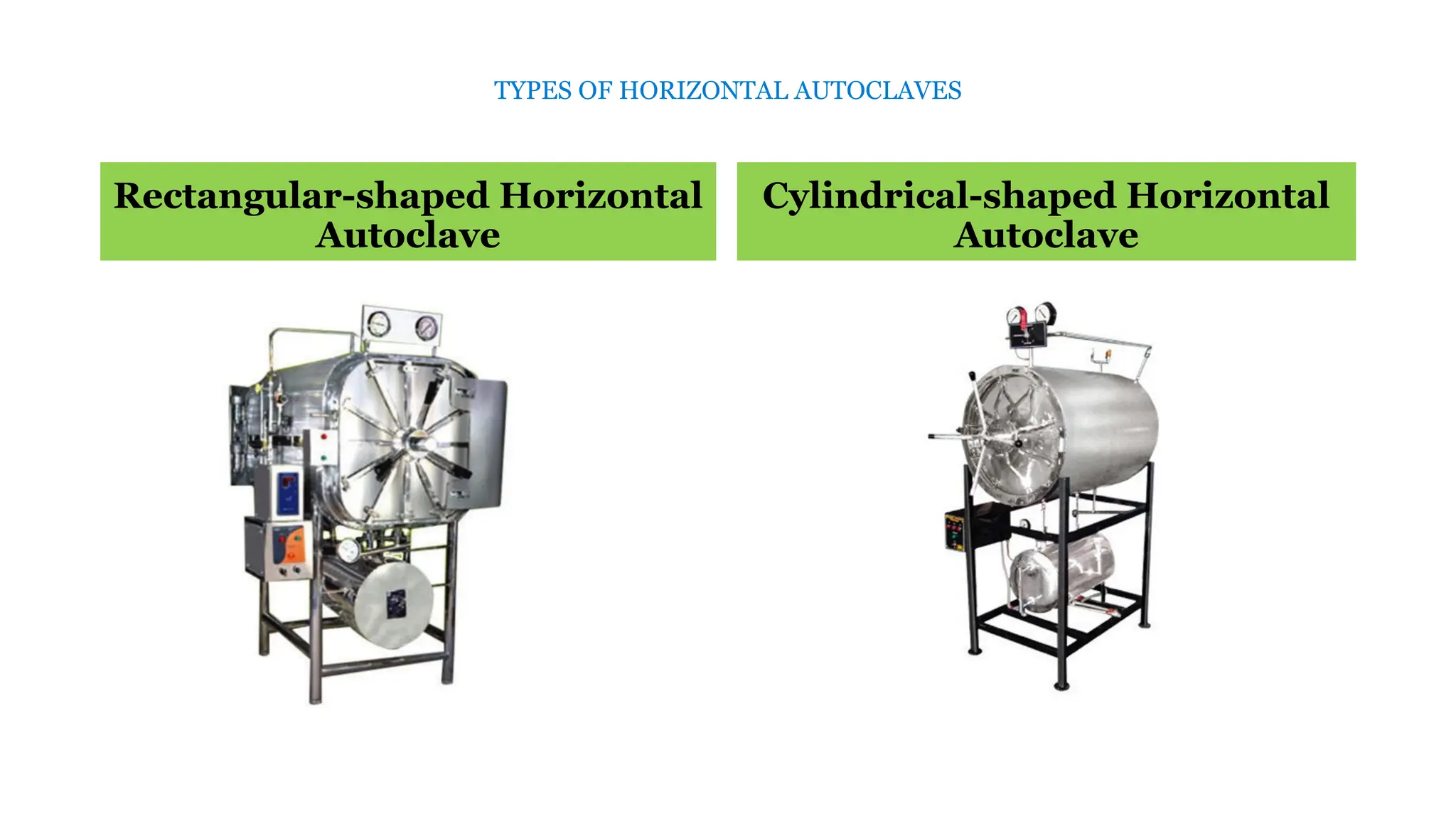
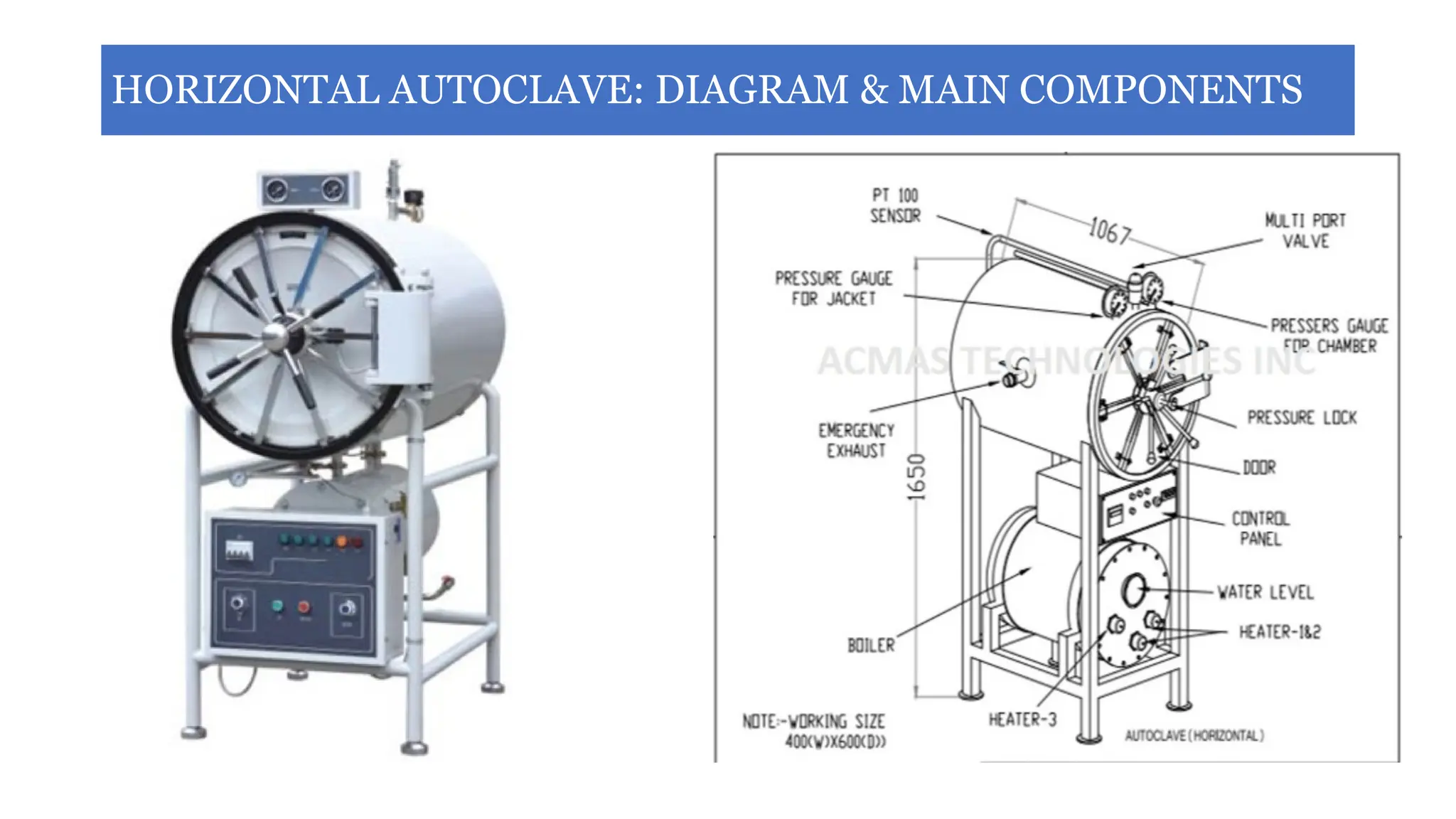
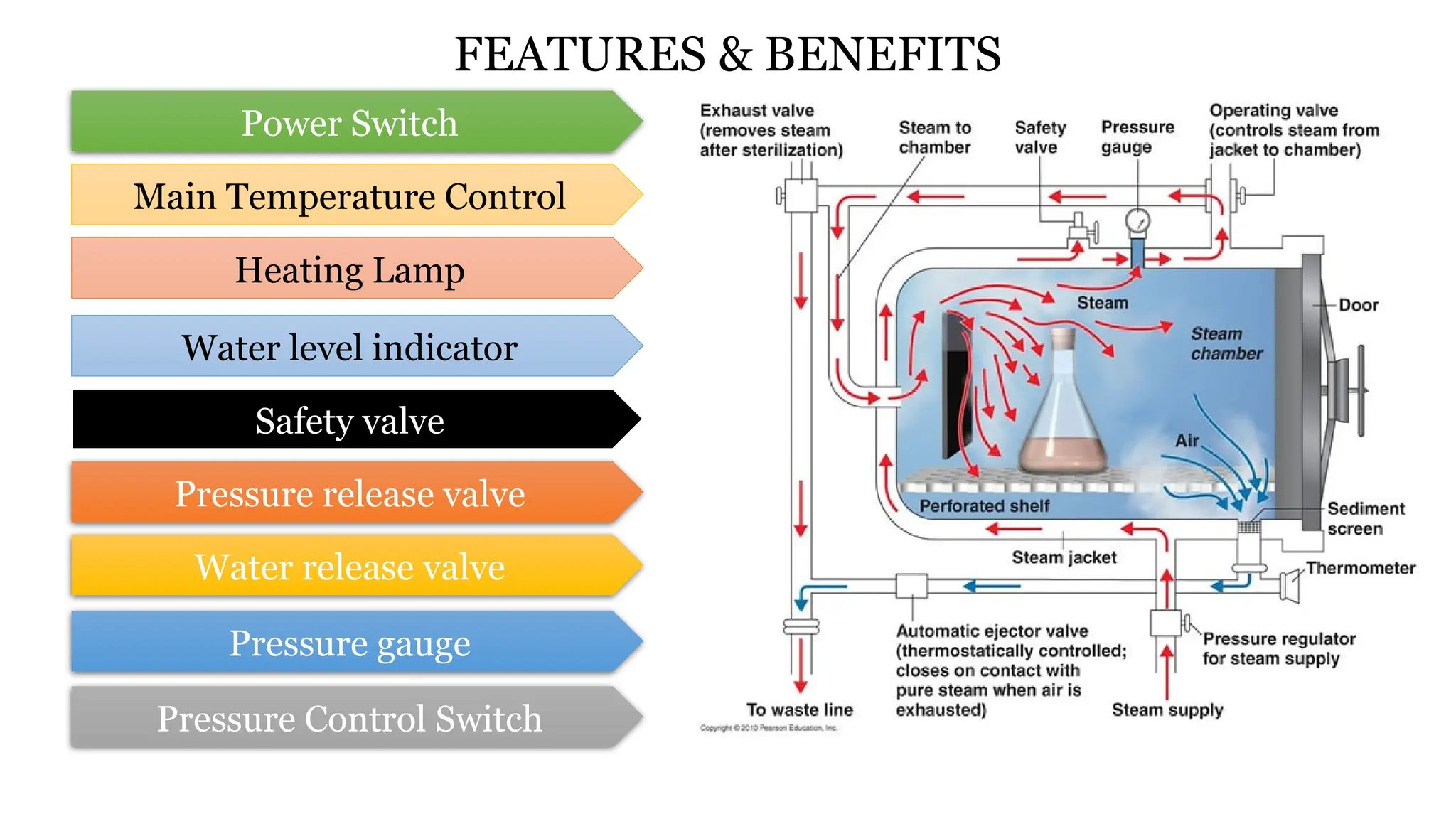
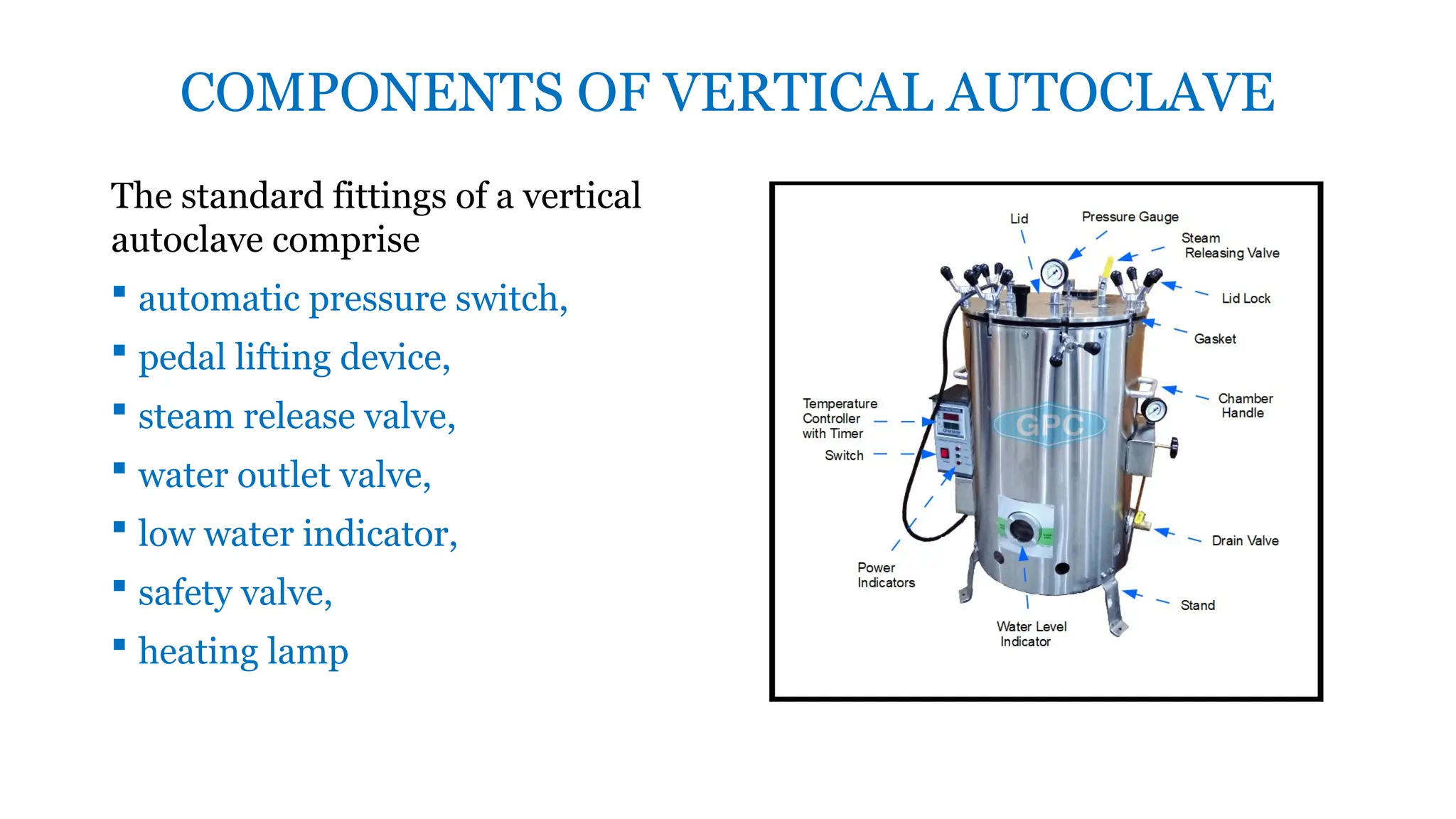
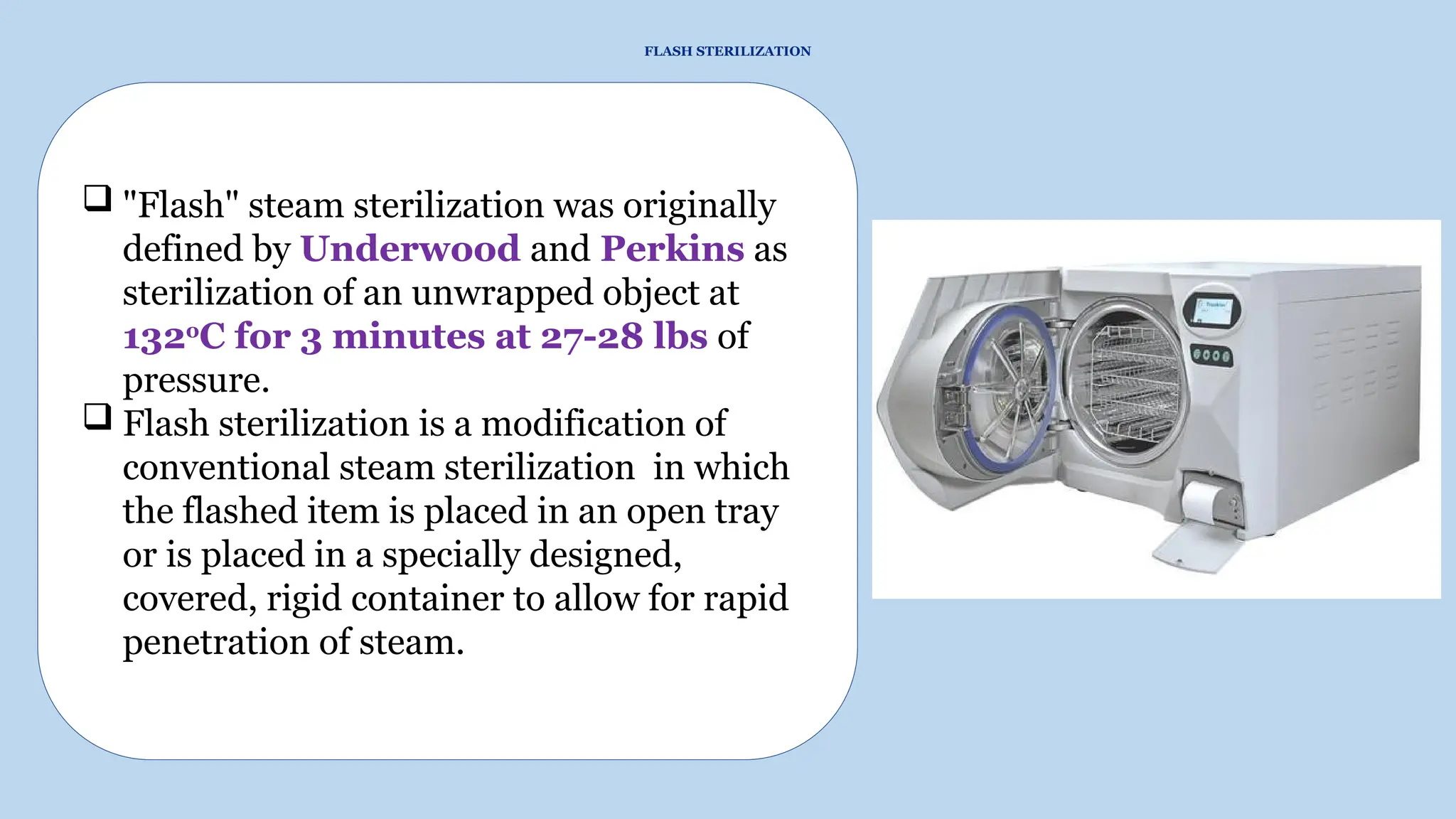
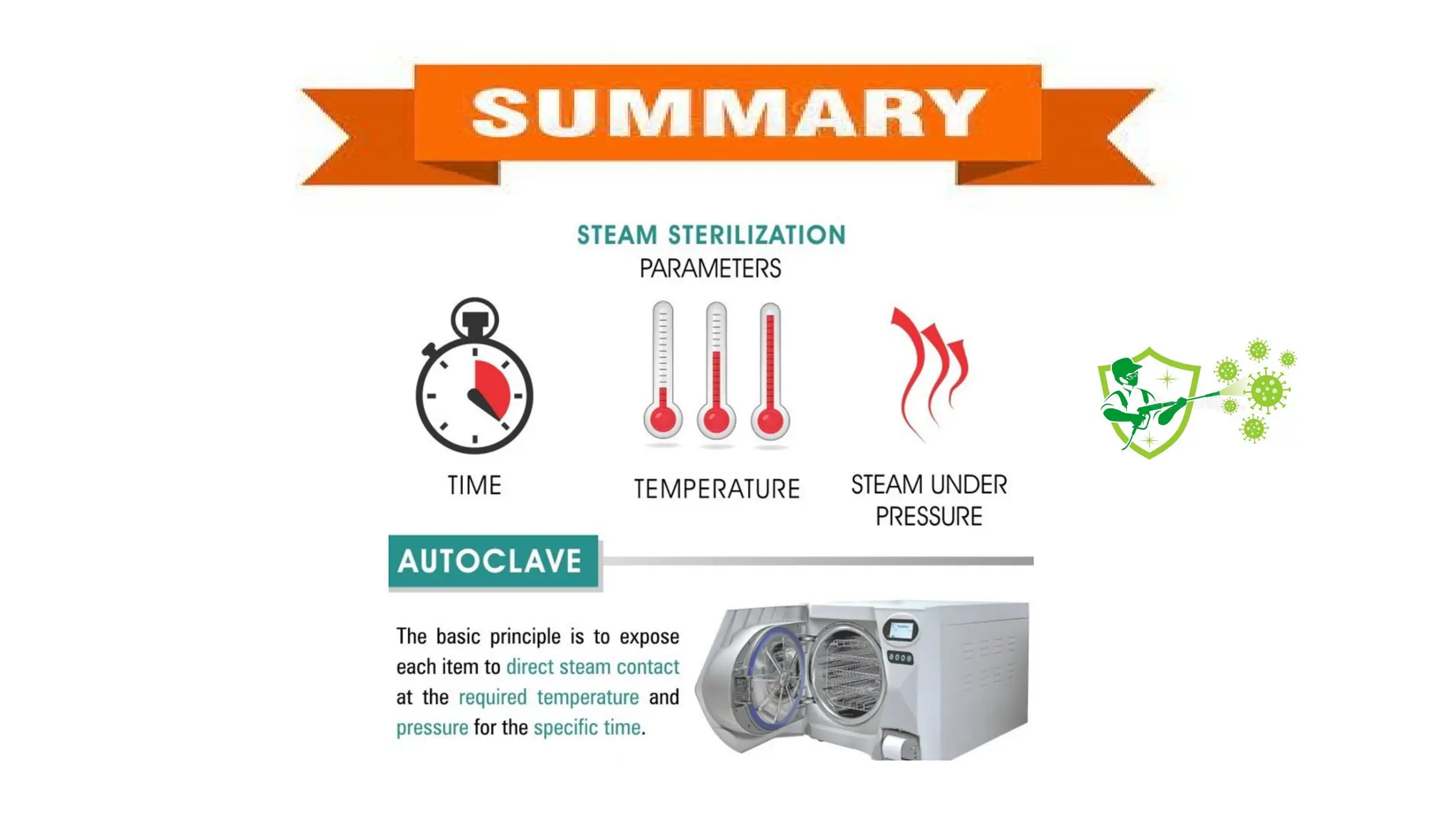
This document outlines the processes of sterilization and disinfection, defining sterilization as the complete elimination of all microorganisms and disinfection as the elimination of vegetative forms. It discusses autoclaves, their operation, types, and features, as well as alternative sterilization methods such as ethylene oxide and plasma sterilizers. Precautions for safe autoclaving and various disinfectants used are also covered.