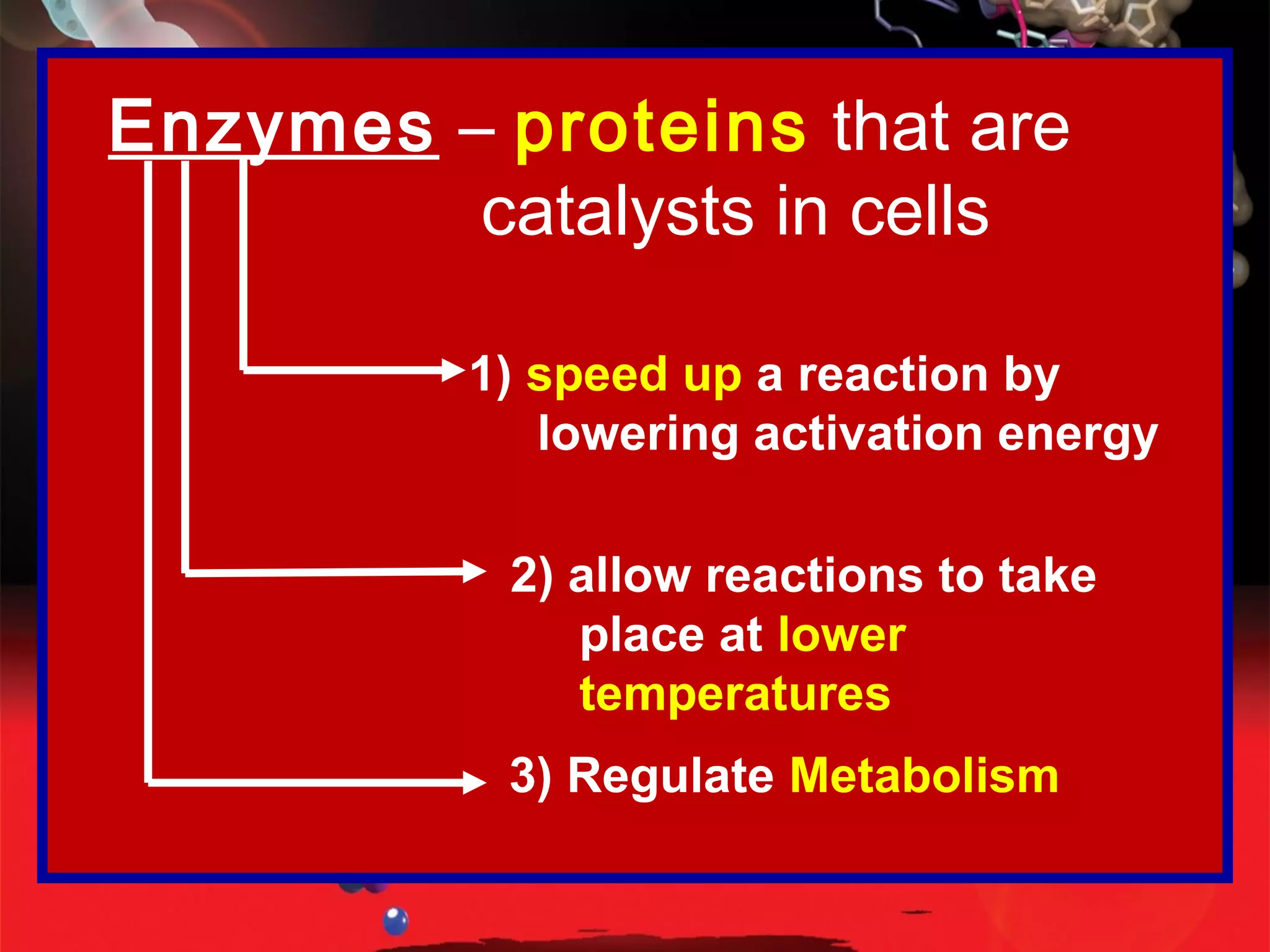
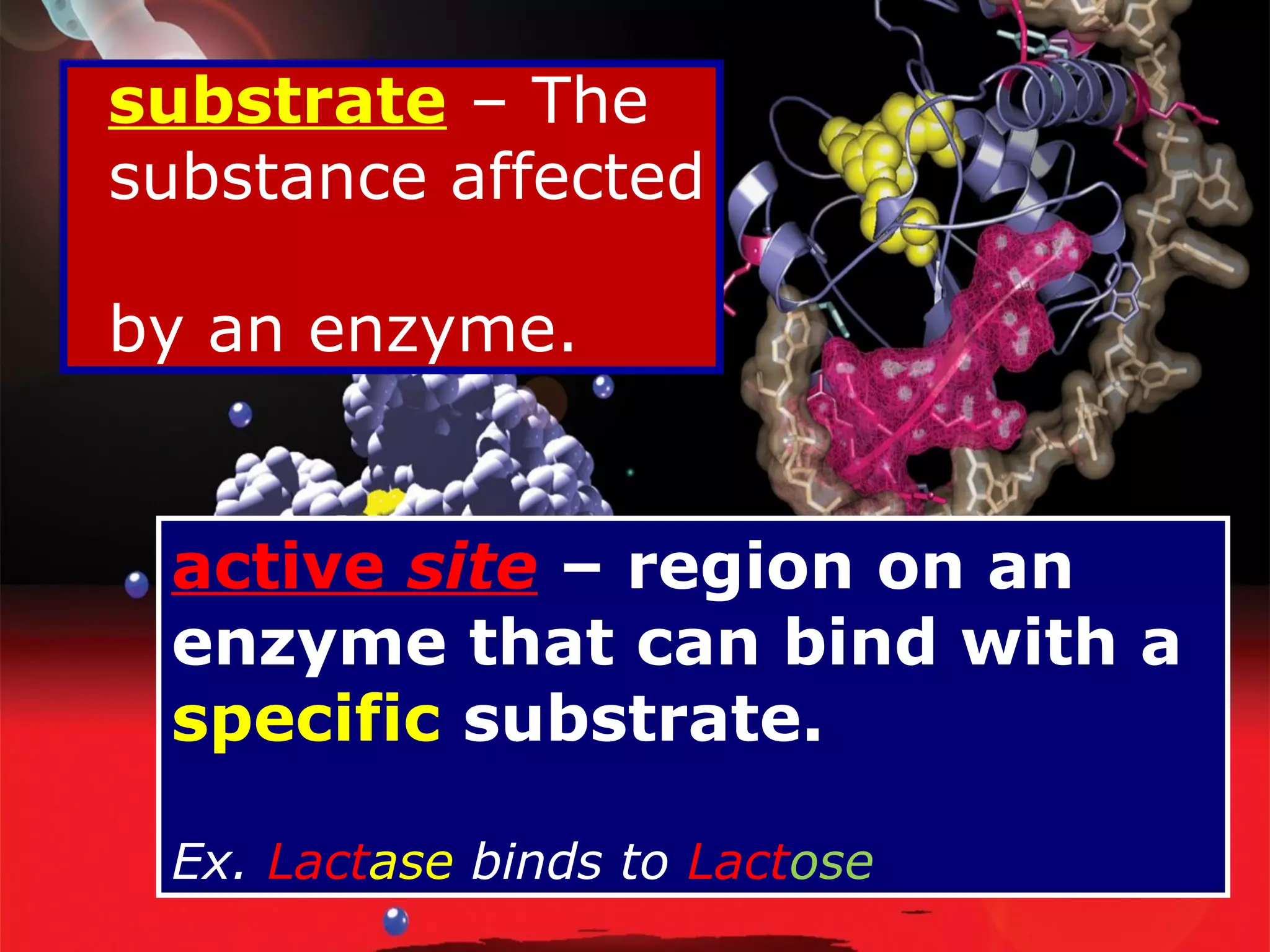
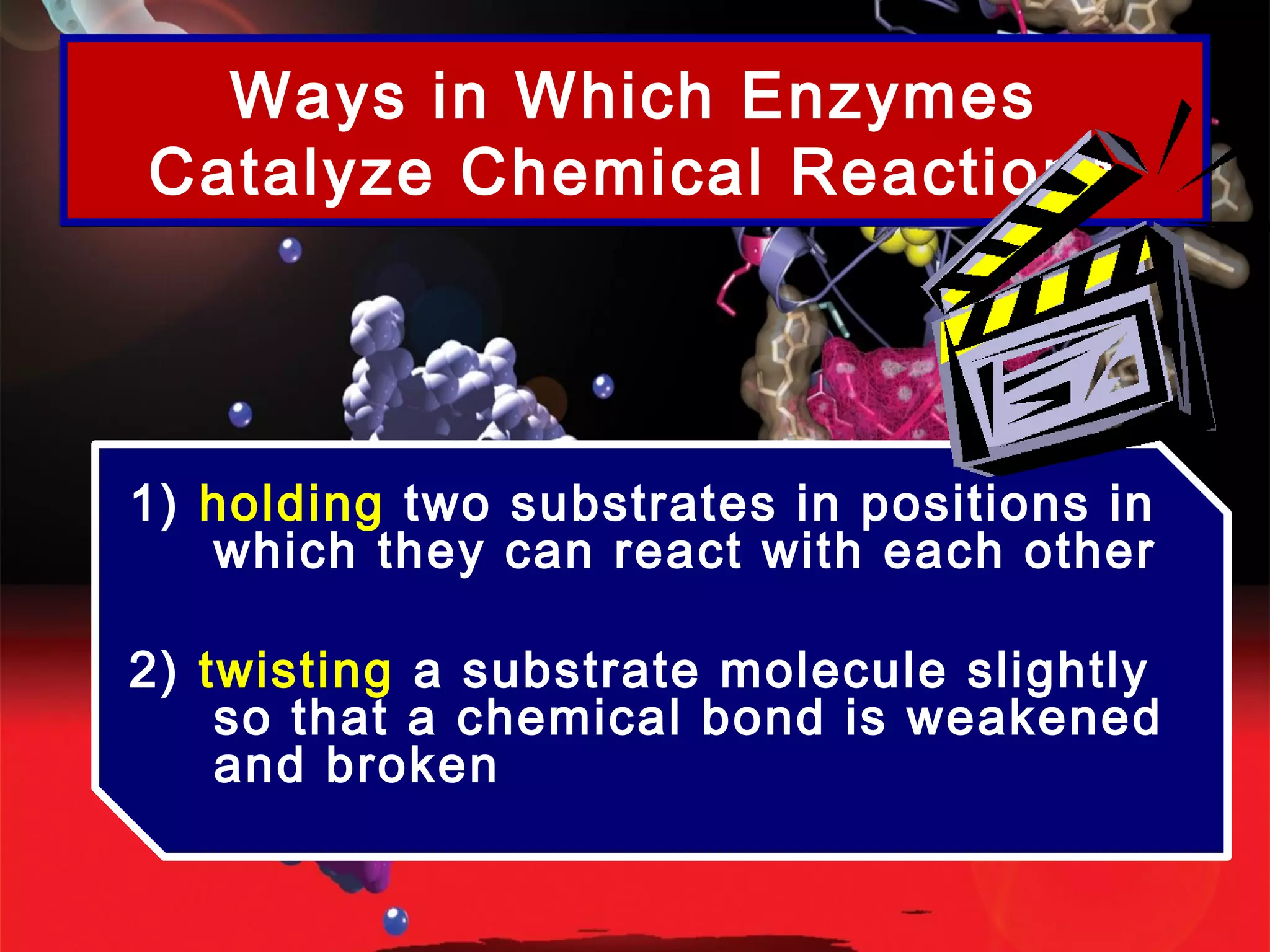
Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts in living organisms. They speed up chemical reactions by lowering their activation energy, allowing reactions to take place at lower temperatures. Enzymes catalyze reactions by binding to specific substrates at their active sites, bringing substrates together or twisting them to weaken bonds for reactions. Metabolism consists of both catabolic reactions that break down molecules to release energy and anabolic reactions that use energy to build up molecules, and enzymes regulate these metabolic reactions through catalysis.