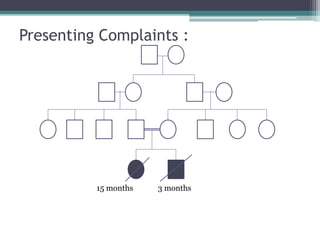
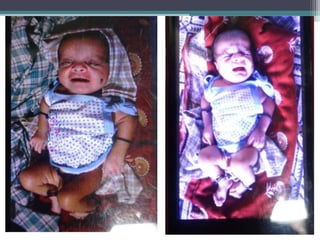
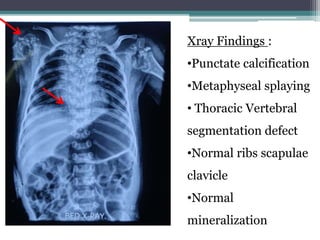
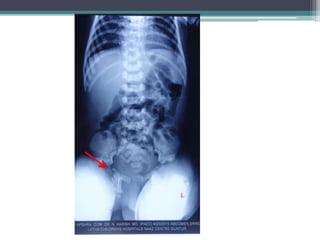
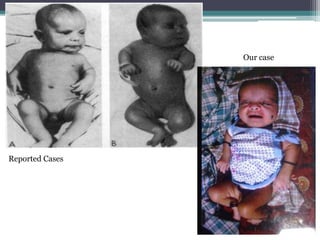
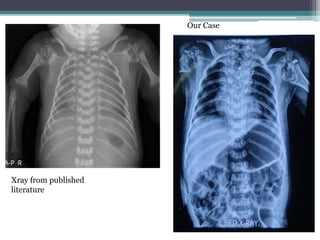
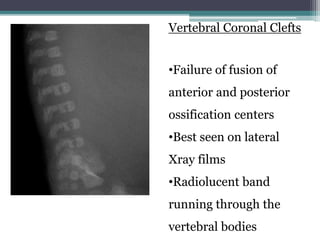
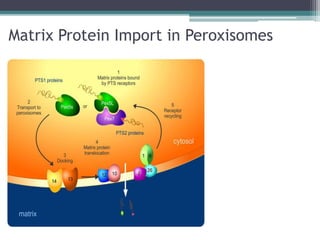
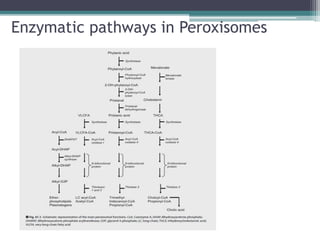
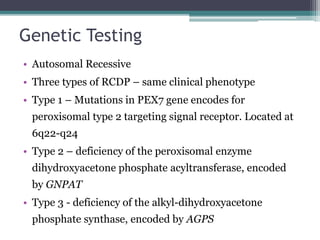
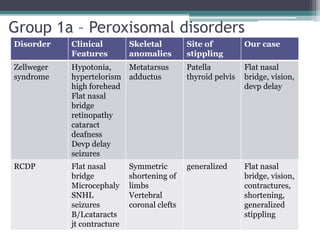
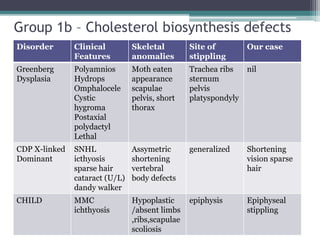
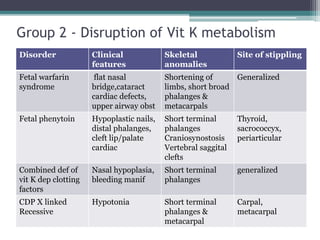
This case presentation describes two siblings who presented with rhizomelic shortening of the limbs, flat nasal bridge, vision impairment, developmental delay, and congenital heart disease. Radiographic findings included punctate calcifications. The differential diagnosis included disorders of peroxisomal function and cholesterol metabolism. Genetic testing confirmed a diagnosis of Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata type 1, a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in peroxisomal protein import.