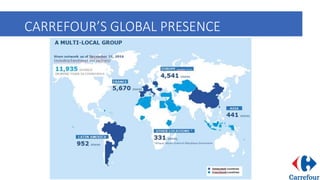
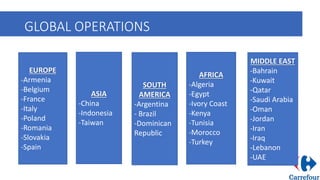
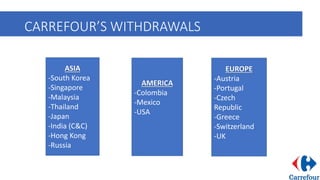
Carrefour is a French multinational retailer founded in 1959, recognized for creating the hypermarket concept. It expanded rapidly throughout France in the 1960s and later globally, adapting its operations to local markets. The company faced challenges in international markets, leading to closures and withdrawals, notably from India due to unfavorable regulations.