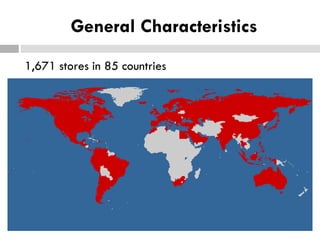
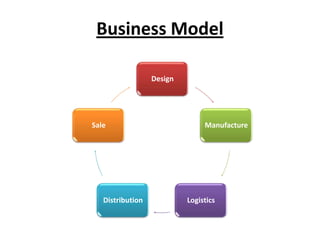
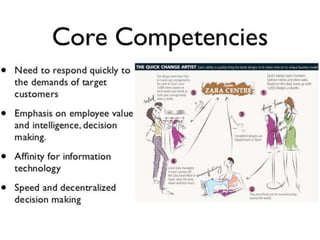
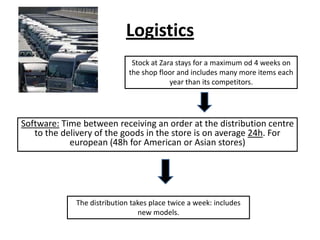
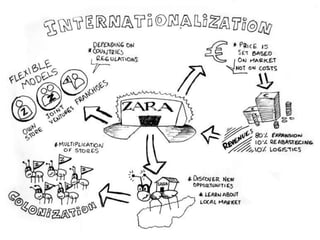
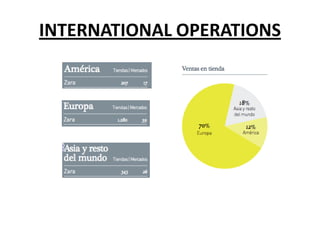
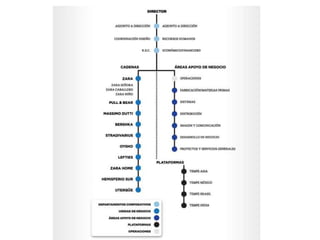
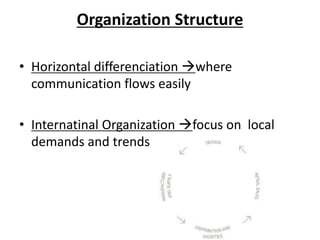
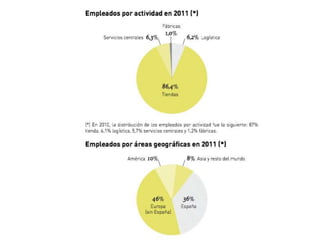
Zara was founded in 1975 in La Coruña, Spain by Amancio Ortega. It has since expanded to over 1,671 stores across 85 countries. Zara designs and manufactures clothing and accessories for men, women, and children. It is known for its rapid response to fashion trends through a vertically-integrated business model that allows it to design, produce, and distribute new products to stores within 2 weeks. Zara owns factories in Europe to maintain tight control over production while contracting out some garment assembly. It has a highly efficient logistics system that delivers new stock to stores twice per week on average within 24-48 hours. Zara's international success is driven by its focus on local demands