Antiarrhythmic agents are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms. They are classified into 5 classes based on their mechanism of action:
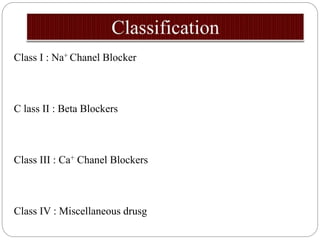
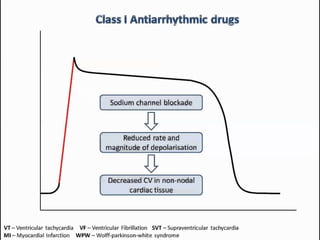
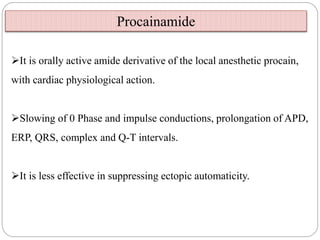
Class I agents block sodium channels. Common examples are quinidine, procainamide, and lidocaine.
Class II agents are beta blockers that block sympathetic nervous system activity. Examples include propranolol and atenolol.
Class III agents prolong the heart's repolarization by blocking potassium channels. Amiodarone, sotalol, and ibutilide are examples.
Class IV agents like verapamil and diltiazem block calcium channels and slow conduction through the AV node.
Class V agents work through other mechanisms and include