This document describes several cardiovascular procedures:
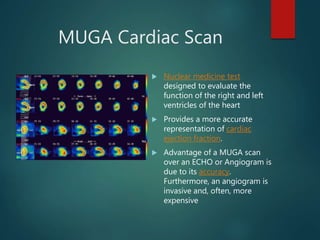
ECG records the electrical activity of the heart over time using skin electrodes. Holter monitoring continuously records various electrical heart activity for hours to days on a portable device, commonly to observe arrhythmias. Doppler ultrasonography uses the Doppler effect to assess blood flow direction and velocity. Echocardiography uses ultrasound to create images of the heart and blood flow. MUGA cardiac scans evaluate right and left ventricular function through nuclear medicine and provide a more accurate ejection fraction than ECHO or angiogram. Cardiac catheterization is an invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions through examination of coronary arteries, cardiac chambers, and valves.