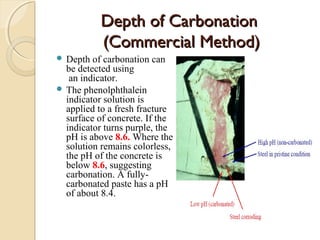
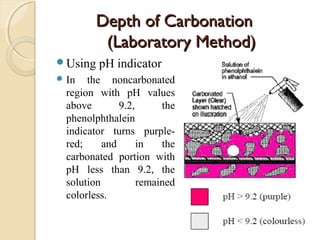
The document discusses the carbonation of concrete, a chemical reaction between carbon dioxide and lime that results in the formation of calcium carbonate. It outlines the detection methods for carbonation, factors affecting its rate, and the negative effects on concrete quality and steel reinforcement, including accelerated corrosion. Prevention strategies emphasize reducing porosity through lower water/cement ratios to mitigate carbonation risks.