1. There are three main options for internalizing externalities: setting norms or standards, levying taxes on polluting activities, and enabling market bargaining.
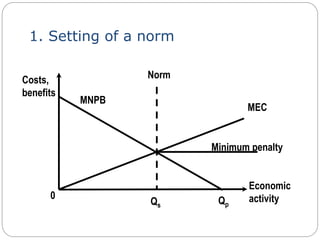
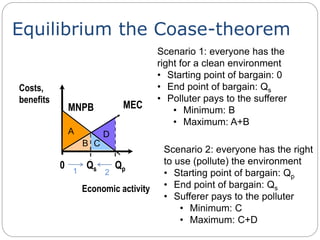
2. Setting norms involves establishing a limit on pollution and penalizing activities that exceed it. Taxes on pollution involve charging polluters per unit of pollution produced. Market bargaining allows polluters and affected parties to negotiate pollution levels directly.
3. An example discusses setting a norm or taxing emissions from a cement factory to reduce air pollution costs to society. Calculations show the effects on production, profits, and social costs with and without regulation.