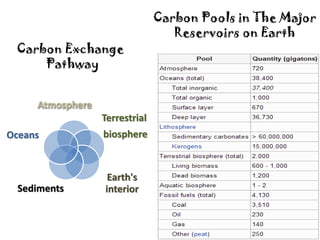
The document discusses the carbon cycle and the role of carbon in the environment. It notes that nature's carbon cycle is self-regulating, with plants absorbing CO2 through photosynthesis and microbes releasing carbon back into the atmosphere through decomposition. However, anthropogenic carbon emissions are excess and not part of the natural cycle. It then discusses how human carbon emissions amplify greenhouse gas concentrations and the greenhouse effect, threatening the environment by causing global warming. The concepts of carbon neutrality, carbon footprint, carbon sequestration, carbon offsets, and carbon credits in addressing this issue are also summarized.