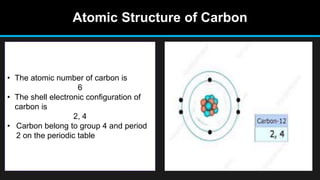
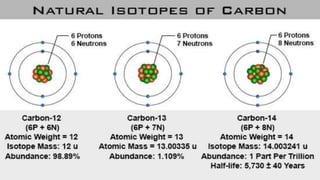
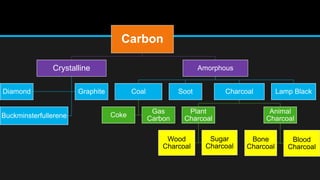
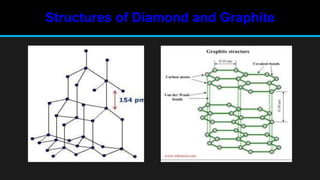
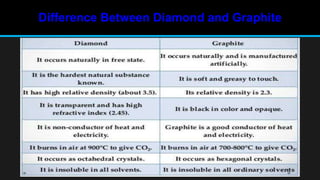
The document discusses carbon and its various forms and properties. It notes that carbon forms more compounds than any other element except hydrogen. It exists in several allotropes including diamond, graphite, and amorphous forms like coal and coke. The formation of coal from buried plant matter over millions of years is described. Different types of coal are classified based on their carbon content. The process of destructive distillation is outlined which produces gases, ammoniacal liquor, coal tar, and coke from coal.