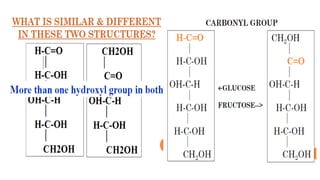
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone compounds that contain at least 3 carbon atoms and a carbonyl functional group that is either an aldehyde or keto group. They are defined as compounds that yield these derivatives upon hydrolysis. Carbohydrates serve important biomedical roles as the chief source of energy, constituents of lipids and proteins, and degradation products that act as promoters or catalysts. Inherited deficiencies in carbohydrate metabolic pathways can cause diseases like galactosemia and glycogen storage diseases.