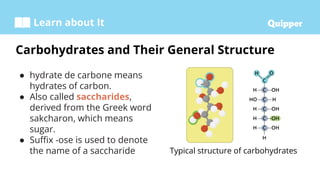
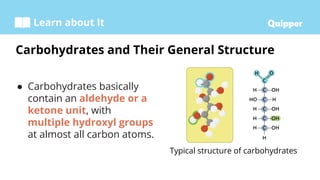
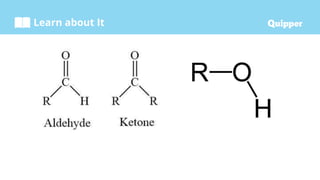
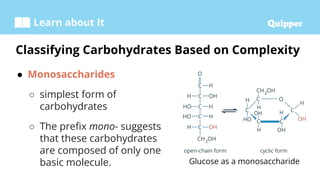
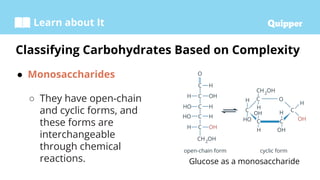
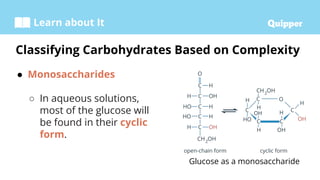
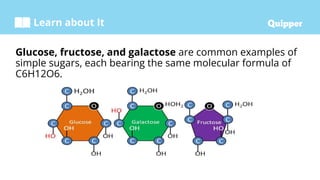
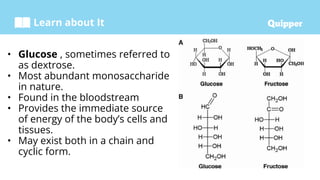
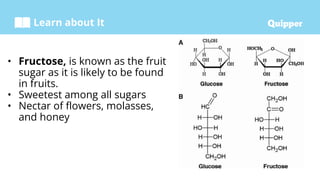
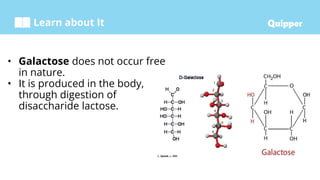
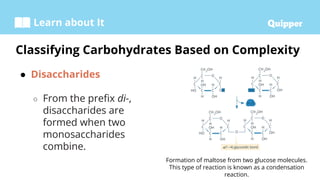
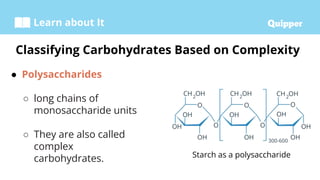
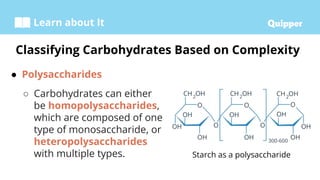
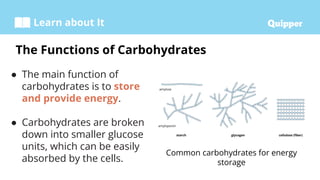
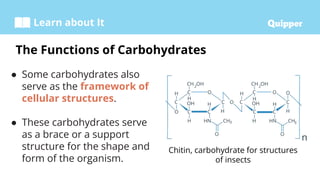
This document provides information about carbohydrates including their structure, types, and functions. It begins with an introduction to carbohydrates and explains that they are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It then discusses the three main types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. The document concludes by describing the key functions of carbohydrates, which include energy storage, forming cellular structures, and bonding to other molecules.