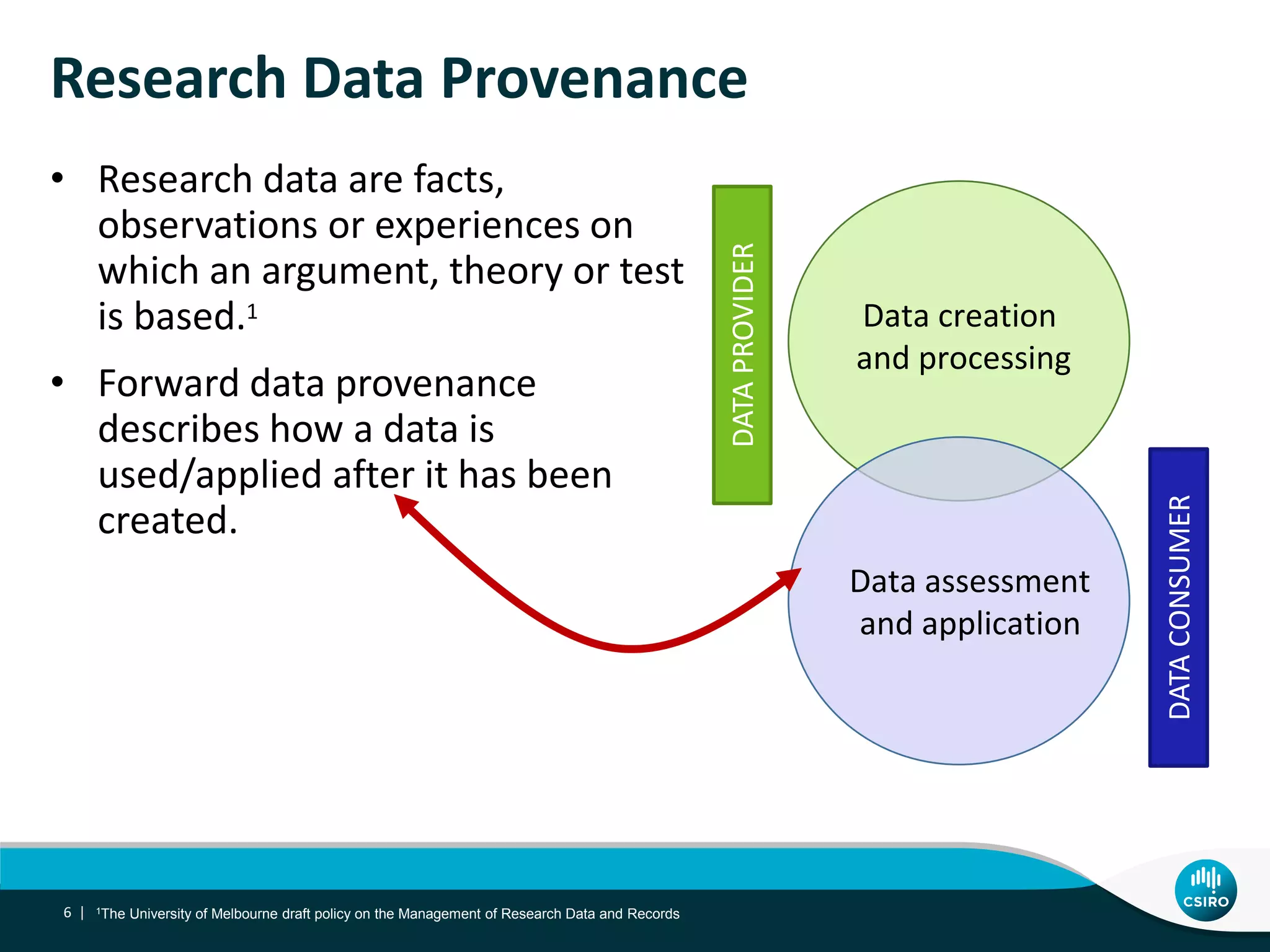
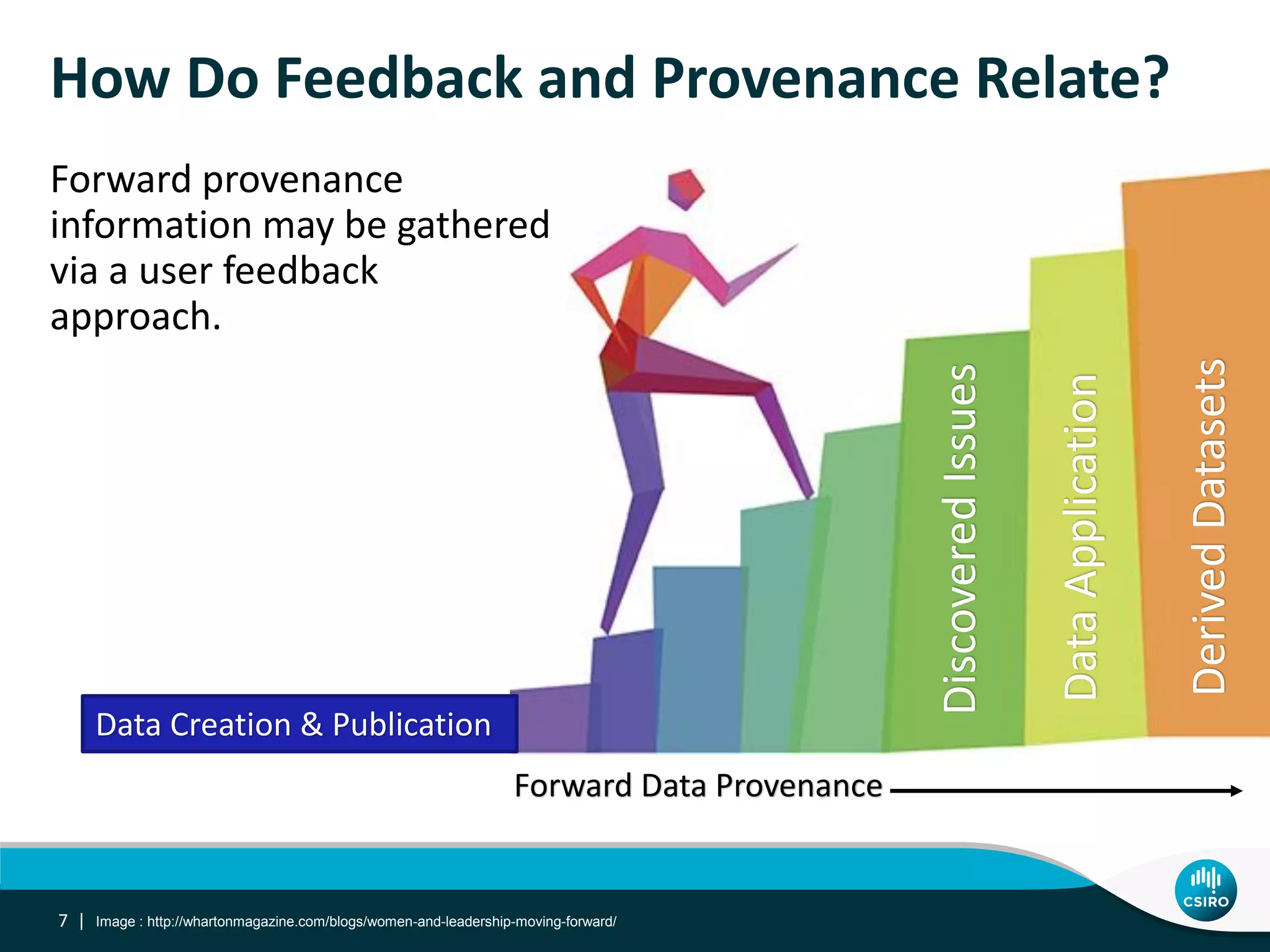
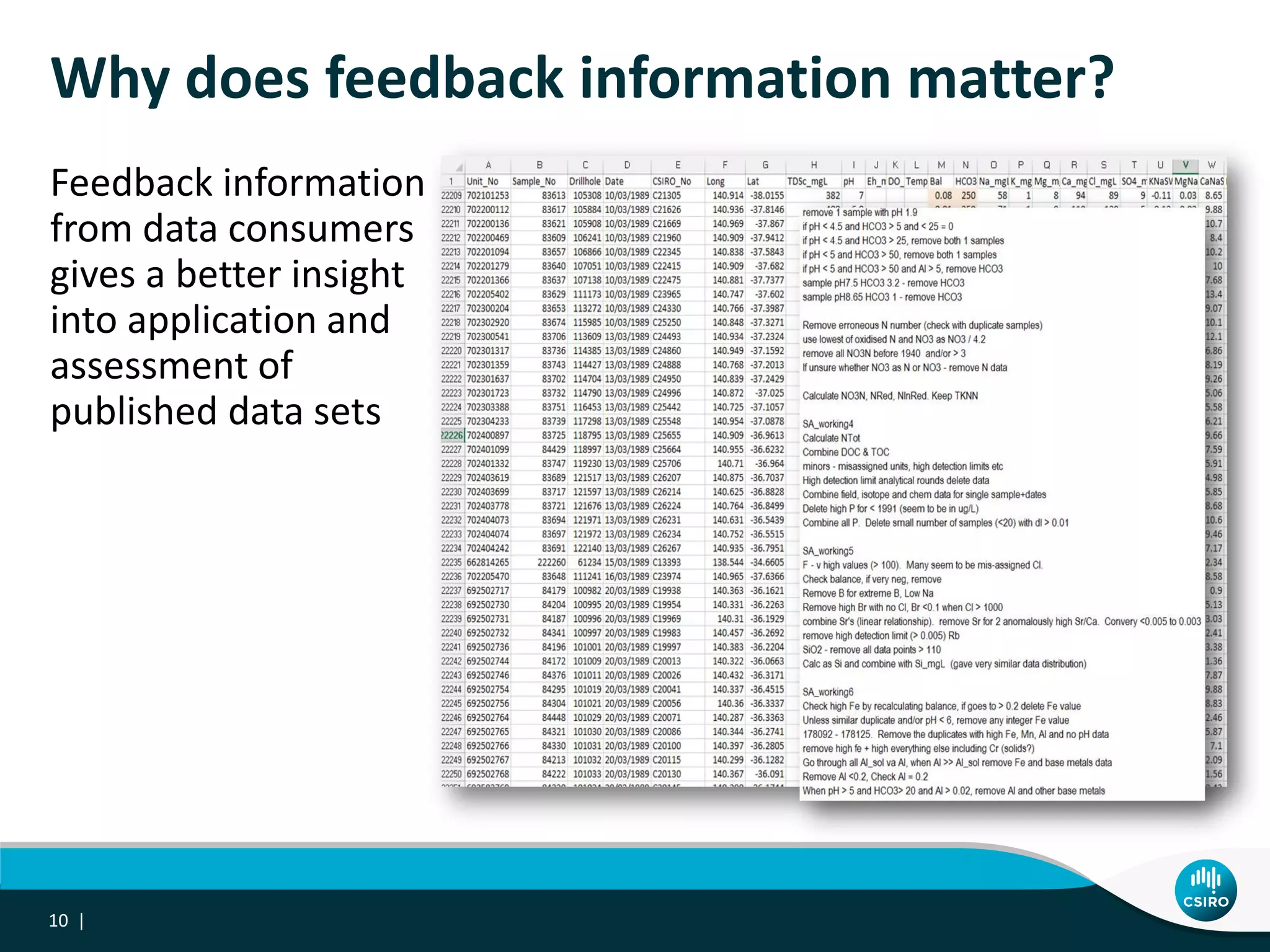
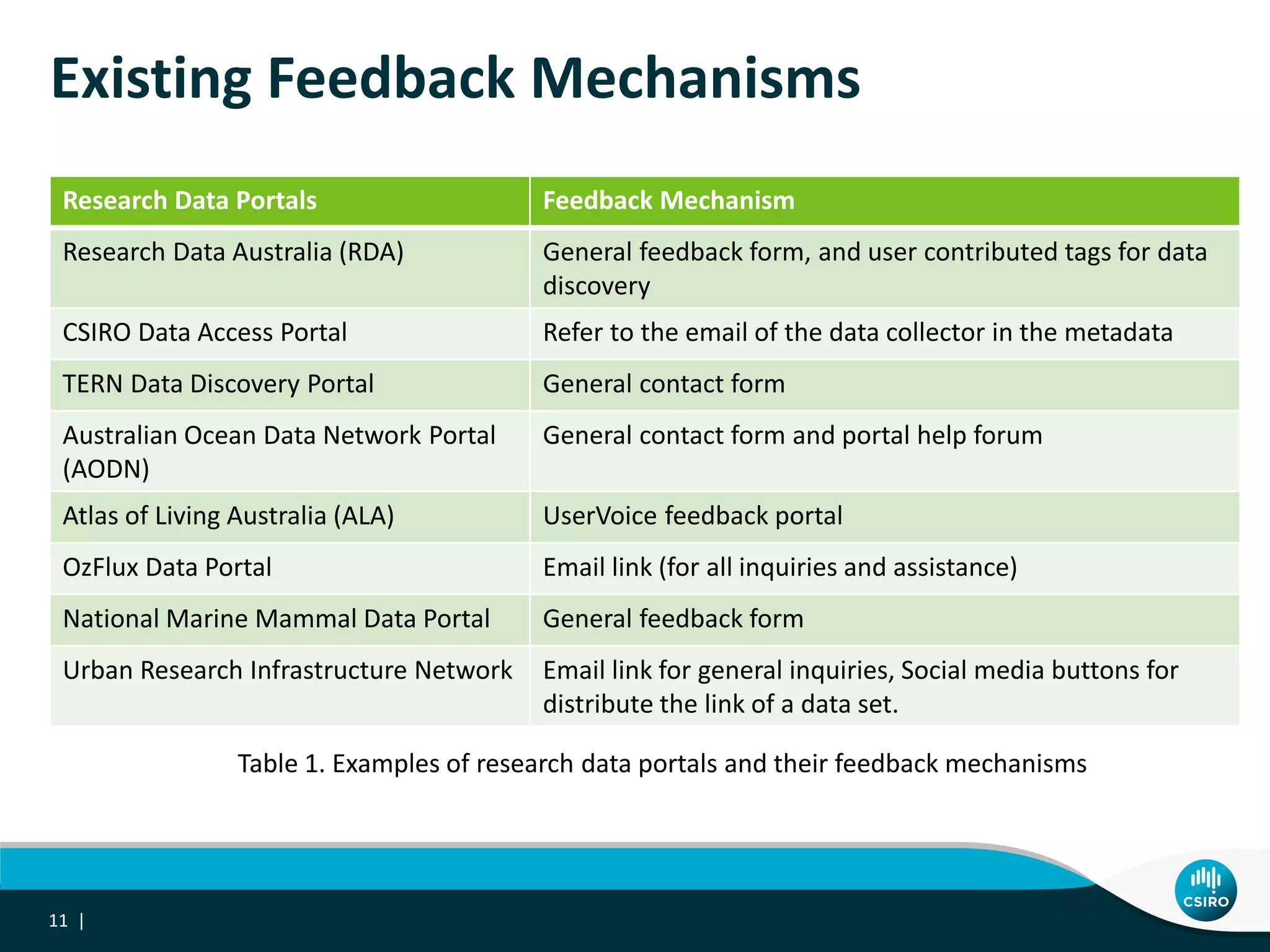
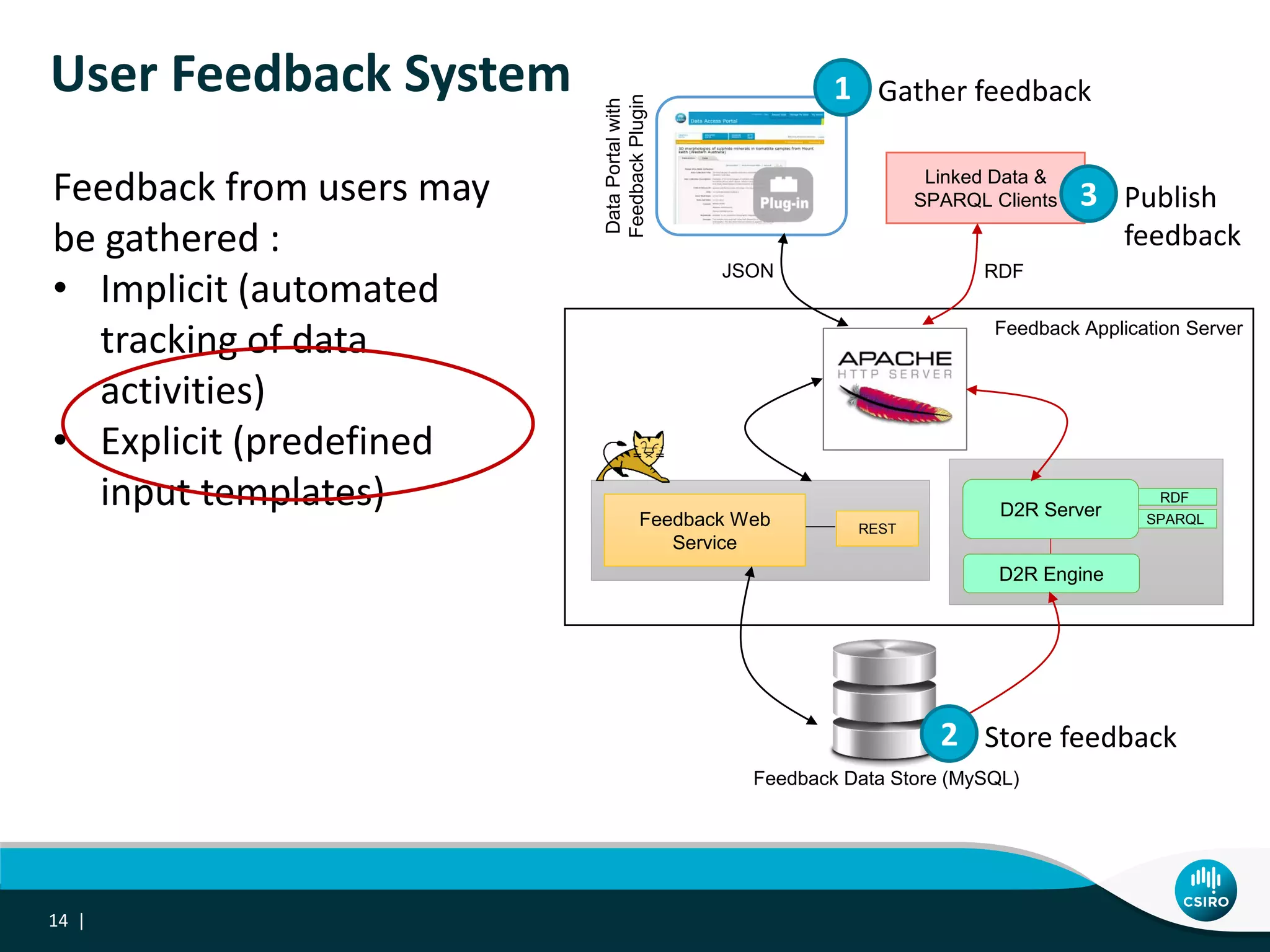
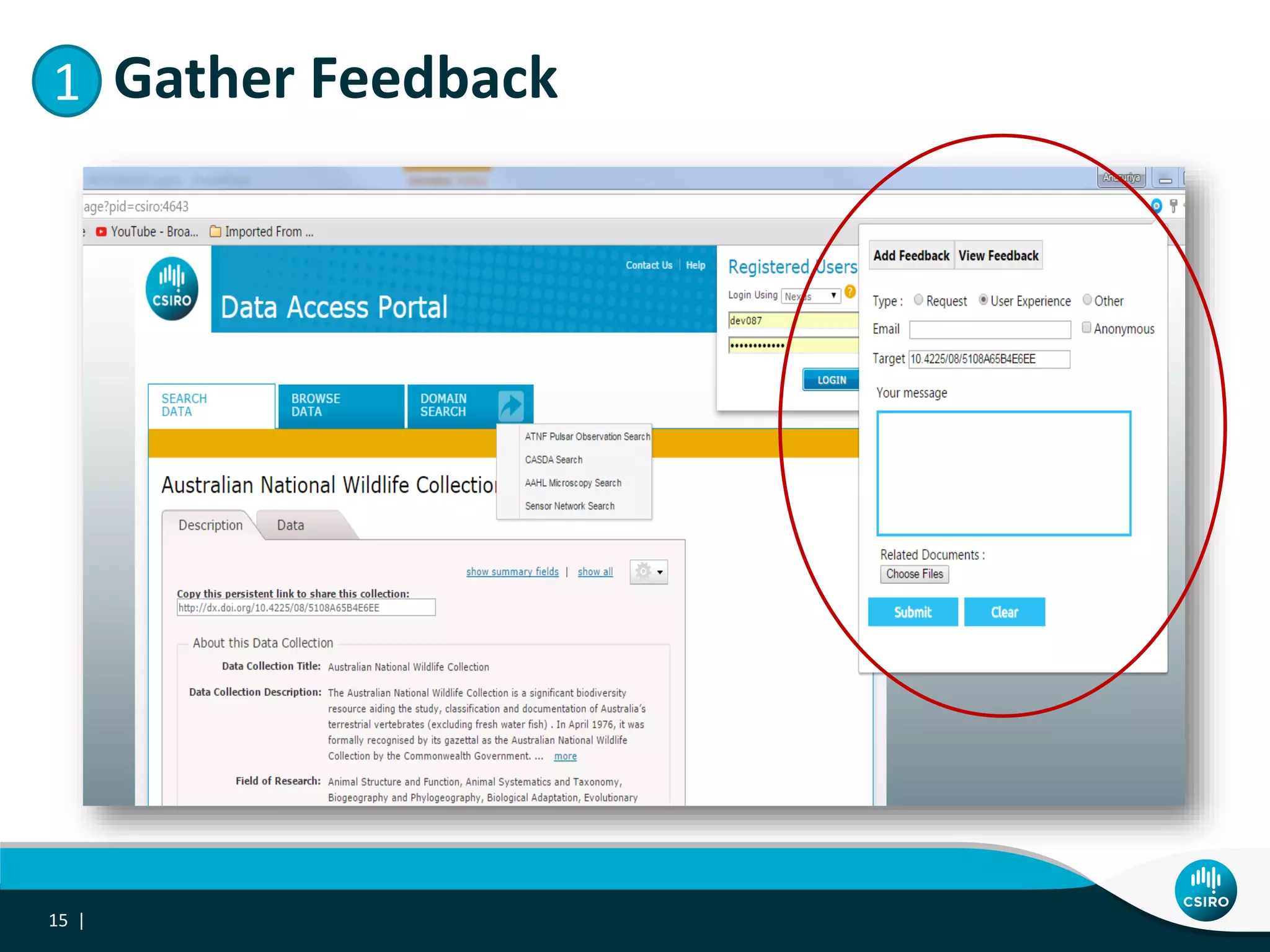
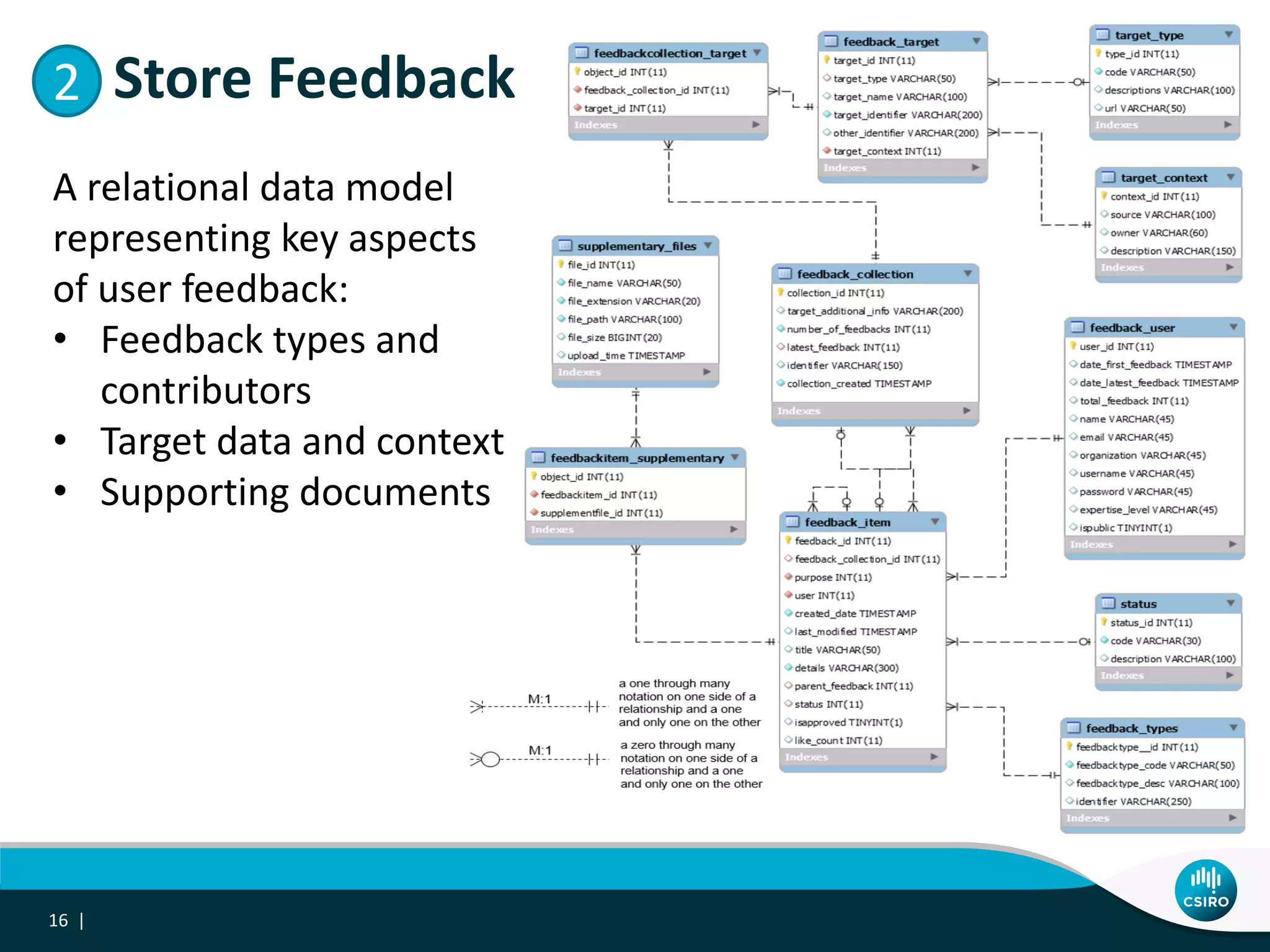
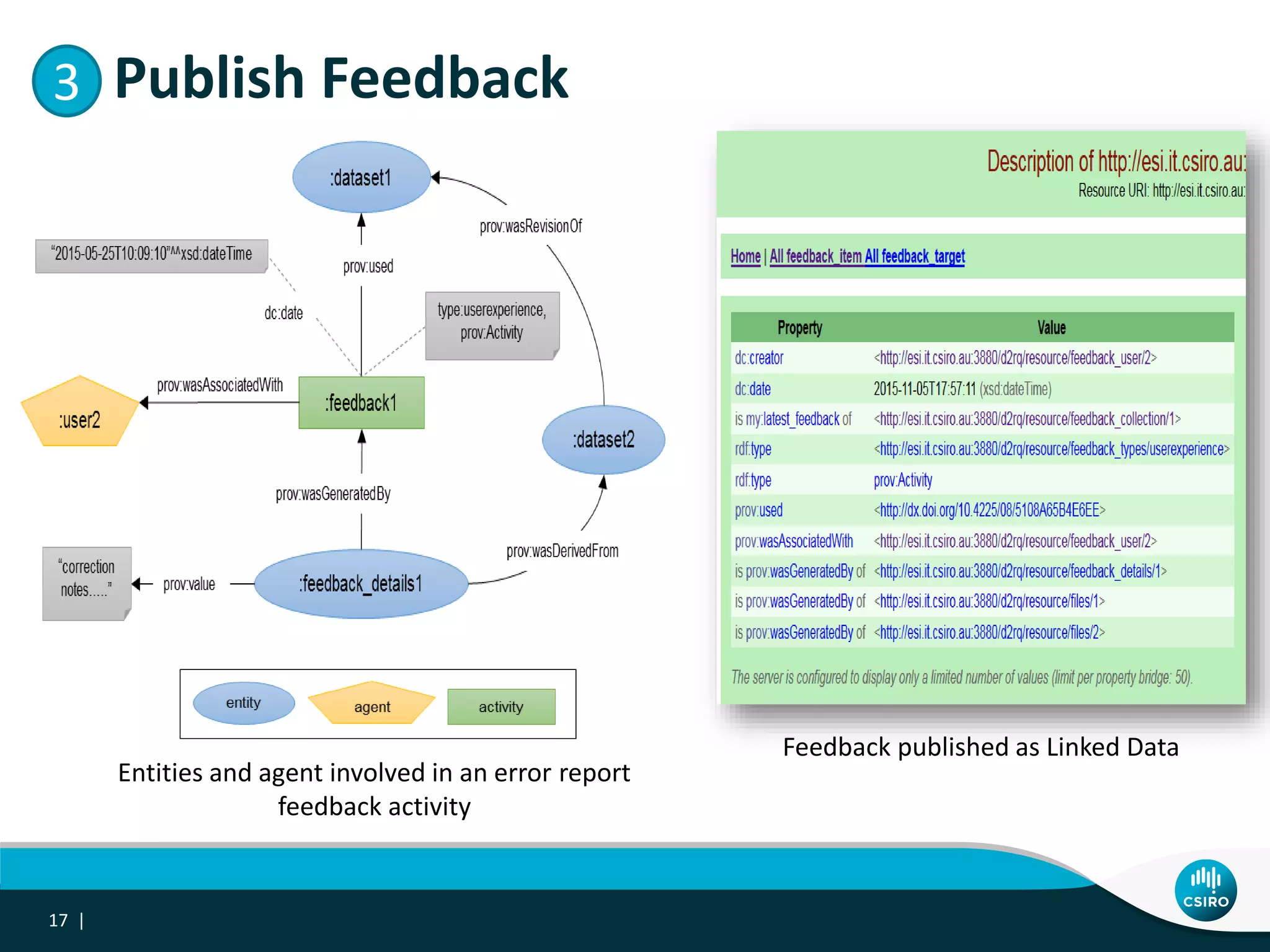
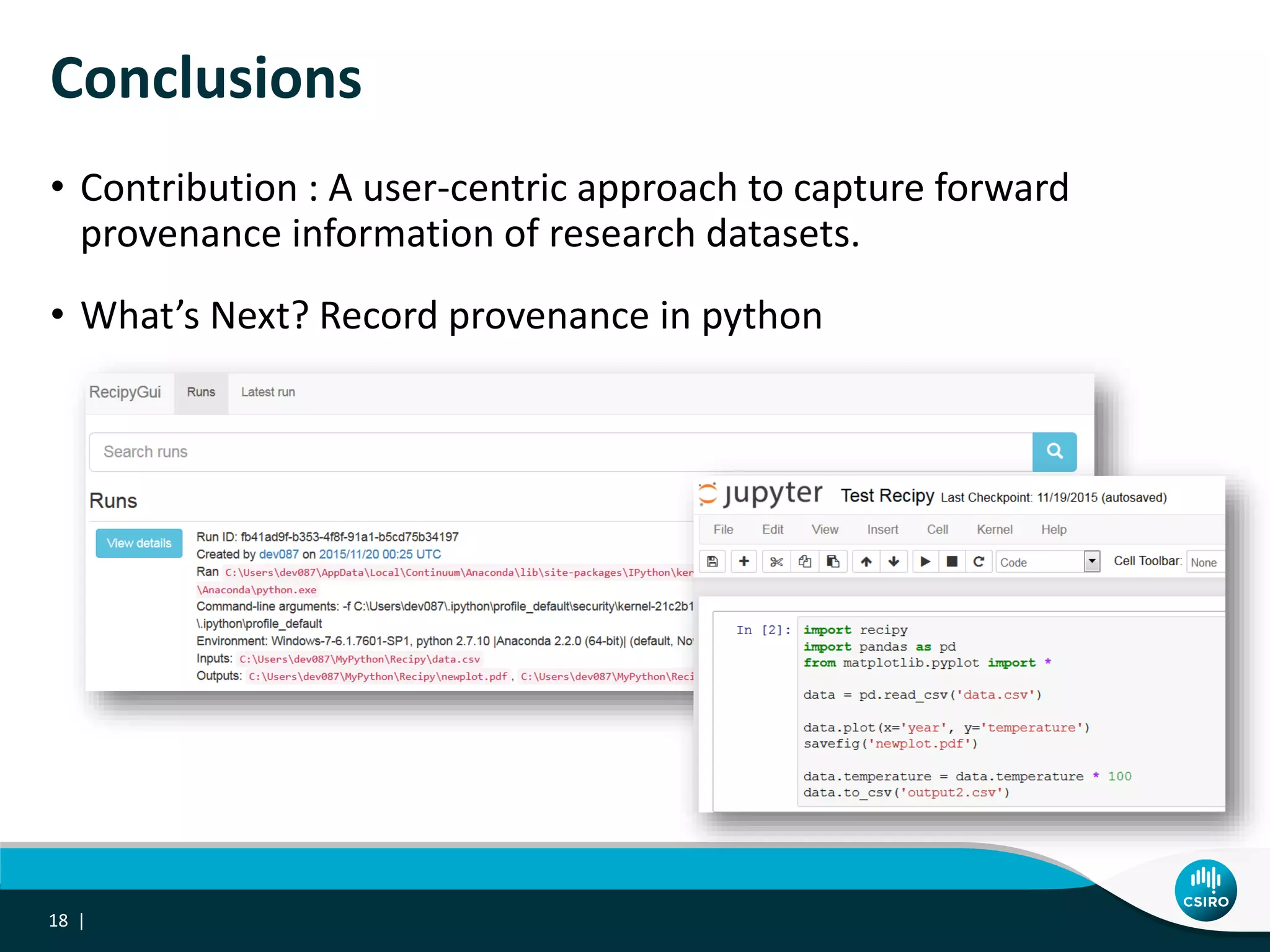
The document discusses the integration of user-driven feedback to capture data provenance in research, outlining essential definitions and types of feedback, as well as the importance of provenance in data management. It proposes a systematic approach to collect, link, and utilize feedback to improve data quality and discovery. The conclusions emphasize a user-centric method for capturing forward provenance information of research datasets.