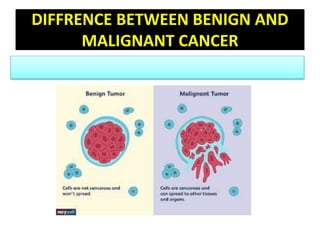
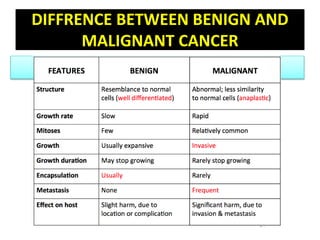
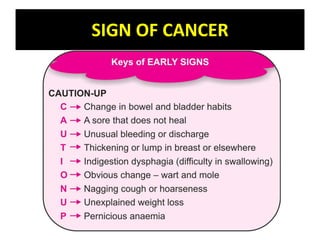
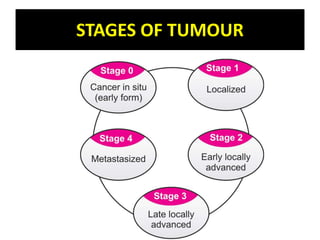
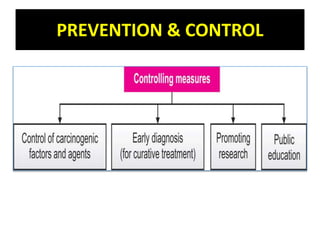
Cancer is an abnormal growth of cells that can be benign or malignant. It begins with genetic mutations in cell DNA. Some causes include viruses, chemicals, physical agents, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms vary depending on the affected system but may include weakness, weight loss, and pain. Diagnosis involves examinations, imaging tests, biopsies, and tumor marker tests. Cancer is staged based on tumor size and spread. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, and bone marrow transplants. Nursing care focuses on pre-operative teaching, pain management, promoting adjustment, and monitoring for complications.