Camera calibration is the process of determining a camera’s internal and external parameters so it can accurately map 3D real-world points to 2D image coordinates. It helps correct lens distortion, estimate focal length, and align the camera’s coordinate system with the physical world. Calibration improves measurement accuracy, object detection, and overall computer vision performance.
![Camera Calibration
W
X
W
Y
W
Z
Object Space Image Space
xc
yc
M
m
m = [Camera Projection Matrix] M
A [R t]
camera intrinsics extrinsics
f x
f y
f x
alpha* ox
oy
0
0 0 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-2-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration
W
X
W
Y
W
Z
Object Space Image Space
xc
yc
M
m
m = [Camera Projection Matrix] M
A [R t]
camera intrinsics extrinsics
f x
f y
f x
alpha* ox
oy
0
0 0 1
• Camera calibration is about
finding the camera intrinsics
• But, why do we need them?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
• ICCV Zhang’99: “Flexible Calibration by
Viewing a Plane From Unknown Orientations”
m = [Camera Projection Matrix] M
A [R t]
observed
estimate: A [R t] M
Minimize:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-5-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
• ICCV Zhang’99: “Flexible Calibration by
Viewing a Plane From Unknown Orientations”
m = [Camera Projection Matrix] M
A [R t]
observed
estimate: A [R t] M
Minimize:
• Two steps:
• Find an initial solution
for A [R t]
• Minimize the objective function
using the initial solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
• Finding an initial solution
– First step
• Estimate the image homography matrix H for each image
[u, v, 1]T
x is the eigenvector of LT
L
with smallest eigenvalue
Initial solution for minimization:
Minimize:
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-7-2048.jpg)
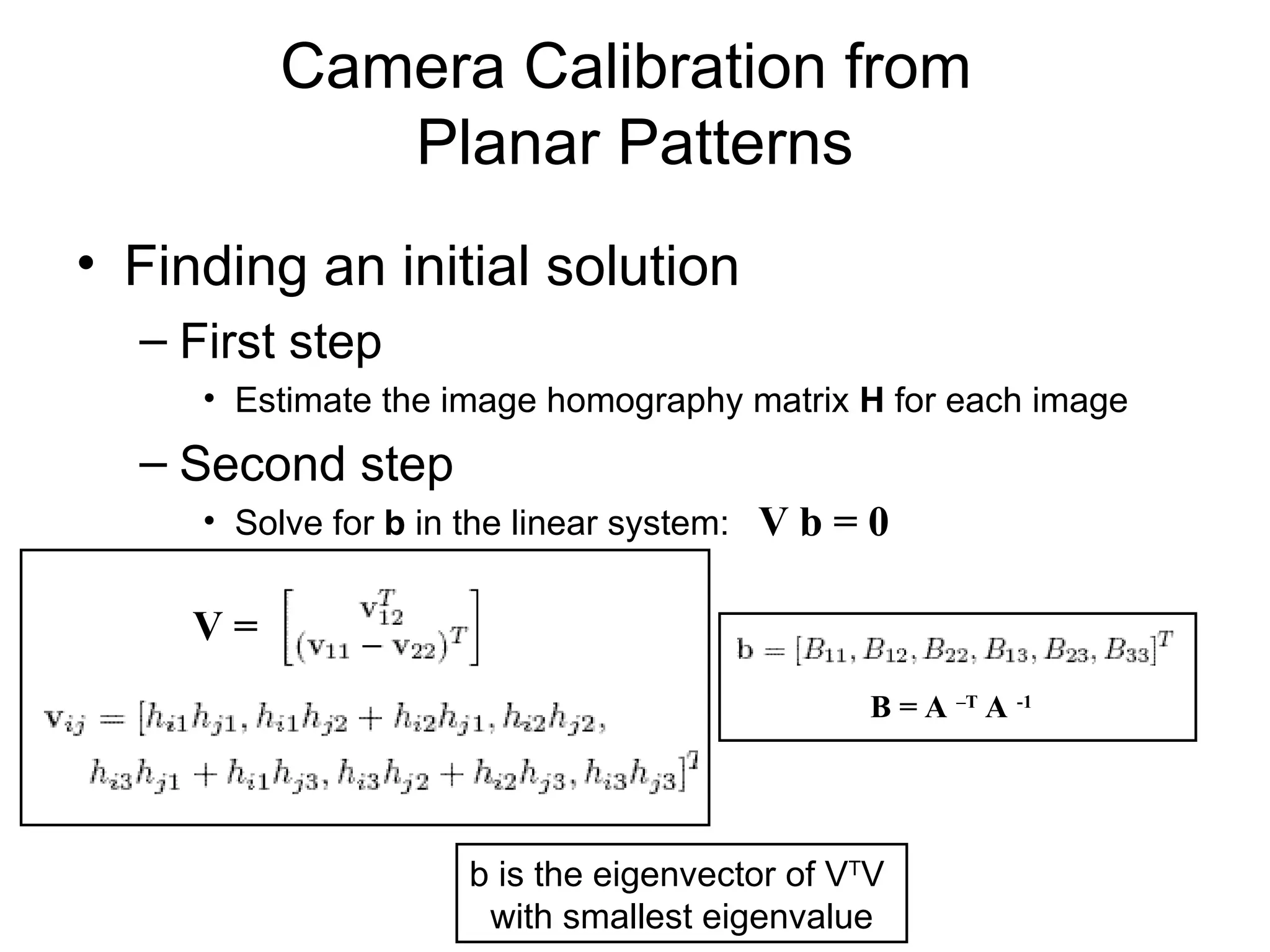
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
• Finding an initial solution
– First step
• Estimate the image homography matrix H for each image
– Second step
• Solve for b in the linear system:
• b yields the intrinsic parameter matrix A.
Rotation matrix [r1 r2 r3] and translation t is computed from:
V b = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-9-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
• Finding an initial solution
– First step
• Estimate the image homography matrix H for each image
– Second step
• Solve for b in the linear system:
• b yields the intrinsic parameter matrix A.
Rotation matrix [r1 r2 r3] and translation t:
• But the computed rotation matrix does not satisfy the properties of
rotation matrix: RT
R=RRT
=I.
One can it enforce by: min||Rnew - R||,
[U D V] = SVD(R),
Rnew = UVT
V b = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-10-2048.jpg)
![Camera Calibration from
Planar Patterns
m = [Camera Projection Matrix] M
A [R t]
observed
estimate: A [R t] M
Minimize:
• Two steps:
• Find an initial solution
for A [R t]
• Minimize the objective function
using the initial solution
use “lsqnonlin” in Matlab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camcal-251125163847-5dc3c4cb/75/cameraCalibrationpowerpointPresesntation-ppt-11-2048.jpg)