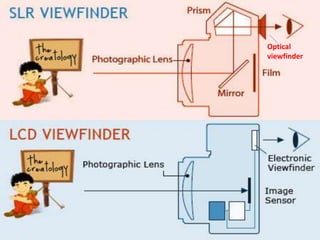
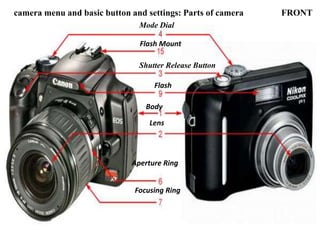
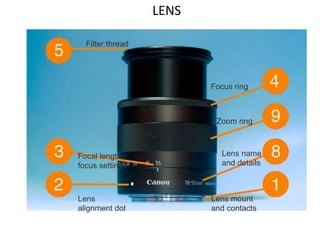
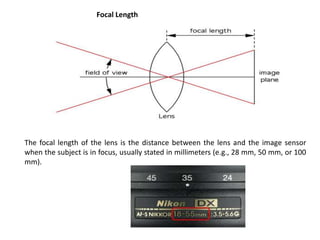
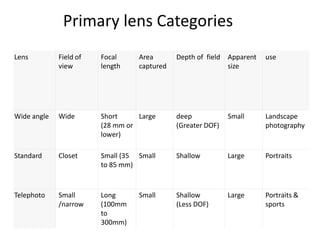
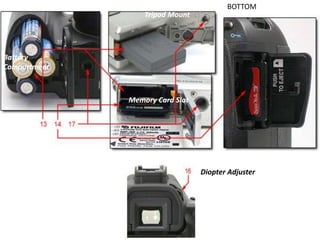
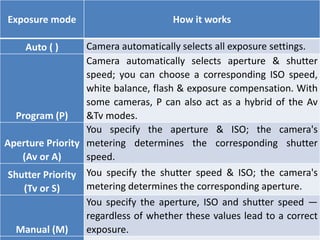
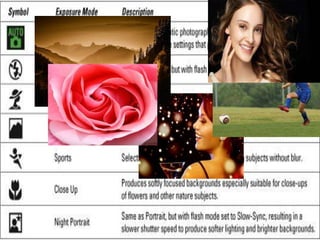
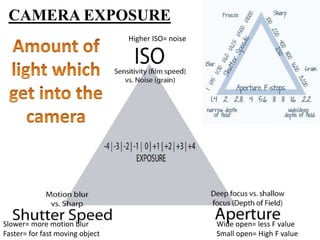
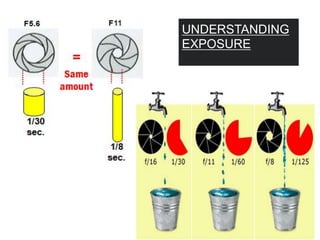
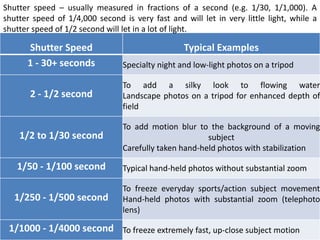
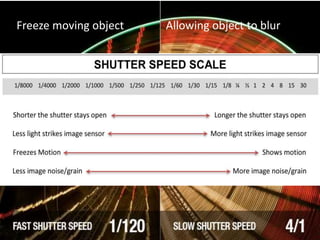
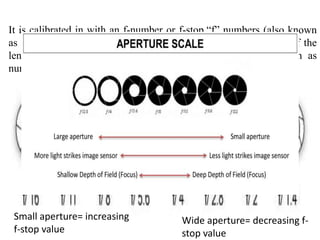
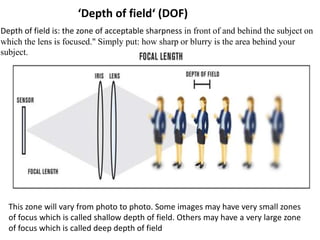
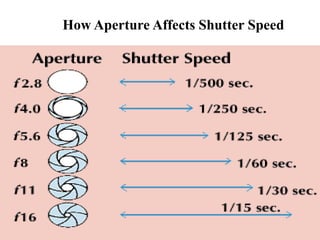
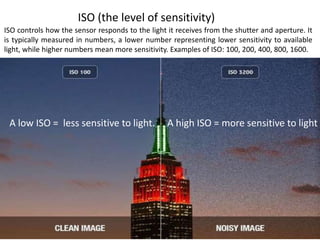
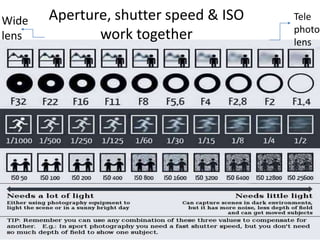
The document provides an extensive overview of photography fundamentals, including types of cameras, basic camera settings, exposure control, and lens types. It explains essential concepts like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO, detailing how they interact to achieve desired photographic effects. Additionally, it covers camera accessories, care, and tips for optimal photographic results.