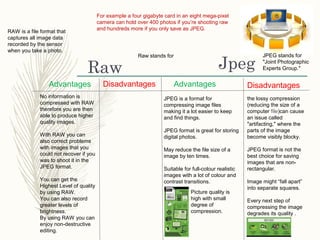
This document provides information on manual camera modes and functions. It discusses the benefits of manual mode, including having independent control over aperture and shutter speed. It also lists some of the best times to use manual mode, such as when lighting conditions are consistent or changing drastically. The document then provides brief explanations of various camera functions and components, including the viewfinder, different lens types, the image sensor, aperture, memory storage, and file formats like JPEG and RAW.