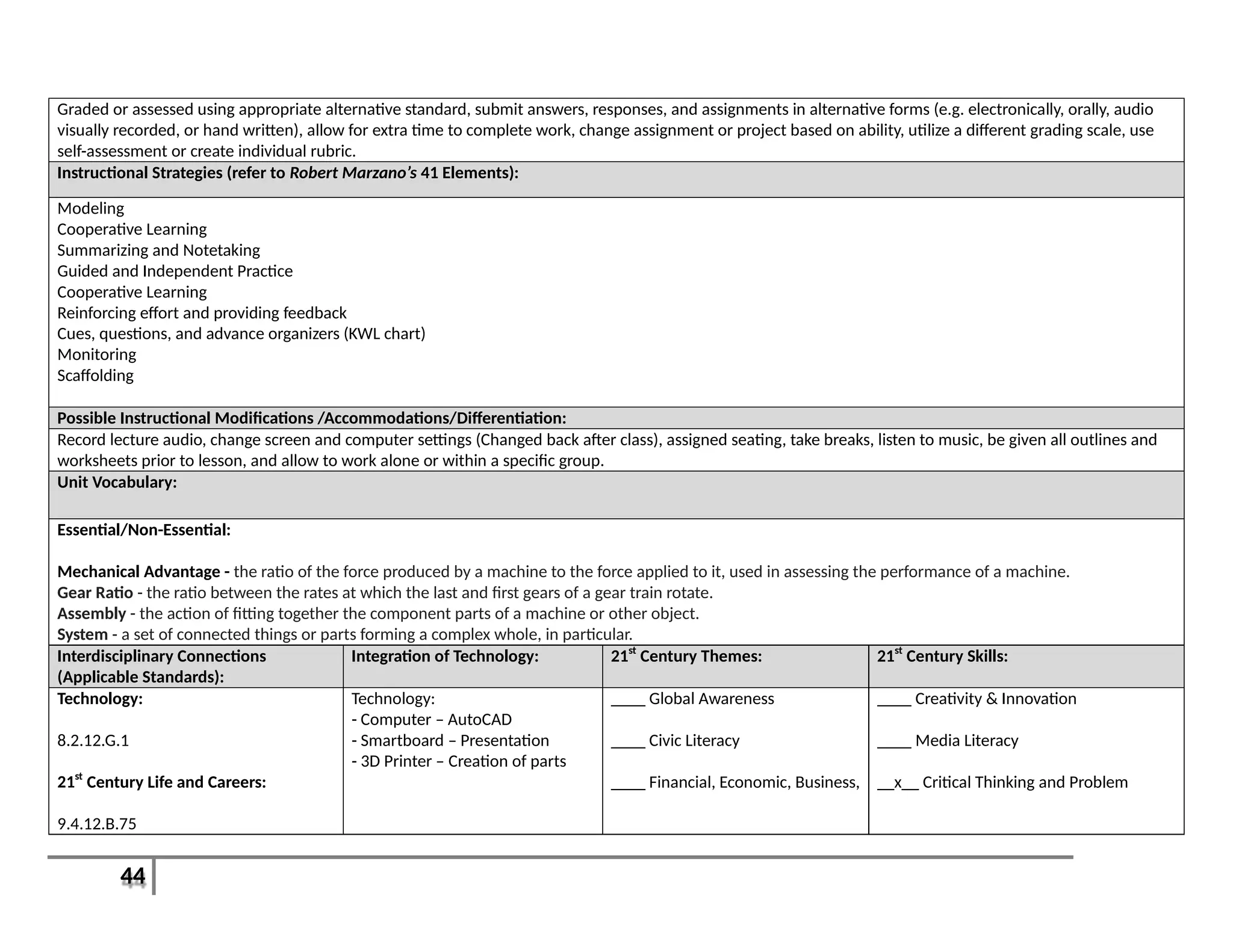
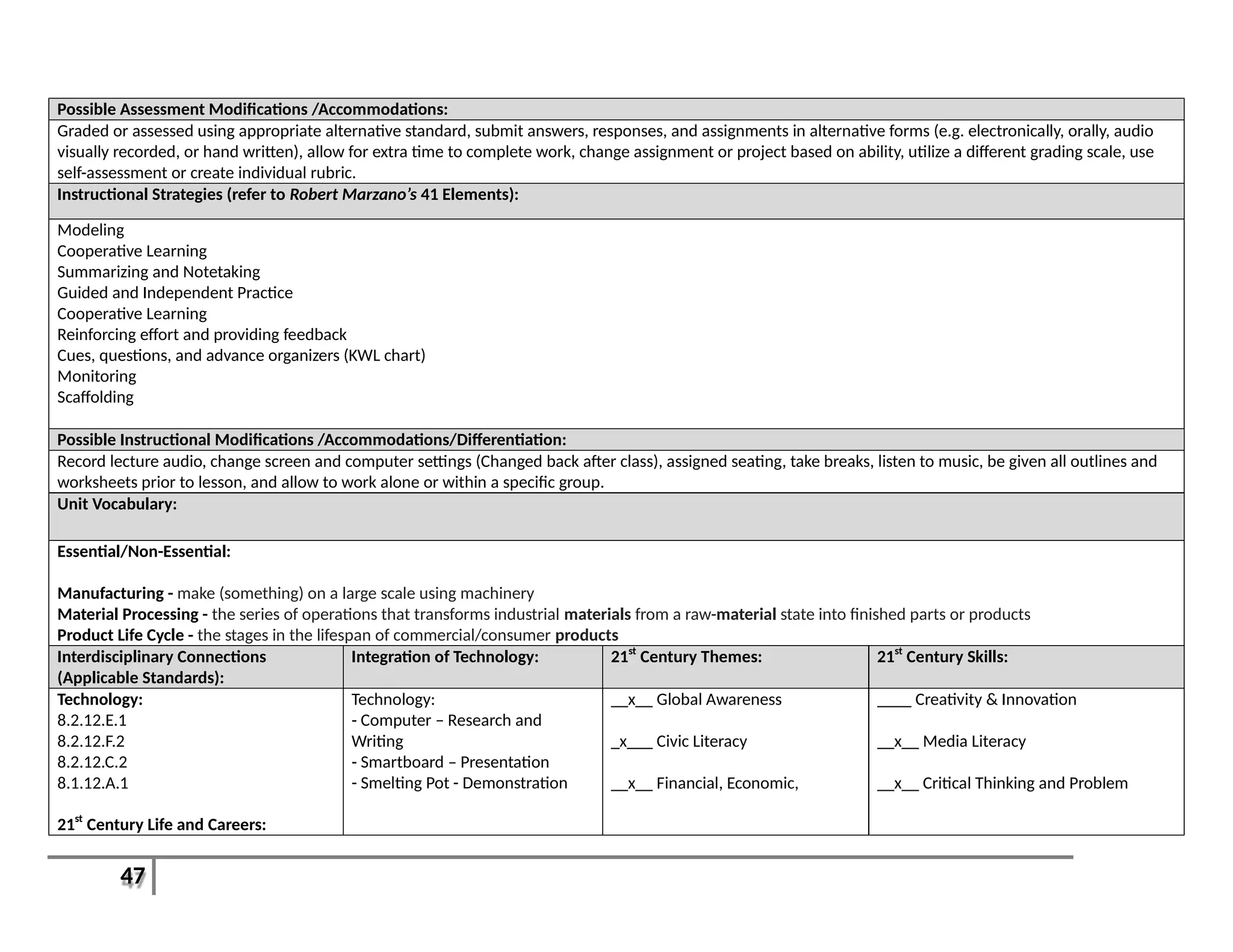
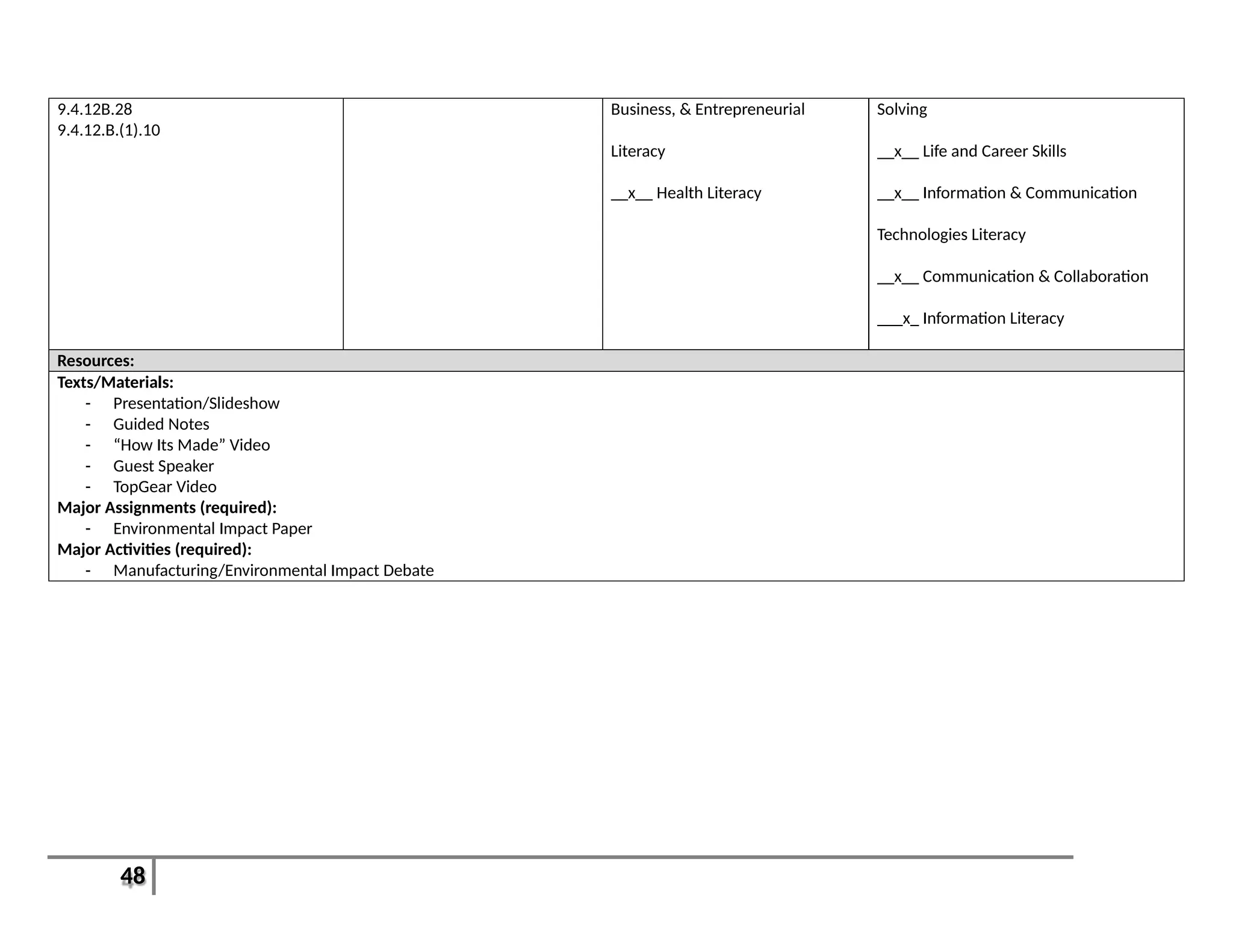
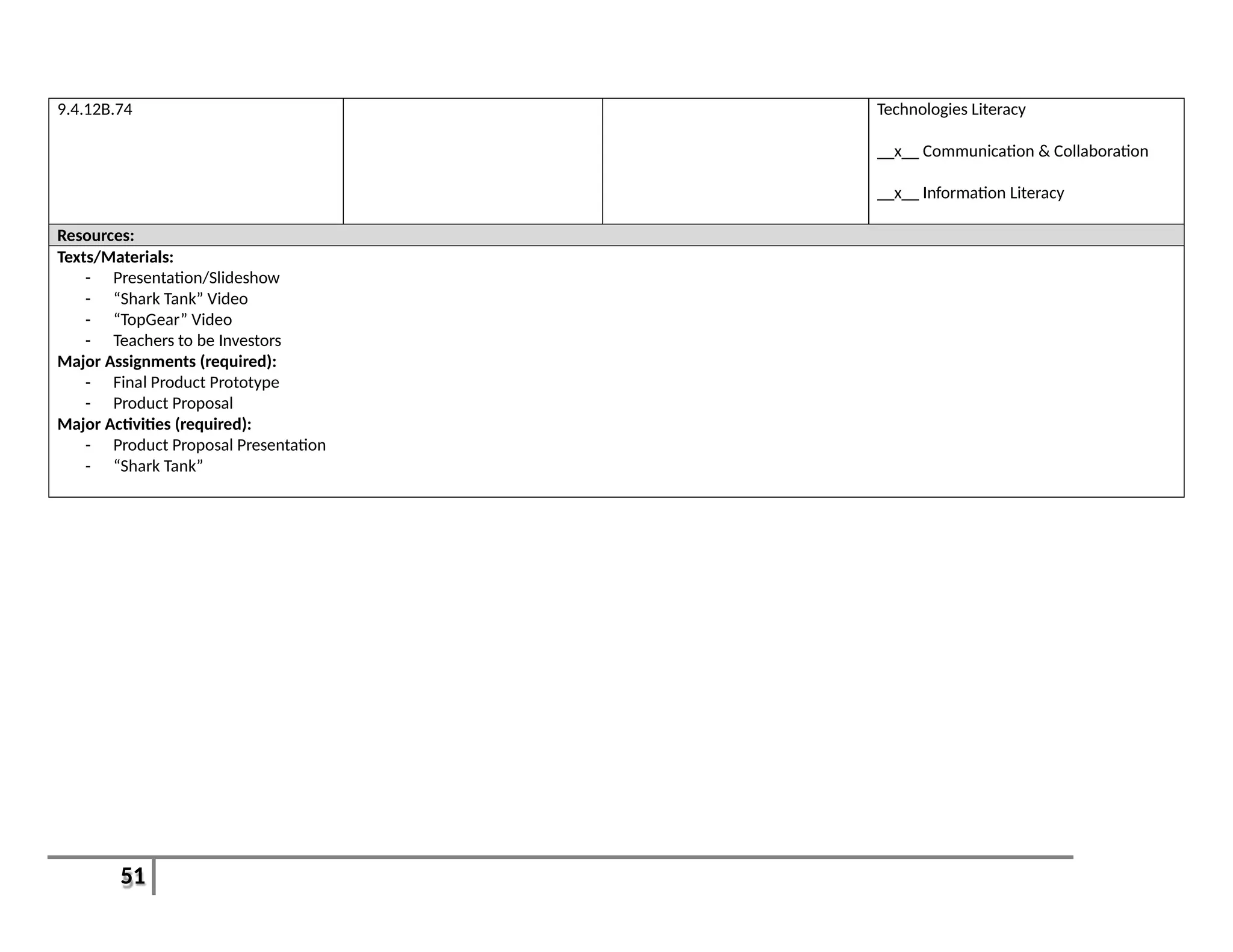
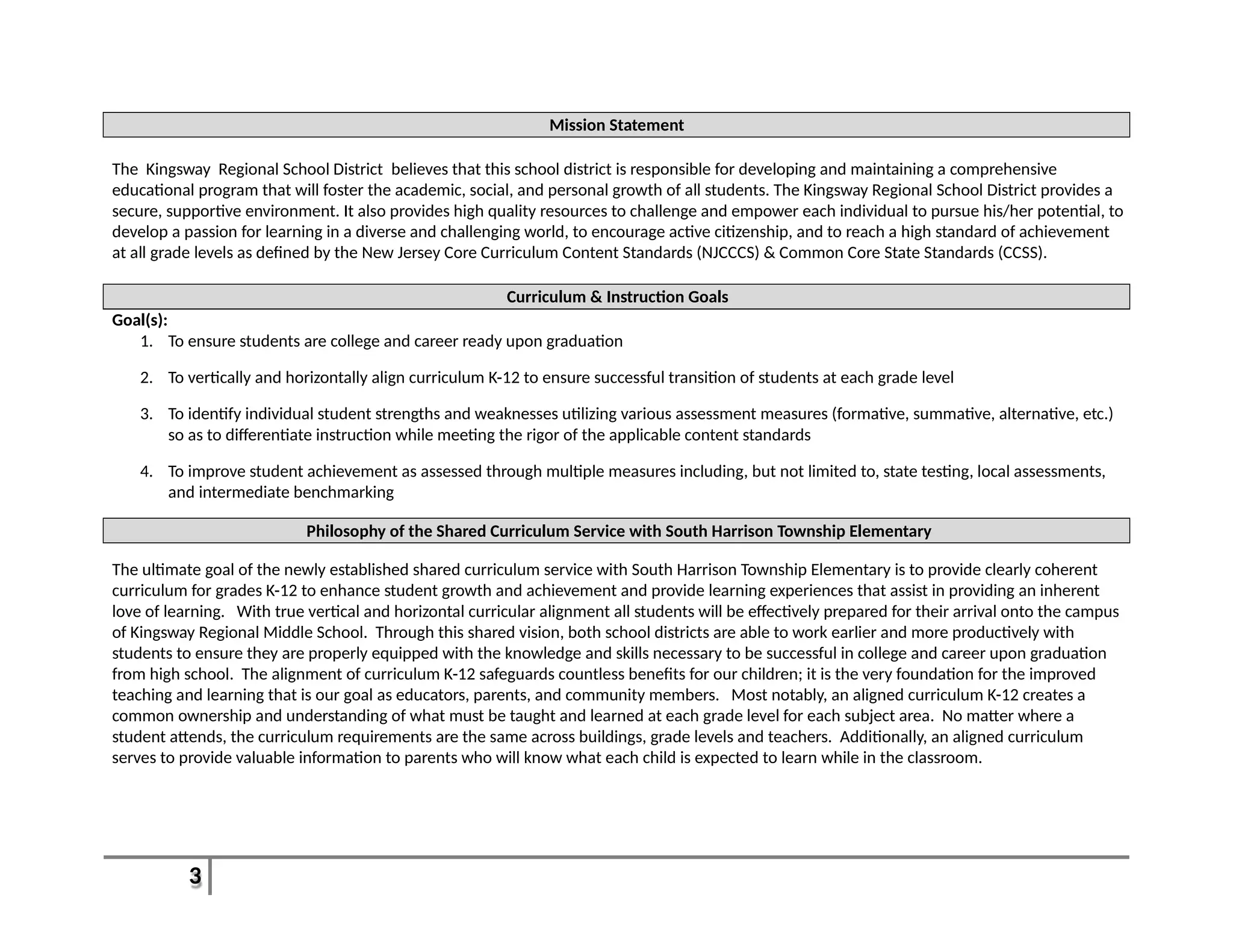
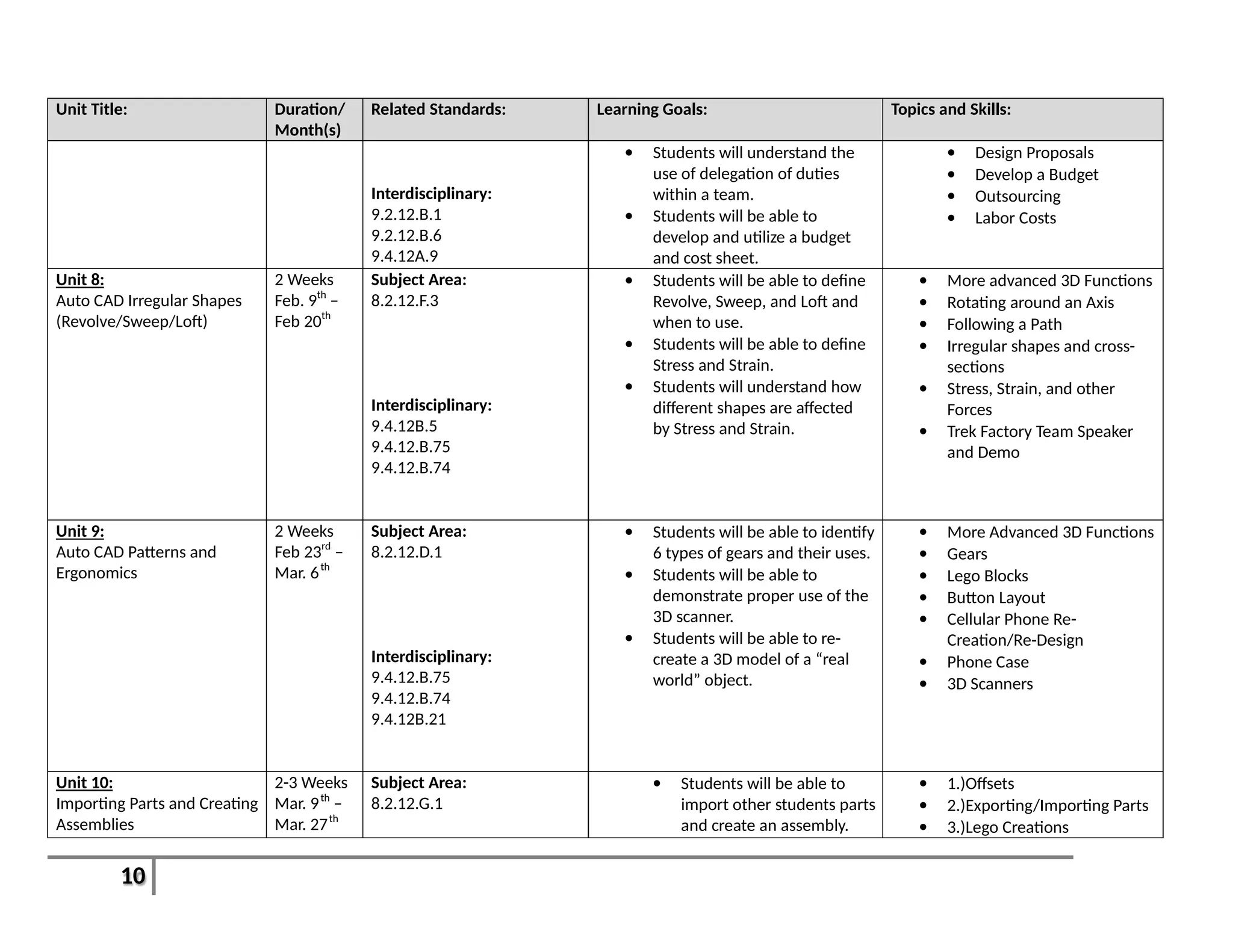
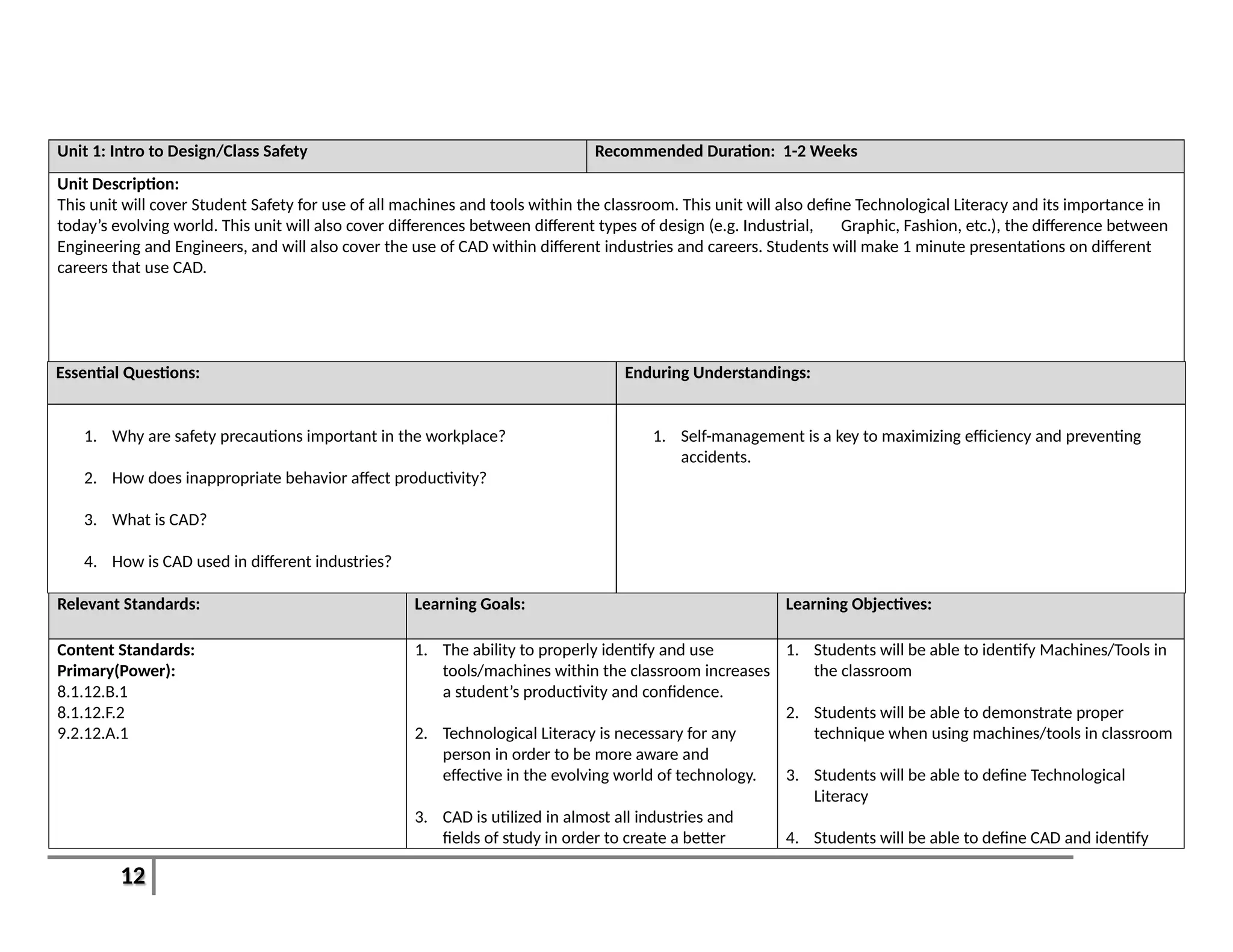
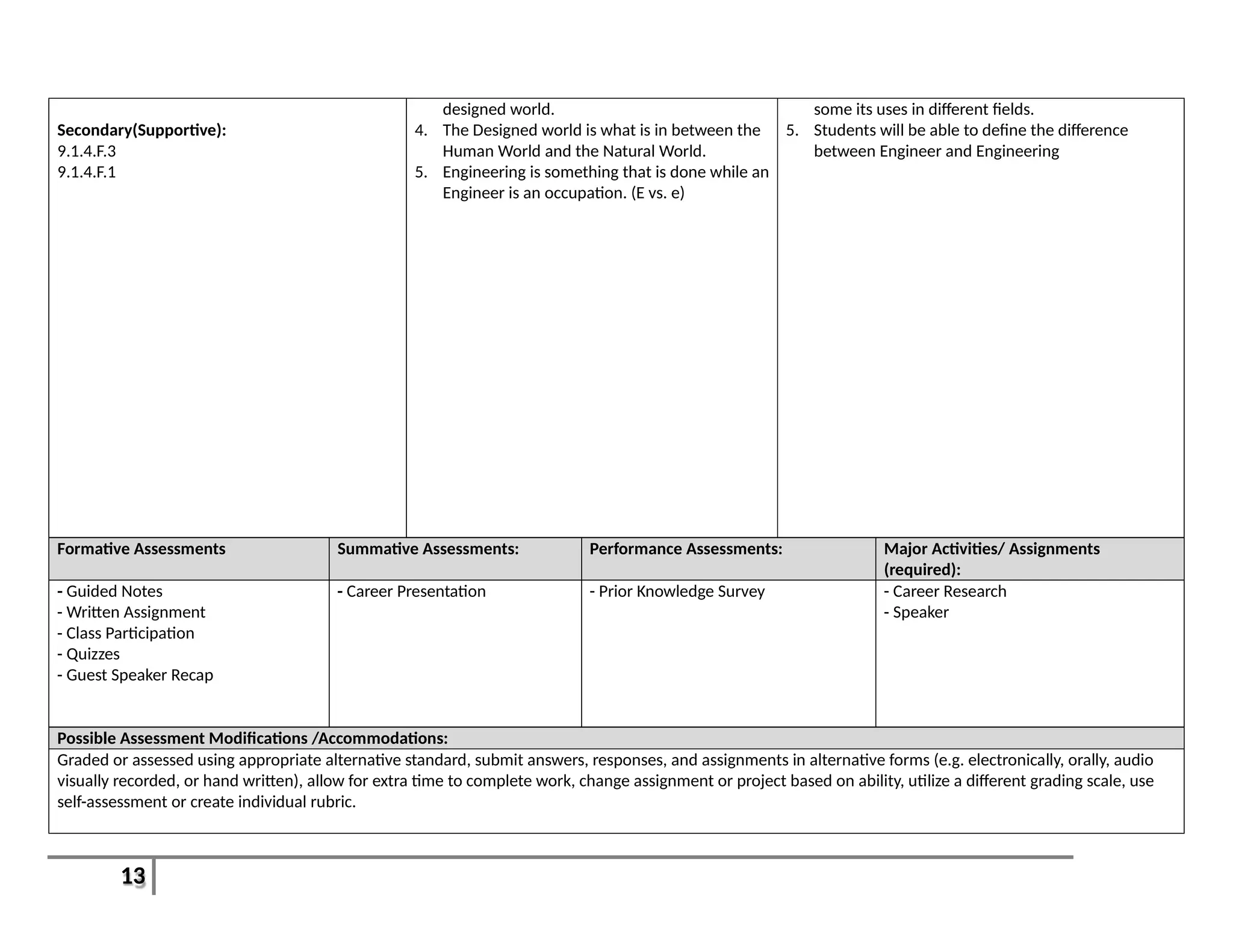
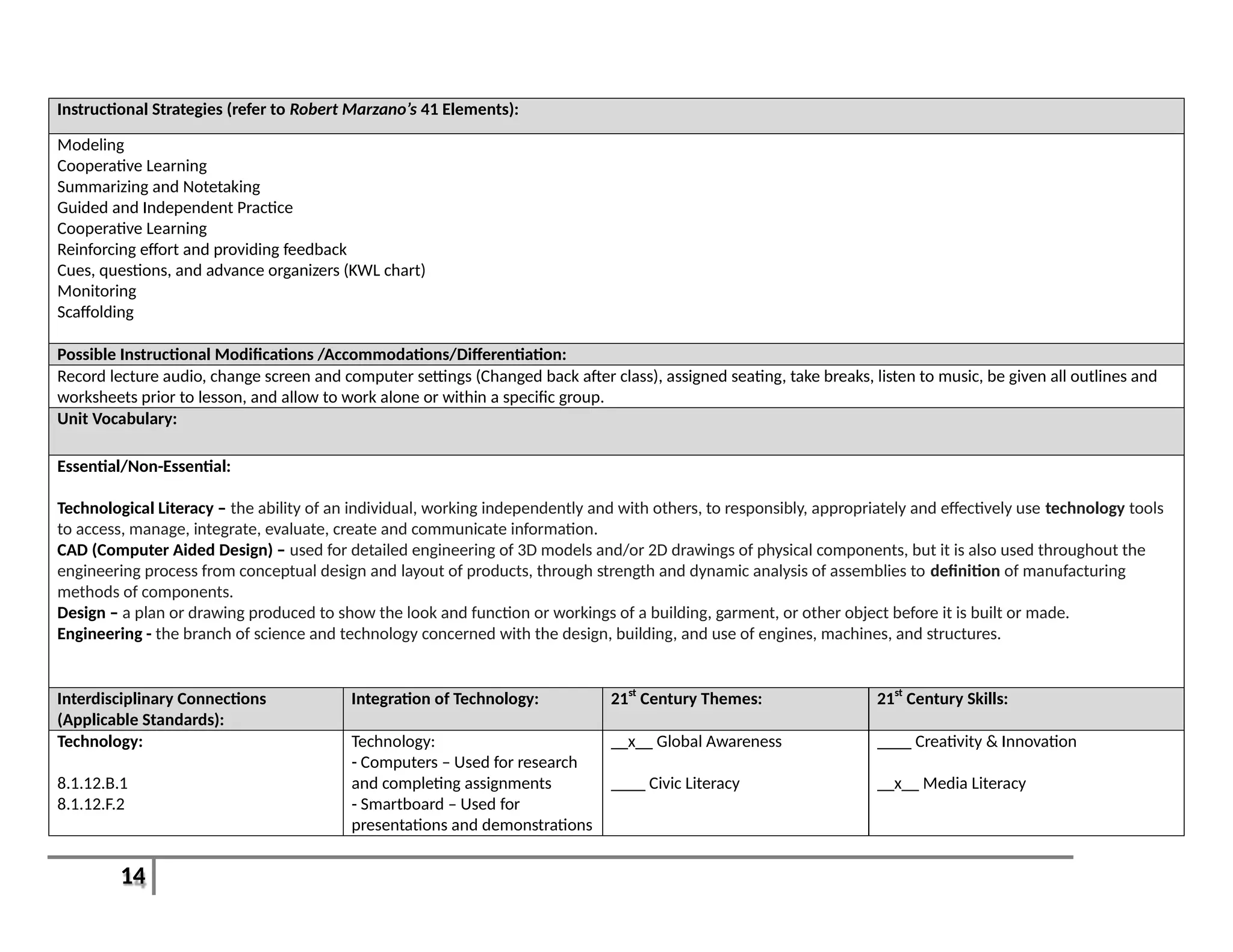
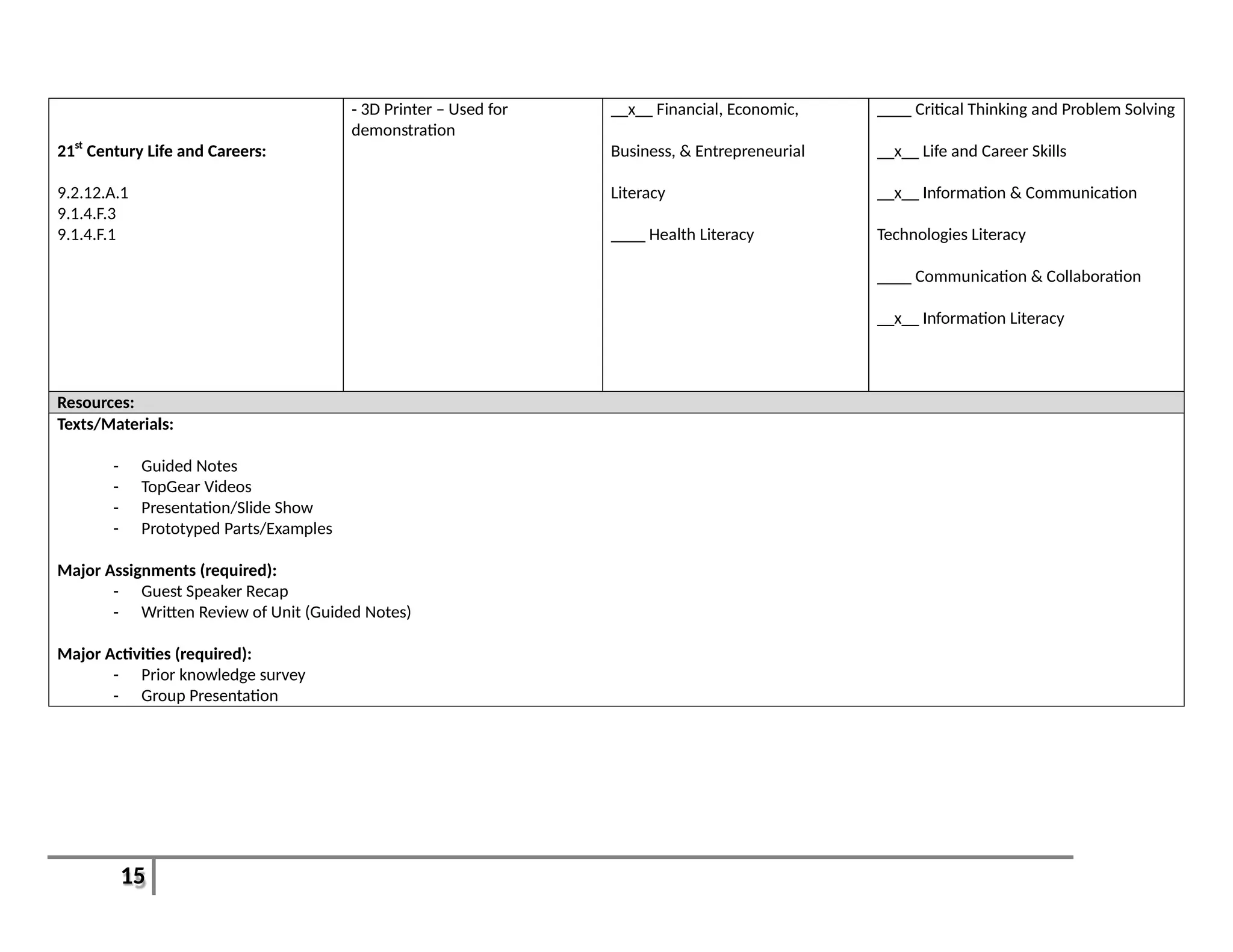
This document provides an overview of the Introduction to Computer Aided Design I (CAD I) course for grades 9-12. The course is designed to teach students how to use AutoCAD software to model construction projects and create basic 2D and 3D drawings. The pacing guide outlines 8 units that will be covered over the school year, including introductions to 2D and 3D modeling in AutoCAD, architectural drawing, 3D printing, and more. Students will develop skills in areas such as technical drawing, modeling, prototyping, and applying the design process. The overall goals are for students to understand how CAD is used in various fields and be prepared for further education in related areas.









![16
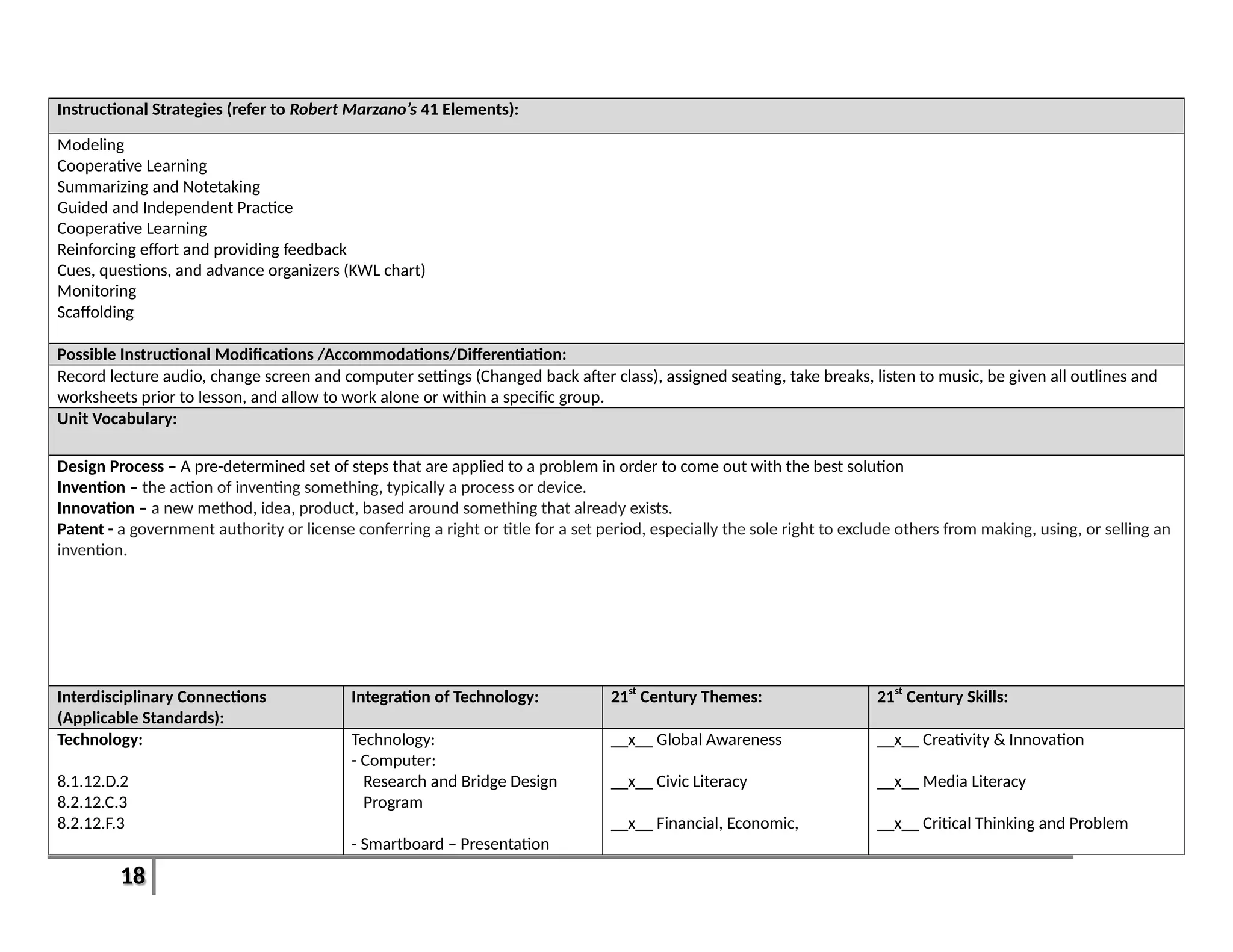
Unit 2: Using the Design Process Recommended Duration: [2-3 Weeks]
Unit Description:
This unit will go through the 7-9 steps of the Design Process and how they are used in problem and project based learning scenarios. This unit will cover the
differences between inventions and innovations and how copyright law and patents play a part. We will discuss reverse engineering and intellectual property.
Students will also be instructed on how to use their Engineering Notebook/Journal for the remainder of the year. This will end with a bridge building
competition to establish team work and student’s roles and relationships within the classroom.
Essential Questions: Enduring Understandings:
1. What are the components of the Design Process?
2. Who uses the Design Process and how does it change?
3. What are some organizational skills?
4. What are the benefits and disadvantages of working in a group instead of
individually?
1. The Design Process is a series of steps taken in order to create a product or
solve a problem.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cadrubrics-190602070825/75/Cad-rubrics-16-2048.jpg)





![27
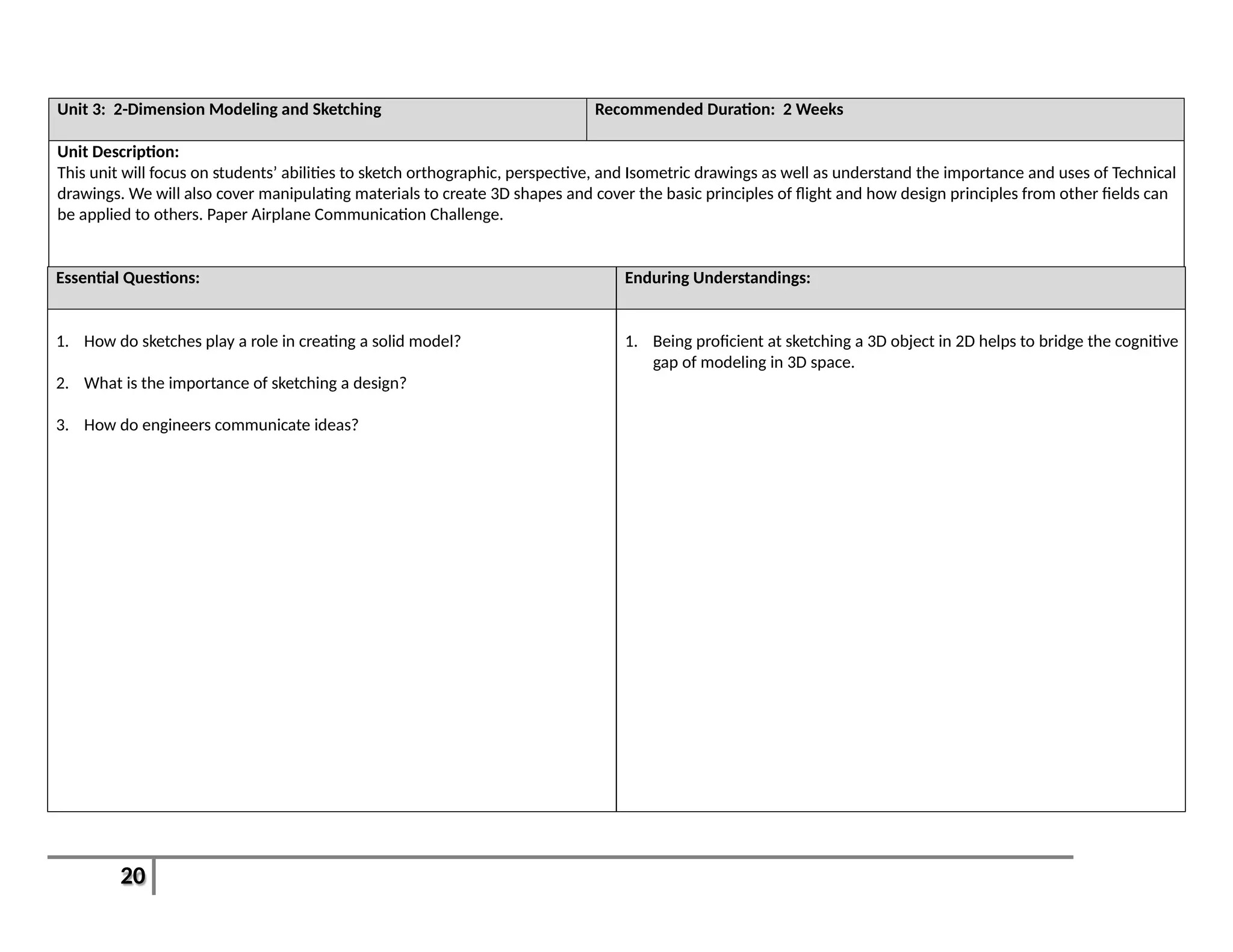
Unit 5: Architecture Recommended Duration: [4-5 Weeks]
Unit Description:
This unit will cover the field of Architecture and how Design plays a role. Students will learn about basic Architectural Styles and parts of a standing structure.
Students will create floor plans and understand how traffic patterns and workflow inspire design. Students will create a scale addition to the high school and
have a printed floor plan to match with exterior features. They will also work on landscape and environmental design around the school.
Essential Questions: Enduring Understandings:
1. How are design and style related?
2. What characteristics are essential to a functional team?
3. Why is time management important?
4. What is efficiency?
1. Innovation in digital tools and products are utilized to aid and simplify
work and maximize efficiency.
Relevant Standards: Learning Goals: Learning Objectives:
Content Standards:
Primary(Power):
8.1.12.C.1
8.2.12.B.1
9.4.12A.19
Secondary(Supportive):
8.2.12.C.3
8.2.12.F.3
9.4.12A.47
9.4.12.B.(1).5
9.4.12.B.(1).11
1. There is a direct relationship between style
and design.
2. Maximizing efficiency doesn’t always mean
minimizing style.
3. When creating a design you will have to
interact with an existing part of the human,
natural, or designed world.
4. Being self-aware and open to criticism allows
for greater personal growth.
2. Students will be able to identify basic parts of a
structure/building.
3. Students will be able to identify common
architectural styles.
4. Students will be able to define and utilize efficiency
in their designs.
5. Students will be able to properly design and
assemble a scale addition to the school.
6. Students will understand the importance of the
natural world.
7. Students will understand the value of self-
assessment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cadrubrics-190602070825/75/Cad-rubrics-27-2048.jpg)

![30
Unit 6: 3D Modeling in AutoCAD Recommended Duration: [2-3 Weeks]
Unit Description:
Students will now expand on their prior knowledge of CAD from 2D to 3D. They will learn about basic functions such as extrude, cut, hole, etc. and working in
different planes. Students will reproduce their 2D sketches from Unit 3 in 3D space and learn about shading, coloring, and rendering an object/scene. Students
will also cover the use of rapid prototyping and how the 3D printer is changing the world of design.
Essential Questions: Enduring Understandings:
1. Why is it essential to follow proper procedure when creating a design?
2. What are the key features of rendering?
3. How is rapid prototyping used in product development?
1. CAD programs require knowledge of proper technique and purpose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cadrubrics-190602070825/75/Cad-rubrics-30-2048.jpg)