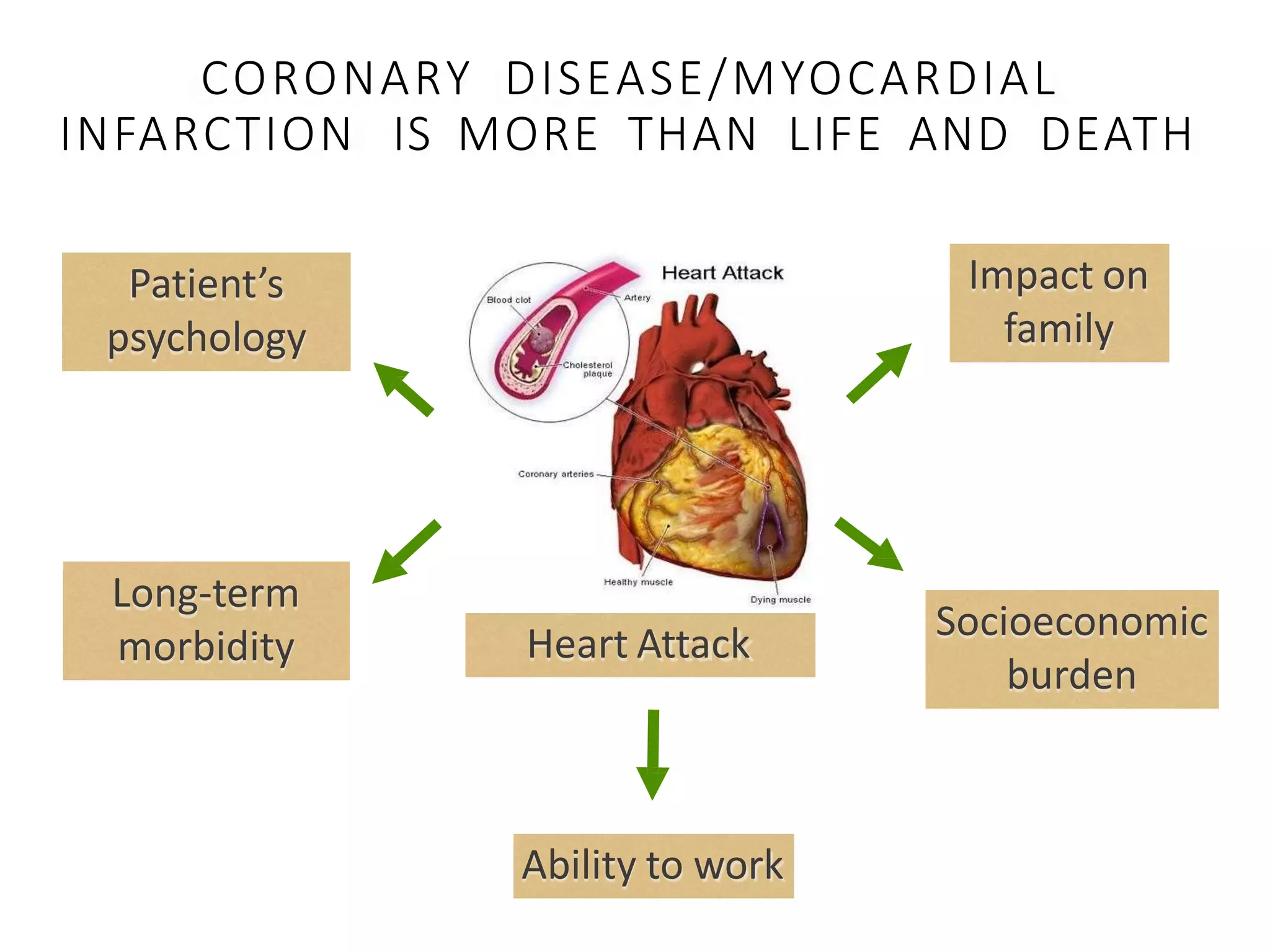
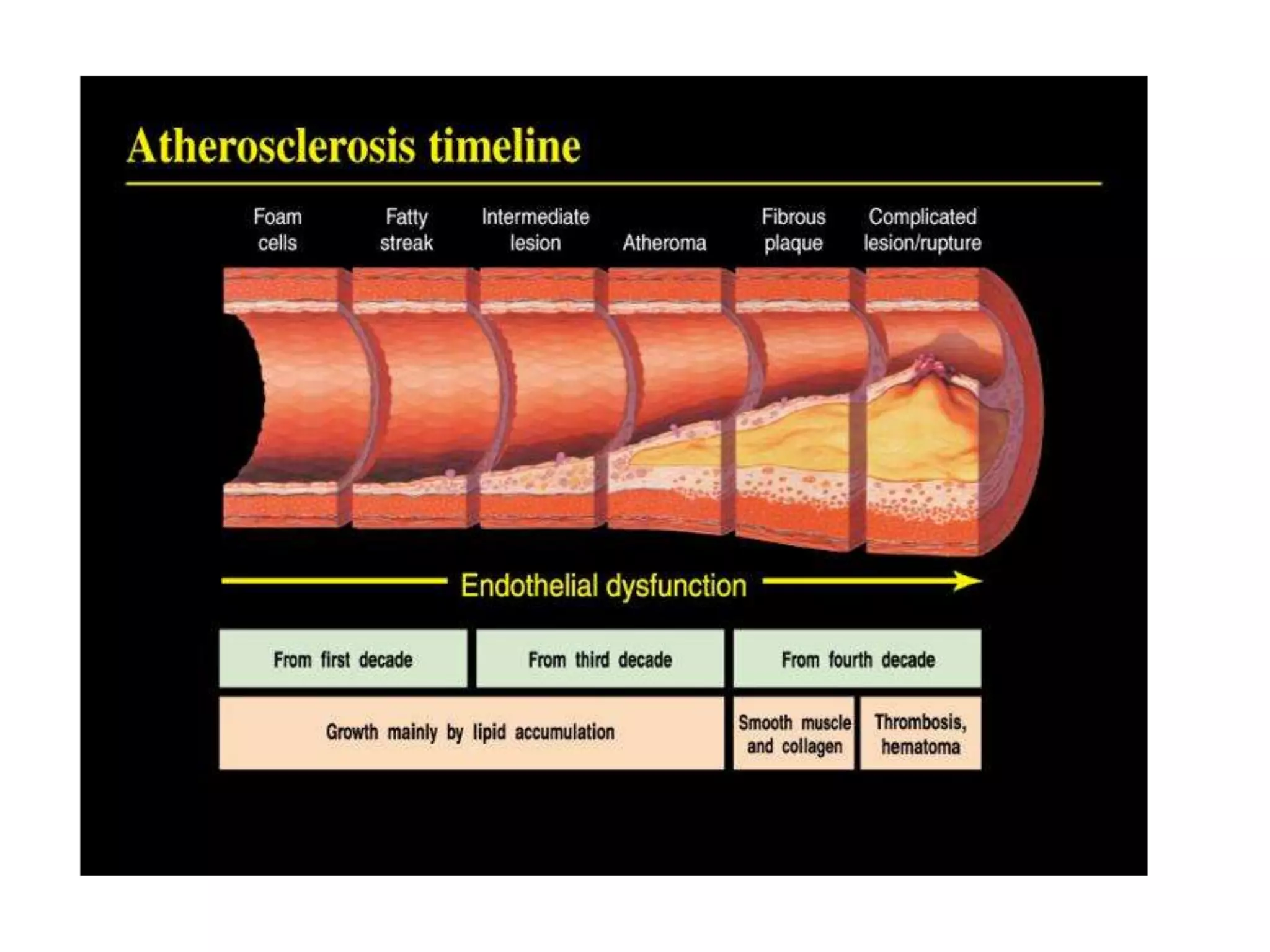
This document discusses coronary heart disease in young adults. It finds that while most coronary disease occurs in older populations, 2-6% of acute coronary events occur in younger "premature" patients under 55 years old. Major risk factors for young adults include smoking, family history of early heart disease, male gender, and hyperlipidemia. Diagnostic tests may include electrocardiograms, stress tests, echocardiograms, CT angiograms, and calcium scoring. Aggressive risk factor modification including smoking cessation and statin therapy is important for prognosis. While short term outcomes of revascularization are good, long term mortality is still elevated compared to the general population.