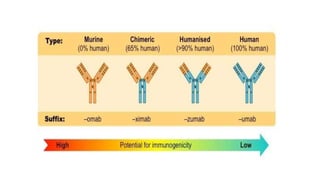
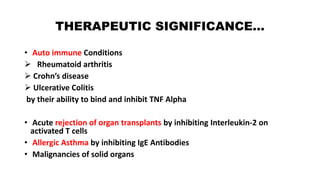
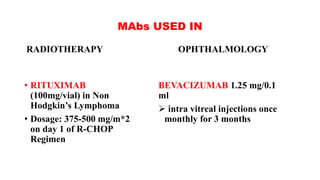
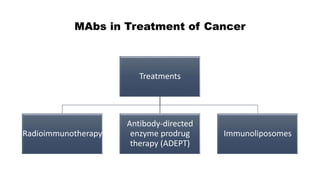
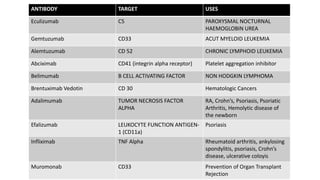
Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific antibodies produced by identical immune cells that are clones of a single parent cell. They bind to the same epitope or antigen. There are several types of monoclonal antibodies including murine, chimeric, humanized, and human antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies have various applications in hematology including as therapeutics for cancers, autoimmune disorders, and transplant rejection by blocking molecular targets, delivering cytotoxic compounds to tumors, or acting as signaling molecules. They can also be used diagnostically in tests like ELISA and immunohistochemistry. Common adverse effects of monoclonal antibodies include infusion reactions, immunosuppression, and increased risk of infection.