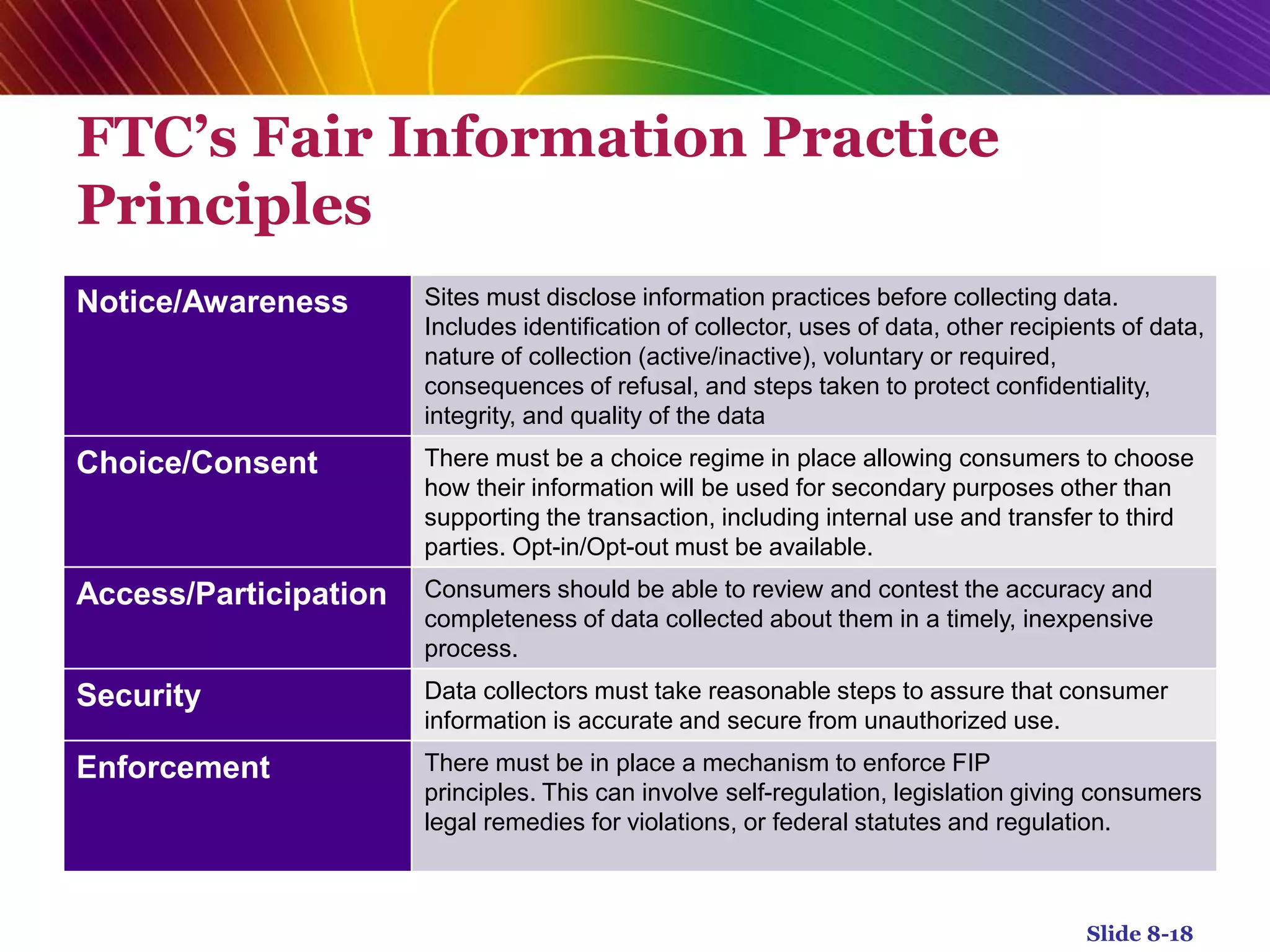
This document outlines some of the key ethical, social, and political issues related to e-commerce, organized into four main categories: information rights, property rights, governance, and public safety/welfare. It discusses challenges like privacy and how personal information is collected and used online. It also covers intellectual property rights around copyright, patents, and trademarks. Governance issues involve questions around who will control the internet and elements of e-commerce. Additional topics include taxation of online sales, net neutrality, and efforts to protect children from inappropriate content.