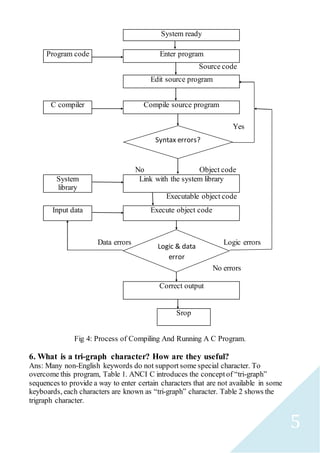
The document provides information about C programming language and its features. It discusses the basic structure of a C program which includes documentation, link, definition, global declaration, main function, and sub-program sections. It also describes the four steps to execute a C program: create, compile, link, and execute. Different forms of the main statement in C are discussed including main(), main(void), int main(), void main(), void main(void), and int main(void).




![6
Letters Digits
Uppercase A….Z All decimal digits 0….9
Lowercase a….z
Special Characters
, comma & ampersand
. period ^ caret
; semicolon * asterisk
: colon - minus
? question mark + plus sign
‘ apostrophe < opening angle bracket(or less than
sign)
“ quotation mark > closing angle bracket(or greater than
sign)
!exclamation mark ( left parenthesis
/ slash ) right parenthesis
backslash [ left bracket
~ tilde ] right bracket
_ under score { left brace
$ dollar sign } right brace
White Spaces
Blank space
Horizontal tab
Carriage return
New line
Table 1: C Character Set
Table 2: ANSI C Tri-graph Sequences
Tri-graph sequence Translation
??= # number
??( [ left bracket
??) ] right bracket
??< { left brace
??> } right brace
??! | vertical bar
??/ back slash
?? ^ caret
??- ~ tilde
6. What are the rules for declaring identifiers?
Ans: An identifier is a name. It can be the name of a variable, function, a structure
or union, a member of a struct, union or enum, a typedef name, a macro name or a
macro variable.
Example:
Sum, toal_marks,sub1, sub2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramminglanguag2repaired-160518181642/85/C-programming-languag-for-cse-students-6-320.jpg)
